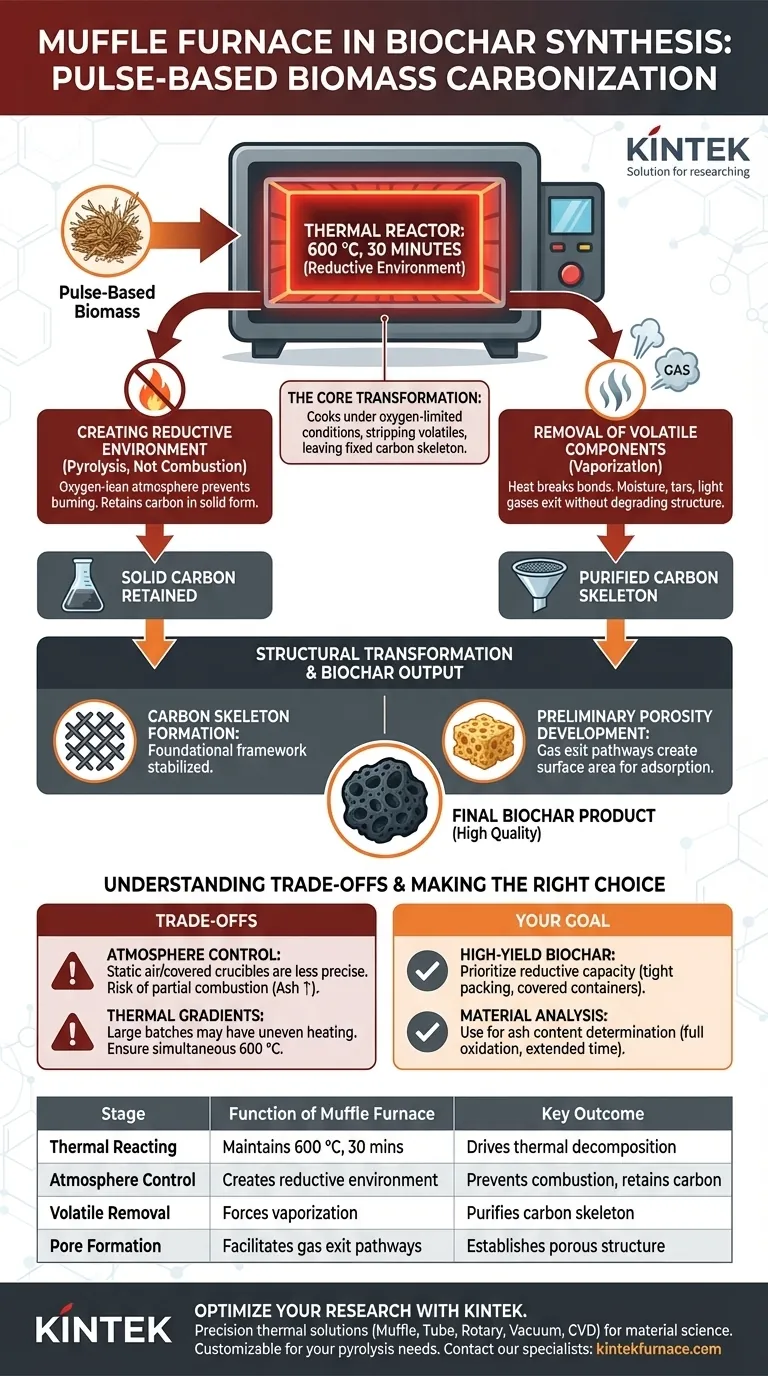
In the synthesis of biochar from pulse-based biomass, the muffle furnace acts as the primary thermal reactor that facilitates pyrolysis by creating a high-temperature, reductive environment. Specifically, by maintaining a steady temperature of 600 °C for 30 minutes, the furnace drives the thermal decomposition necessary to convert raw plant residues into a stable carbon structure.
The Core Transformation The muffle furnace does not simply "burn" the biomass; it cooks it under oxygen-limited conditions. This process strips away volatile organic compounds, leaving behind a fixed carbon skeleton with a preliminary porous structure that defines the biochar's quality.

The Mechanism of Carbonization
To understand the muffle furnace's role, you must look beyond simple heating. It acts as a controlled chamber that dictates the chemical pathway of the biomass.
Creating a Reductive Environment
The most critical function of the muffle furnace in this context is establishing a reductive environment. Unlike open combustion, which turns biomass into ash, the furnace operates under conditions that limit oxidation.
This oxygen-lean atmosphere prevents the material from burning away completely. Instead, it forces the biomass to undergo pyrolysis, ensuring that carbon is retained in a solid form rather than escaping as carbon dioxide.
Removal of Volatile Components
At the target temperature of 600 °C, the muffle furnace supplies enough energy to break the chemical bonds of the pulse-based biomass.
This heat forces non-carbon elements and volatile compounds (such as moisture, tars, and light gases) to vaporize and exit the material. The precise duration of 30 minutes is calibrated to ensure thorough removal of these volatiles without degrading the remaining carbon structure.
Structural Transformation of the Biomass
The physical architecture of the final biochar is determined during this heating phase. The muffle furnace is responsible for "setting" the structure.
Formation of the Carbon Skeleton
As volatiles are expelled, the remaining material stabilizes into a fixed carbon skeleton.
This is the foundational framework of the biochar. The furnace's ability to maintain a constant temperature is vital here; fluctuations could lead to incomplete carbonization or structural collapse, weakening the material's mechanical strength.
Development of Preliminary Porosity
The exit pathways created by escaping gases transform the biomass from a dense solid into a porous material.
The muffle furnace facilitates the creation of this preliminary porous structure. These pores are essential for the biochar's future application, as they provide the surface area required for adsorption activities, such as holding water or trapping contaminants.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While effective, using a muffle furnace for carbonization requires careful management of its limitations compared to other methods like tube furnaces.
Atmosphere Control Limitations
Standard muffle furnaces often rely on static air or covered crucibles to create oxygen-limited conditions.
This is less precise than systems that actively purge oxygen using inert gases like nitrogen. If the environment becomes too oxygen-rich, the process may shift from pyrolysis to partial combustion, increasing ash content and reducing the yield of fixed carbon.
Thermal Gradients
In larger batch processes, muffle furnaces can sometimes exhibit temperature gradients.
Ensuring the entire sample reaches 600 °C simultaneously is critical. Uneven heating can result in a heterogeneous product, where some particles are fully carbonized while others retain unreacted biomass cores.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Depending on your specific requirements for the biochar, the muffle furnace plays a slightly different role in your workflow.
- If your primary focus is synthesizing high-yield biochar: Prioritize the "reductive" capability by tightly packing samples or using covered containers to minimize oxygen exposure at 600 °C.
- If your primary focus is analyzing material composition: Use the muffle furnace for "ash content" determination by extending the time and allowing full oxidation (combustion), rather than pyrolysis.
The muffle furnace is the tool that bridges the gap between raw organic waste and functional, stable carbon material.
Summary Table:
| Stage of Process | Function of Muffle Furnace | Key Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Reacting | Maintains steady 600 °C for 30 minutes | Drives thermal decomposition of pulse biomass |
| Atmosphere Control | Creates oxygen-limited / reductive environment | Prevents combustion; retains carbon as solid biochar |
| Volatile Removal | Forces vaporization of moisture and tars | Purifies the carbon skeleton and reduces mass |
| Pore Formation | Facilitates gas exit pathways | Establishes preliminary porous structure for adsorption |
Optimize Your Carbonization Research with KINTEK
Precision temperature control is the difference between high-quality biochar and simple ash. KINTEK provides industry-leading thermal solutions, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, specifically engineered to meet the rigorous demands of material science.
Backed by expert R&D and world-class manufacturing, our lab high-temp furnaces are fully customizable to your unique pyrolysis and carbonization requirements. Ensure a stable reductive environment and superior structural outcomes for your research today.
Ready to upgrade your lab efficiency? Contact our specialists now to find your perfect furnace solution!
Visual Guide
References
- Muradiye Şahin, Ronaldo Câmara Cozza. Removal of Primamycin La from Milk Sample Using ZnCl2-Activated Biochar Prepared from Bean Plant as Adsorbent: Kinetic and Equilibrium Calculations. DOI: 10.3390/pr13010230
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
People Also Ask
- What are the temperature and voltage specifications of the muffle furnace? Key Specs for Your Lab Needs
- What is the function of a Muffle Furnace in simulated friction and wear testing? Optimize Your Industrial Tool Coatings
- What experimental conditions does a small high-temperature electric heating furnace provide for graphite bearings?
- How does a high-precision resistance furnace ensure T6 solution treatment? Achieve Peak Alloy Strength with KINTEK
- What process function does a high-temperature muffle furnace perform in pre-sintering spinel ceramics?
- How are high-temperature muffle furnaces and AAS utilized in lipstick heavy metal detection for consumer safety?
- How is a muffle furnace applied in the active sulfur coating process? Achieve 155 °C Precision for Catalyst Composites
- How does a high-temperature muffle furnace contribute to the formation of the ZrO2-ZnO heterojunction?



















