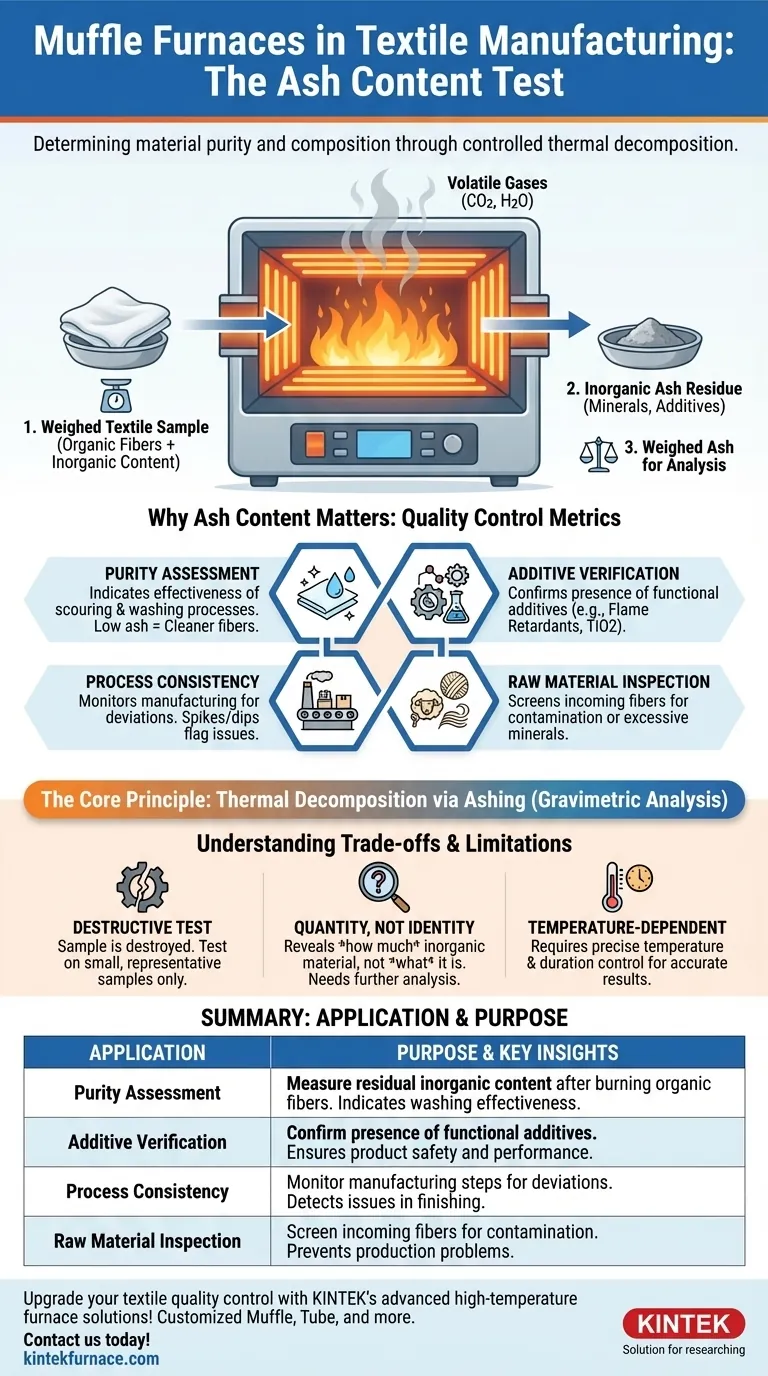
In textile manufacturing, a muffle furnace serves one primary and critical function: determining the ash content of a material through a process called ashing. This test involves using the furnace's high, controlled temperatures to completely burn away all organic fibers from a fabric, yarn, or wool sample. What remains is a small amount of inorganic residue, or "ash," which is then weighed to assess purity and composition.
A muffle furnace acts as a high-temperature incinerator in a controlled lab setting. For textiles, its purpose is to burn off the organic fiber to isolate and quantify the non-combustible, inorganic materials left behind, which is a key indicator of quality and composition.

The Core Principle: Thermal Decomposition via Ashing
A muffle furnace provides an enclosed chamber that heats materials to very high temperatures without direct contact with flames, ensuring uniform and clean combustion.
What is Ashing?
Ashing is a form of gravimetric analysis, where a substance's mass is used to measure its composition. The process leverages heat to force a chemical change.
In this test, a precisely weighed textile sample is placed in the furnace. The heat causes complete combustion, breaking down the organic polymers of the fibers (like cellulose in cotton or protein in wool) into volatile gases like carbon dioxide and water vapor.
What Remains is "Ash"
The only thing that doesn't burn away is the inorganic content. This includes naturally occurring mineral salts in the raw fiber, or, more importantly, residual chemicals and additives from the manufacturing process.
Why Ash Content Matters in Textiles
Measuring the percentage of ash is not an academic exercise; it is a vital quality control metric that reveals crucial information about the material.
A Measure of Purity
For natural fibers like cotton or wool, a very low ash content indicates that the material has been effectively scoured and washed. High ash content can signal that residual dirt, mineral salts, or processing chemicals have not been properly removed.
Verifying Functional Additives
Many modern textiles are treated with inorganic compounds to give them specific properties. Ashing is used to confirm these additives are present in the correct amounts.
Common examples include titanium dioxide (TiO2) used as a delustering agent to reduce shine, or inorganic flame retardants applied to meet safety standards. The ashing test verifies that the specified percentage of these functional materials is in the final product.
Ensuring Process Consistency
By regularly testing ash content, manufacturers can monitor the consistency of their scouring, bleaching, and finishing processes. A sudden spike or dip in the ash percentage of a production batch is an immediate red flag that points to a problem upstream.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While powerful, the ashing test is not a universal solution and has important limitations to consider.
It is a Destructive Test
The textile sample is completely destroyed during the process. This means testing can only be performed on a small, representative sample from a larger batch, not on the final product itself.
It Provides Quantity, Not Identity
The test tells you how much inorganic material is present, but it does not tell you what it is. An ash content of 1% could be from harmless residual salts or an incorrectly applied chemical.
Identifying the specific chemical composition of the ash requires more advanced analytical techniques, such as spectroscopy, after the ashing is complete.
Results Are Temperature-Dependent
The temperature and duration of the ashing process must be carefully controlled according to established standards. If the temperature is too low, combustion may be incomplete. If it is too high, some inorganic compounds may volatilize, leading to an inaccurately low ash reading.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The value of ashing lies in its ability to provide a simple, quantitative benchmark for complex chemical processes. You can apply it to diagnose issues and validate your production.
- If your primary focus is process validation: Use ashing to confirm that washing and scouring steps are effectively removing inorganic impurities from raw fibers.
- If your primary focus is product specification: Use ashing to verify that the correct percentage of functional additives, like flame retardants or delusterants, is present in your finished fabric.
- If your primary focus is raw material inspection: Use ashing to screen incoming fibers for excessive mineral content or contamination before they enter your production line.
Ultimately, this straightforward thermal test provides critical, data-driven insight into the quality and consistency of your textile products.
Summary Table:
| Application | Purpose | Key Insights |
|---|---|---|
| Purity Assessment | Measure residual inorganic content after burning organic fibers | Indicates effectiveness of scouring and washing processes |
| Additive Verification | Confirm presence of functional additives like flame retardants | Ensures product meets safety and performance standards |
| Process Consistency | Monitor manufacturing steps for deviations | Detects issues in scouring, bleaching, and finishing |
| Raw Material Inspection | Screen incoming fibers for contamination | Prevents production problems from poor-quality inputs |
Upgrade your textile quality control with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise alignment with your unique experimental needs, helping you achieve accurate ash content analysis and superior process validation. Contact us today to discuss how our tailored solutions can enhance your textile manufacturing efficiency and product quality!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does a laboratory muffle furnace facilitate the biomass carbonization process? Achieve Precise Biochar Production
- What metals cannot be heated by induction? Understanding Material Suitability for Efficient Heating
- What is the primary function of a muffle furnace for BaTiO3? Master High-Temp Calcination for Ceramic Synthesis
- What substances are prohibited from being introduced into the furnace chamber? Prevent Catastrophic Failure
- What role does a muffle furnace play in the preparation of MgO support materials? Master Catalyst Activation



















