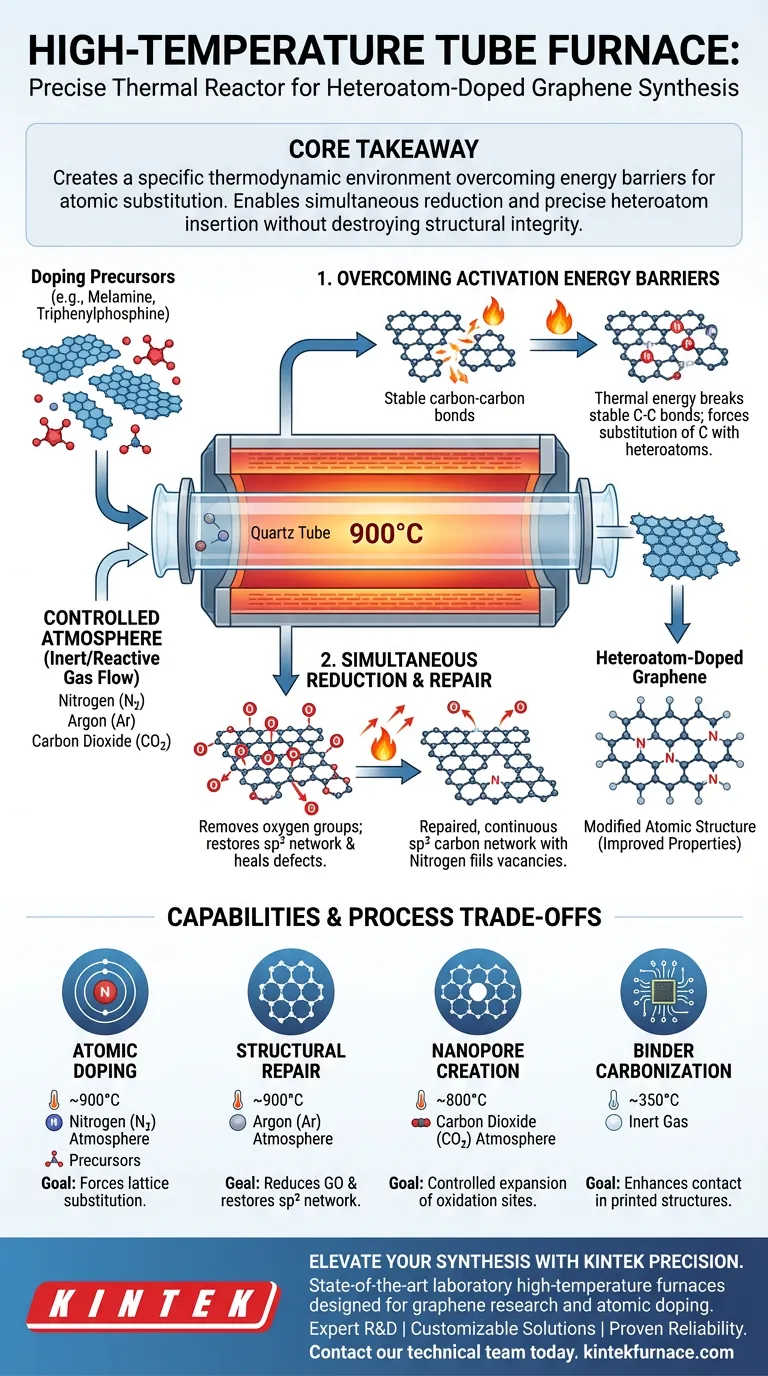
A high-temperature tube furnace functions as a precise thermal reactor necessary to modify the atomic structure of graphene. It provides the controlled, high-heat environment—typically around 900°C—required to break down chemical precursors and force heteroatoms, such as nitrogen or phosphorus, into the graphene lattice.
Core Takeaway The tube furnace does not simply heat the material; it creates a specific thermodynamic environment that overcomes the energy barriers required for atomic substitution. By strictly controlling temperature, heating rates, and atmospheric gases, it enables the simultaneous reduction of graphene oxides and the precise insertion of heteroatoms without destroying the material's structural integrity.

The Mechanisms of Lattice Modification
Overcoming Activation Energy Barriers
To successfully dope graphene, you must break the stable carbon-carbon bonds or fill vacancies within the lattice. This requires significant thermal energy.
The tube furnace heats the system to high temperatures (e.g., 900°C) to decompose doping precursors like melamine or triphenylphosphine.
This thermal energy drives the chemical reaction where carbon atoms in the monolayer graphene are substituted by heteroatoms like nitrogen or phosphorus.
Controlling the Reaction Atmosphere
Temperature is only half the equation; the chemical environment inside the tube is equally critical.
The furnace allows for a constant flow of inert or reactive gases, such as nitrogen or argon, to protect the graphene from combustion during heating.
By maintaining this specific atmosphere, the furnace ensures that the dopants react with the graphene lattice rather than reacting with ambient oxygen, which would simply burn the sample away.
Simultaneous Reduction and Repair
Removing Oxygen Groups
In many synthesis routes, specifically those starting with graphene oxide, the material is heavily oxygenated and insulating.
The high-temperature environment (up to 900°C) thermally reduces the graphene oxide, effectively stripping away oxygen-containing functional groups.
Restoring the sp2 Network
As the furnace removes these impurities, the thermal energy helps re-organize the carbon atoms.
This process repairs the sp2 hybridized network, healing defects in the structure.
Simultaneously, nitrogen atoms (from sources like ammonium or nitrate residues) utilize this thermal energy to occupy the vacancies left by the removed oxygen groups, locking them into the lattice.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Capabilities
Selective Structural Engineering
While the primary goal is often doping, the tube furnace's versatility allows for other structural modifications depending on the gas used.
For example, introducing carbon dioxide (CO2) at 800°C can drive the controlled expansion of oxidation sites to create ultra-thin nanopores.
However, this requires strict control; improper gas selection or temperature management can create non-selective, large pores that ruin the material's mechanical strength.
Temperature Specificity
Not all processes require maximum heat; the furnace allows for stage-specific treatment.
For printed graphene structures, a lower temperature (e.g., 350°C) is sufficient to carbonize binder copolymers and enhance contact between graphene layers.
Operating at unnecessary high temperatures for these applications could degrade the substrate or lead to unwanted thermal decomposition.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To maximize the utility of your high-temperature tube furnace, align your process parameters with your specific material objectives:
- If your primary focus is atomic doping: Target temperatures around 900°C under a Nitrogen flow, utilizing precursors like melamine to force substitution within the lattice.
- If your primary focus is structural repair and conductivity: Use an Argon atmosphere at 900°C to thermally reduce graphene oxide and restore the sp2 network.
- If your primary focus is creating ion-sieving filters: utilize a CO2 atmosphere at 800°C to nucleate specific nanopores rather than doping the lattice.
Precision in thermal and atmospheric control is the difference between destroying your sample and engineering a high-performance material.
Summary Table:
| Process Objective | Optimal Temperature | Atmosphere | Key Function |
|---|---|---|---|
| Heteroatom Doping | ~900°C | Nitrogen (N2) | Overcomes activation energy for atomic substitution |
| Structural Repair | ~900°C | Argon (Ar) | Reduces graphene oxide and restores sp2 network |
| Nanopore Creation | ~800°C | Carbon Dioxide (CO2) | Drives controlled expansion of oxidation sites |
| Binder Carbonization | ~350°C | Inert Gas | Enhances contact in printed graphene structures |
Elevate Your Materials Synthesis with KINTEK Precision
Precise thermal and atmospheric control is the critical difference between material degradation and high-performance engineering. KINTEK provides state-of-the-art laboratory high-temperature furnaces, including specialized Tube, Vacuum, and CVD systems, specifically designed to handle the rigorous demands of graphene research and atomic doping.
Why choose KINTEK?
- Expert R&D: Systems engineered for strict temperature uniformity and atmosphere integrity.
- Customizable Solutions: Tailored configurations to meet your specific doping precursors and gas flow requirements.
- Proven Reliability: Trusted by leading researchers for thermal reduction and structural modification.
Ready to achieve superior lattice modification? Contact our technical team today to find the perfect furnace for your unique synthesis needs.
Visual Guide
References
- Yong Gao, Hongge Pan. Experimentally validated design principles of heteroatom-doped-graphene-supported calcium single-atom materials for non-dissociative chemisorption solid-state hydrogen storage. DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-45082-9
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- What role does an industrial vertical tube furnace play in Si-O equilibria? Master High Silicon Steel Experiments
- What recent advancements have enhanced the performance of lab tubular furnaces? Achieve Unprecedented Precision & Control
- What are the different types of tube furnaces? Find Your Perfect High-Temp Solution
- How is the application scope of vertical fluidized bed tube furnaces expected to evolve? Discover Future Innovations in Precision Heating
- How does a vacuum tube furnace contribute to the annealing of FePC amorphous alloys? Precision Microstructural Control
- What are the advantages of using an induction heated quartz tube furnace for β-Ga2O3 annealing? Boost Your Throughput
- What are the main components of an atmosphere tube furnace? Unlock Precision in Material Processing
- What are the key takeaways for optimizing a split tube furnace? Boost Precision and Efficiency in Your Lab



















