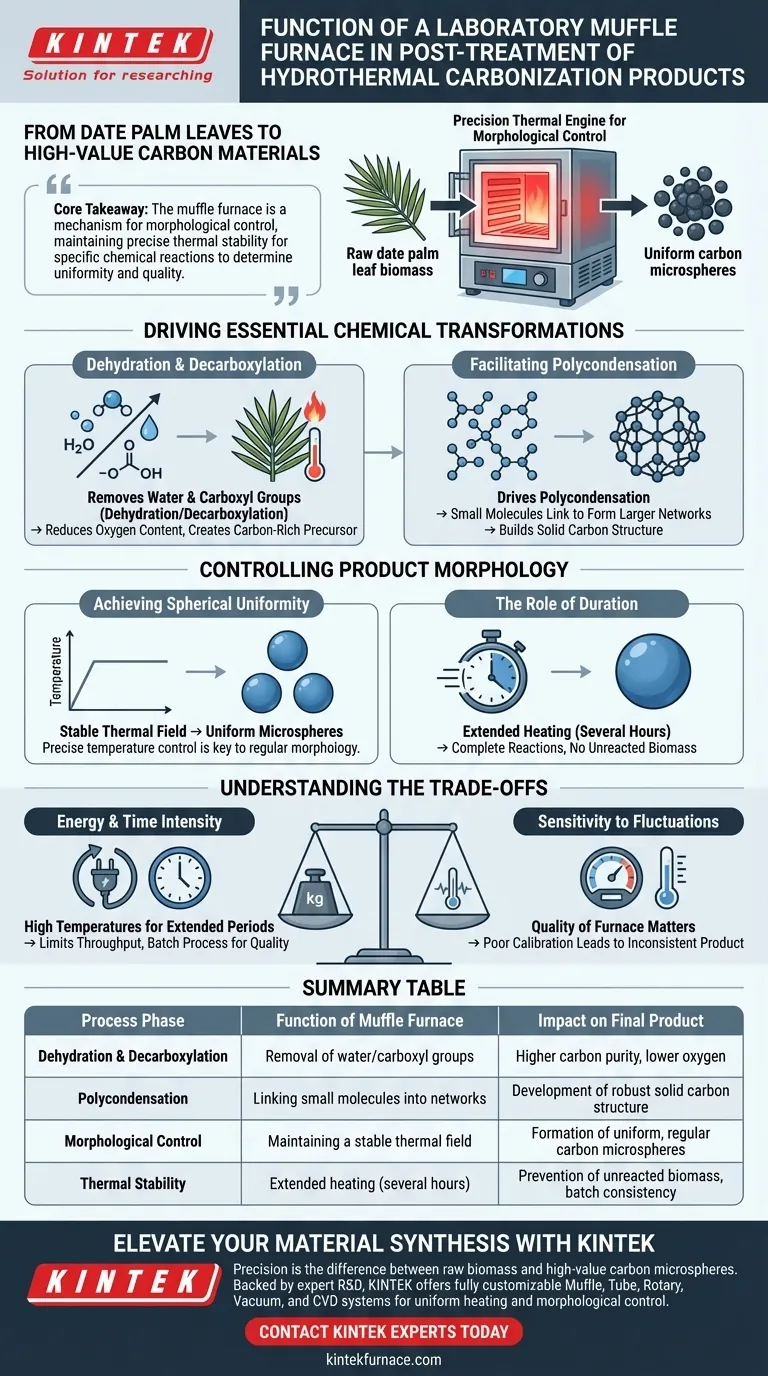
A laboratory muffle furnace acts as the precision thermal engine driving the conversion of date palm leaf biomass into high-value carbon materials. It provides a constant, high-temperature environment around the reaction vessel, which is essential for forcing the biomass to undergo the complete chemical restructuring required to stabilize the final product.
Core Takeaway The muffle furnace is not simply a heating device; it is a mechanism for morphological control. By maintaining precise thermal stability over long durations, it enables the specific chemical reactions—dehydration, decarboxylation, and polycondensation—that determine the uniformity and quality of the resulting carbon microspheres.

Driving Essential Chemical Transformations
The primary role of the muffle furnace in this context is to supply the energy required to break down the complex structure of raw biomass and rebuild it into stable carbon.
Dehydration and Decarboxylation
The consistent heat provided by the furnace initiates the removal of water (dehydration) and carboxyl groups (decarboxylation) from the date palm leaves.
This step is critical for reducing the oxygen content of the biomass, effectively converting the organic plant matter into a more carbon-rich precursor.
Facilitating Polycondensation
Once the initial breakdown occurs, the furnace’s sustained heat drives polycondensation reactions.
During this phase, small molecules link together to form larger, more complex molecular networks. This polymerization is the fundamental process that builds the solid structure of the carbon product.
Controlling Product Morphology
Beyond basic chemical conversion, the muffle furnace is instrumental in defining the physical shape of the final carbon product.
Achieving Spherical Uniformity
The primary reference indicates that precise temperature control is the deciding factor in forming carbon microspheres.
Fluctuations in temperature can lead to irregular shapes. The muffle furnace ensures a stable thermal field, allowing the carbon to organize into a regular, spherical morphology, which is often preferred for advanced material applications.
The Role of Duration
These transformations are not instantaneous. The muffle furnace is designed to maintain these high temperatures for heating periods lasting several hours.
This extended duration ensures that the reactions are not just started, but completed thoroughly, preventing the presence of unreacted biomass in the final sample.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While the muffle furnace is essential for high-quality carbonization, it is important to recognize the operational constraints inherent to this method.
Energy and Time Intensity
The process described requires maintaining high temperatures for extended periods ("several hours").
This makes the process energy-intensive and limits the throughput rate. It is a batch process designed for quality and precision rather than high-speed mass production.
Sensitivity to Thermal Fluctuations
Because the formation of regular microspheres relies on "precise temperature control," the quality of the furnace matters.
An older or poorly calibrated furnace that struggles to maintain a constant environment may fail to produce the desired spherical morphology, resulting in inconsistent product batches.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To maximize the effectiveness of the muffle furnace in your specific application, align your operational parameters with your desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is Structural Integrity: Ensure the furnace is programmed for a duration long enough to allow complete polycondensation, preventing brittle or incomplete carbon structures.
- If your primary focus is Morphological Consistency: Prioritize the precision of the temperature controller to ensure the thermal environment remains absolutely constant, which is the key to obtaining uniform microspheres.
The muffle furnace converts raw potential into engineered reality by enforcing the strict thermal discipline required for advanced material synthesis.
Summary Table:
| Process Phase | Function of Muffle Furnace | Impact on Final Product |
|---|---|---|
| Dehydration & Decarboxylation | Removal of water and carboxyl groups | Higher carbon purity and lower oxygen content |
| Polycondensation | Linking small molecules into networks | Development of a robust solid carbon structure |
| Morphological Control | Maintaining a stable thermal field | Formation of uniform, regular carbon microspheres |
| Thermal Stability | Extended heating (several hours) | Prevention of unreacted biomass and batch consistency |
Elevate Your Material Synthesis with KINTEK
Precision is the difference between raw biomass and high-value carbon microspheres. At KINTEK, we understand that advanced material research requires absolute thermal discipline.
Backed by expert R&D and world-class manufacturing, KINTEK offers a comprehensive range of Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems. Our lab high-temp furnaces are fully customizable to meet your unique hydrothermal carbonization and post-treatment requirements, ensuring uniform heating and precise morphological control for every batch.
Ready to achieve superior consistency in your lab?
Visual Guide
References
- Saeed Alhawtali, Chun‐Yang Yin. Date Palm Leaflet-Derived Carbon Microspheres Activated Using Phosphoric Acid for Efficient Lead (II) Adsorption. DOI: 10.3390/c10010026
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- How does a muffle furnace support controlled atmosphere operations? Ensure Purity and Precision in Your Lab
- What advantages do rapid heating and cooling features offer in some muffle furnace models? Boost Efficiency and Control in Your Lab
- What are the primary uses of muffle furnaces? Essential for Contamination-Free High-Temp Processing
- How do box resistance furnaces facilitate the tempering process for quenched 60Si2CrV spring steel? Precision Hardening
- What are the primary uses of a muffle furnace? Achieve Precise High-Temperature Processing
- What is a box furnace and what are its main characteristics? Discover Versatile Batch Heating Solutions
- What types of controllers are used in muffle furnaces? Choose the Right One for Precise Thermal Control
- How are muffle furnaces applied in textile manufacturing? Ensure Quality with Precise Ashing Tests



















