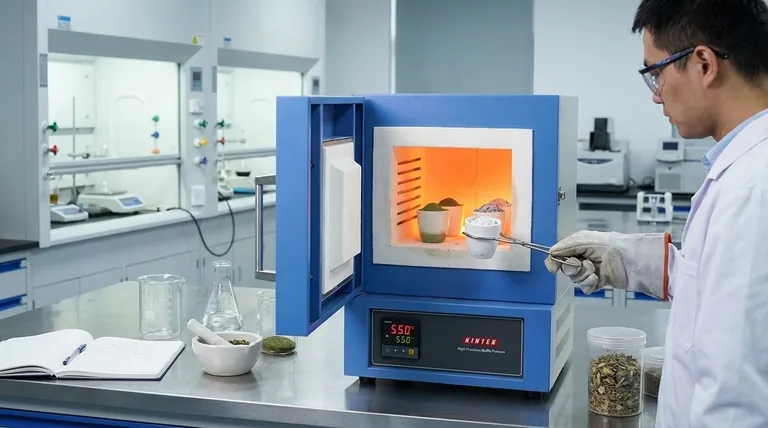
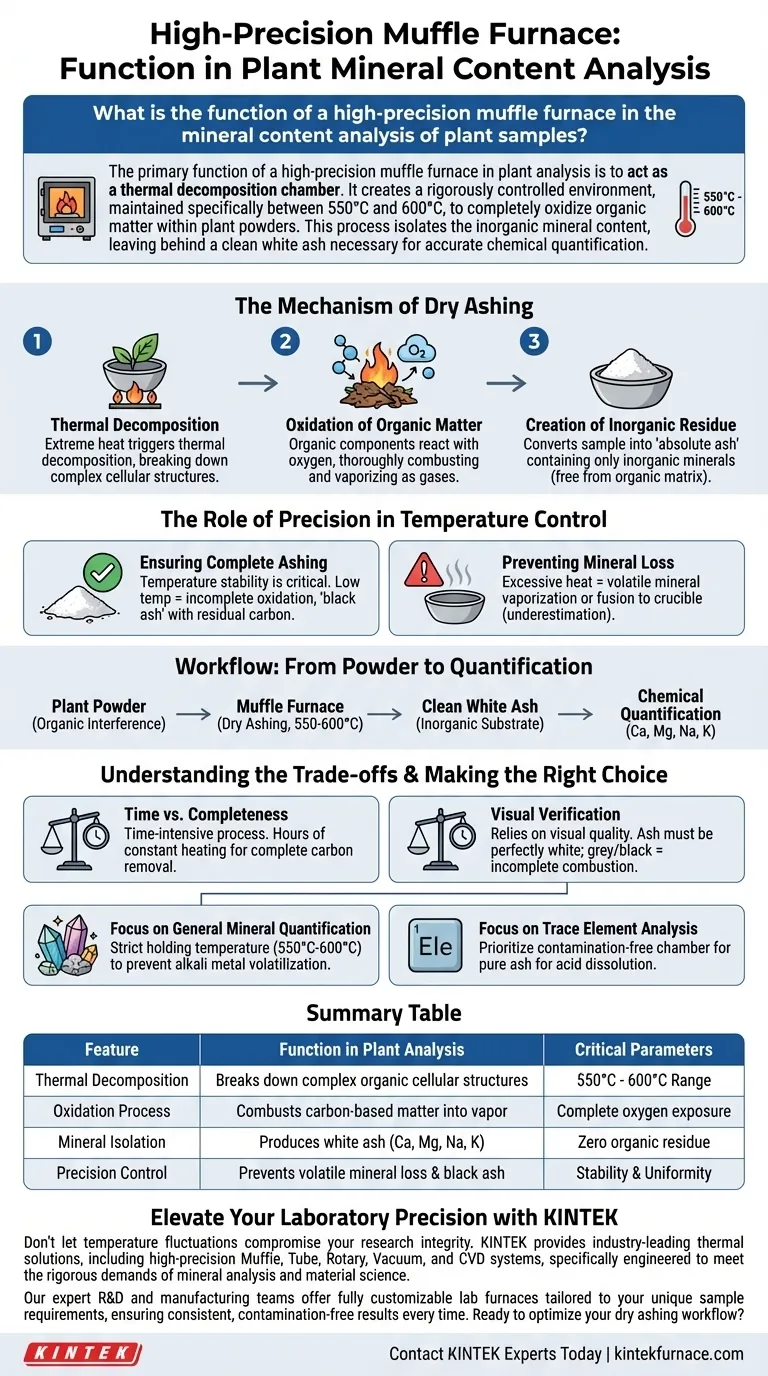
The primary function of a high-precision muffle furnace in plant analysis is to act as a thermal decomposition chamber. It creates a rigorously controlled environment, maintained specifically between 550°C and 600°C, to completely oxidize organic matter within plant powders. This process isolates the inorganic mineral content, leaving behind a clean white ash necessary for accurate chemical quantification.
The Core Objective By subjecting plant samples to stable, high-intensity heat, the muffle furnace eliminates carbon-based interference through a process called dry ashing. This effectively separates the organic biomass from the inorganic nutrients, creating a pure residue that allows for the precise measurement of elements like sodium, potassium, calcium, and magnesium.

The Mechanism of Dry Ashing
Thermal Decomposition
The furnace operates by raising the temperature of plant powder samples to extreme levels.
This heat triggers thermal decomposition, breaking down the complex cellular structures of the plant material.
Oxidation of Organic Matter
As the temperature holds steady within the 550°C to 600°C range, the organic components of the plant react with oxygen.
This reaction causes the thorough combustion and removal of carbon-based substances, effectively vaporizing them as gases.
Creation of Inorganic Residue
The physical result of this process is the conversion of the sample into "absolute ash."
This residue contains only the inorganic minerals originally present in the plant, free from the organic matrix that would otherwise obscure chemical analysis.
The Role of Precision in Temperature Control
Ensuring Complete Ashing
High-precision furnaces are essential because temperature stability is critical for validity.
If the temperature fluctuates or drops too low, the organic matter may not oxidize completely, resulting in "black ash" containing residual carbon that skews results.
Preventing Mineral Loss
Conversely, precision prevents the temperature from spiking beyond the target range.
Excessive heat can cause certain volatile minerals to vaporize or the ash to fuse to the crucible, leading to an underestimation of mineral content.
Workflow: From Powder to Quantification
Pre-Treatment Necessity
The muffle furnace does not perform the chemical analysis itself; it is a preparation tool.
Direct chemical analysis of raw plant powder is often impossible due to the interference of organic compounds.
Enabling Chemical Quantification
Once the process yields a clean white ash, the sample is ready for the next phase.
This ash serves as the requisite substrate for subsequent chemical tests, allowing scientists to accurately quantify specific nutrients such as calcium, magnesium, sodium, and potassium.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Time vs. Completeness
Dry ashing in a muffle furnace is a time-intensive process compared to some wet chemistry methods.
It often requires hours of constant heating to ensure that every trace of organic carbon is removed from the sample.
Visual Verification
The process relies heavily on the visual quality of the output.
Operators must verify that the ash is perfectly white; any grey or black discoloration indicates incomplete combustion, requiring the process to be repeated or adjusted, which can impact laboratory throughput.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To ensure the highest quality data from your plant samples, align your furnace usage with your specific analytical targets.
- If your primary focus is General Mineral Quantification: Ensure your furnace can maintain a strict holding temperature between 550°C and 600°C to prevent the volatilization of alkali metals like sodium and potassium.
- If your primary focus is Trace Element Analysis: Prioritize a furnace with a contamination-free chamber design, as the "clean white ash" must remain pure for subsequent acid dissolution and testing.
Ultimately, the muffle furnace converts complex biological material into simple chemical data, serving as the bridge between raw nature and precise laboratory insight.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Function in Plant Analysis | Critical Parameters |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Decomposition | Breaks down complex organic cellular structures | 550°C - 600°C Range |
| Oxidation Process | Combusts carbon-based matter into vapor | Complete oxygen exposure |
| Mineral Isolation | Produces white ash (Ca, Mg, Na, K) | Zero organic residue |
| Precision Control | Prevents volatile mineral loss & black ash | Stability & Uniformity |
Elevate Your Laboratory Precision with KINTEK
Don't let temperature fluctuations compromise your research integrity. KINTEK provides industry-leading thermal solutions, including high-precision Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, specifically engineered to meet the rigorous demands of mineral analysis and material science.
Our expert R&D and manufacturing teams offer fully customizable lab furnaces tailored to your unique sample requirements, ensuring consistent, contamination-free results every time.
Ready to optimize your dry ashing workflow? Contact KINTEK Experts Today to discover the perfect high-temperature furnace for your laboratory needs.
Visual Guide
References
- Javid Ali, Inayat Ur Rehman. Nutrient evaluation, minerals quantification and antibacterial potential of <i>Mentha longifolia</i> (L.) flower, leaves and stem against foodborne bacterial pathogens. DOI: 10.4314/ijest.v16i4.1
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- What role does a muffle furnace play in the analytical chemical industry? Ensure Accurate, Contamination-Free Sample Processing
- How is a high-temperature muffle furnace utilized to evaluate the oxidation resistance of Cr2AlC ceramics?
- What types of materials can a box furnace handle? Versatile Solutions for Metals, Ceramics, and More
- What role does a muffle furnace play in biochar synthesis? Expert Insights on Pulse-Based Biomass Carbonization
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in CeAlOx/NiO/Ni-foam catalyst production? Master Precision Calcination
- What function does a muffle furnace perform in converting precursors into CSO? Key Insights for Material Synthesis
- What are the primary process objectives when using a laboratory high-temperature Muffle Furnace for precursor treatment?
- What are the common uses of muffle furnaces in laboratory settings? Essential for Ashing, Heat Treatment, and Sintering



















