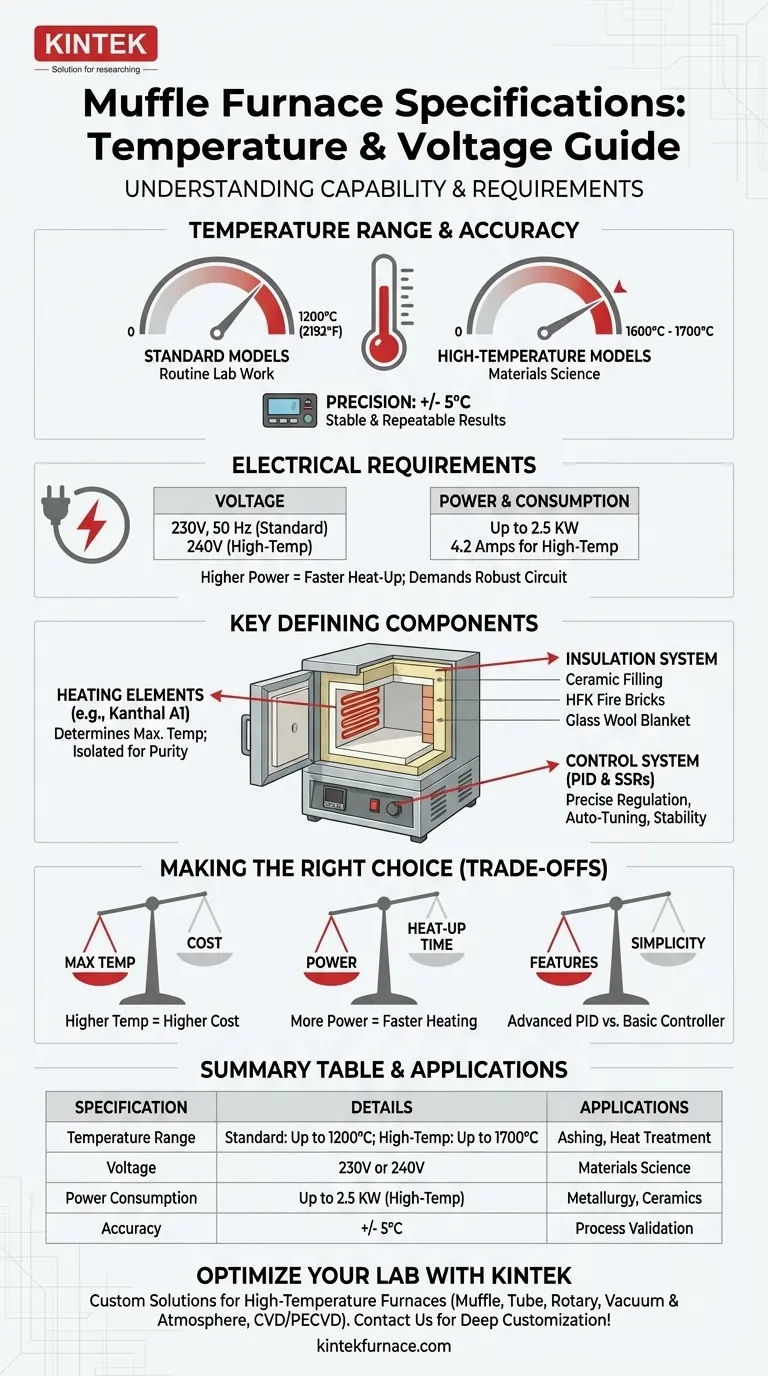
While muffle furnace specifications vary by model, a common configuration operates up to 900°C or 1200°C (2192°F) and requires a 230V or 240V power supply. Higher-performance models are available that can reach extreme temperatures of 1600°C to 1700°C, with electrical requirements tailored to their heating capacity.
The specific temperature and voltage of a muffle furnace are not universal figures. Instead, they reflect a direct trade-off between the furnace's intended application, its material construction, and its cost, making it critical to match the specifications to your specific task.

Deconstructing the Specifications
To select or properly utilize a muffle furnace, you must understand what the numbers for temperature and power actually represent in terms of capability and requirements.
Understanding the Temperature Range
Most muffle furnaces fall into one of two categories. Standard models are designed for a working temperature of up to 900°C, with a maximum rating often reaching 1200°C (2192°F).
High-temperature models, built for more demanding applications like materials science, can reach 1400°C, 1600°C, or even 1700°C. The maximum stated temperature is a limit, not a recommended daily operating point.
Crucially, modern furnaces offer high precision. A typical accuracy is +/- 5°C, ensuring that the set temperature is reliably maintained for repeatable experimental results.
Analyzing the Electrical Requirements
The power supply requirement is directly linked to the furnace's heating power. A standard furnace might require a 230V, 50 Hz single-phase supply, common in many labs.
More powerful, high-temperature units may demand a 240V circuit and draw a higher current, such as 4.2 Amps, resulting in a power rating around 2.5 KW. This is necessary to energize the heating elements to achieve higher temperatures quickly.
Key Components That Define Performance
The specifications on a data sheet are a direct result of the quality and type of components used in the furnace's construction.
The Heating Element and Chamber
The maximum temperature is primarily determined by the heating elements, which are often made of Kanthal A1 wire. These elements are typically isolated from the inner chamber to prevent sample contamination and ensure chemical purity.
The chamber itself is made of high-grade ceramic to withstand thermal shock and ensure uniform temperature distribution through both convection and radiation.
The Insulation System
To reach and hold high temperatures efficiently, a multi-layered insulation system is essential. This includes an inner chamber with ceramic filling, door insulation made from HFK fire bricks, and a body insulated with a high-grade density imported glass wool blanket. This robust insulation provides maximum thermal efficiency and operator safety.
The Control System
Modern furnaces use a Proportional-Integral-Derivative (PID) controller for precise temperature regulation. This system, often paired with Solid-State Relays (SSRs) for the heaters, allows for features like auto-tuning to quickly stabilize at a setpoint and maintain it with minimal fluctuation.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a furnace involves balancing performance with practical constraints. There is no single "best" model, only the one that is best for your needs.
Maximum Temperature vs. Cost
Higher maximum temperatures require more advanced, durable, and expensive materials for the heating elements and insulation. A furnace that can reach 1700°C will be a significantly larger investment than a 1200°C model.
Power Consumption vs. Heat-Up Time
A furnace with a higher power rating (more kilowatts) will generally heat up to its target temperature much faster. However, this demands a more robust electrical circuit and results in higher energy consumption during operation.
Feature Set vs. Simplicity
An advanced, programmable PID controller offers exceptional precision and the ability to run complex heating cycles automatically. For simple, single-temperature applications, a basic digital controller may be sufficient and easier to operate.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Use your primary goal to guide your selection, focusing on the specification that matters most for that task.
- If your primary focus is routine lab work like ashing or general heat treatment: A standard furnace operating up to 1200°C with a 230V supply is a reliable and cost-effective choice.
- If your primary focus is materials science, metallurgy, or ceramics: You will need a high-temperature model (1400°C+) and must ensure your facility can support its 240V or higher power requirements.
- If your primary focus is process validation and absolute repeatability: Prioritize a furnace with an advanced PID controller, SSR-based heaters, and a documented temperature accuracy of +/- 5°C or better.
Ultimately, understanding these core specifications empowers you to choose a furnace that is not just capable, but perfectly suited to your specific scientific or industrial goals.
Summary Table:
| Specification | Details |
|---|---|
| Temperature Range | Standard: Up to 1200°C, High-Temp: Up to 1700°C |
| Voltage Requirements | 230V or 240V, depending on model |
| Power Consumption | Up to 2.5 KW for high-temperature models |
| Temperature Accuracy | Typically +/- 5°C for reliable results |
| Key Applications | Ashing, materials science, metallurgy, ceramics |
Ready to optimize your laboratory with the perfect muffle furnace? At KINTEK, we specialize in high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your unique needs. Leveraging our exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer a diverse product line including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise alignment with your experimental requirements, enhancing efficiency and accuracy. Don't settle for less—contact us today to discuss how we can support your scientific goals!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the key role of a muffle furnace in the pretreatment of boron sludge and szaibelyite? Unlock Higher Process Efficiency
- What is the primary function of a muffle furnace for BaTiO3? Master High-Temp Calcination for Ceramic Synthesis
- How does a laboratory muffle furnace facilitate the biomass carbonization process? Achieve Precise Biochar Production
- What role does a muffle furnace play in the preparation of MgO support materials? Master Catalyst Activation
- What substances are prohibited from being introduced into the furnace chamber? Prevent Catastrophic Failure



















