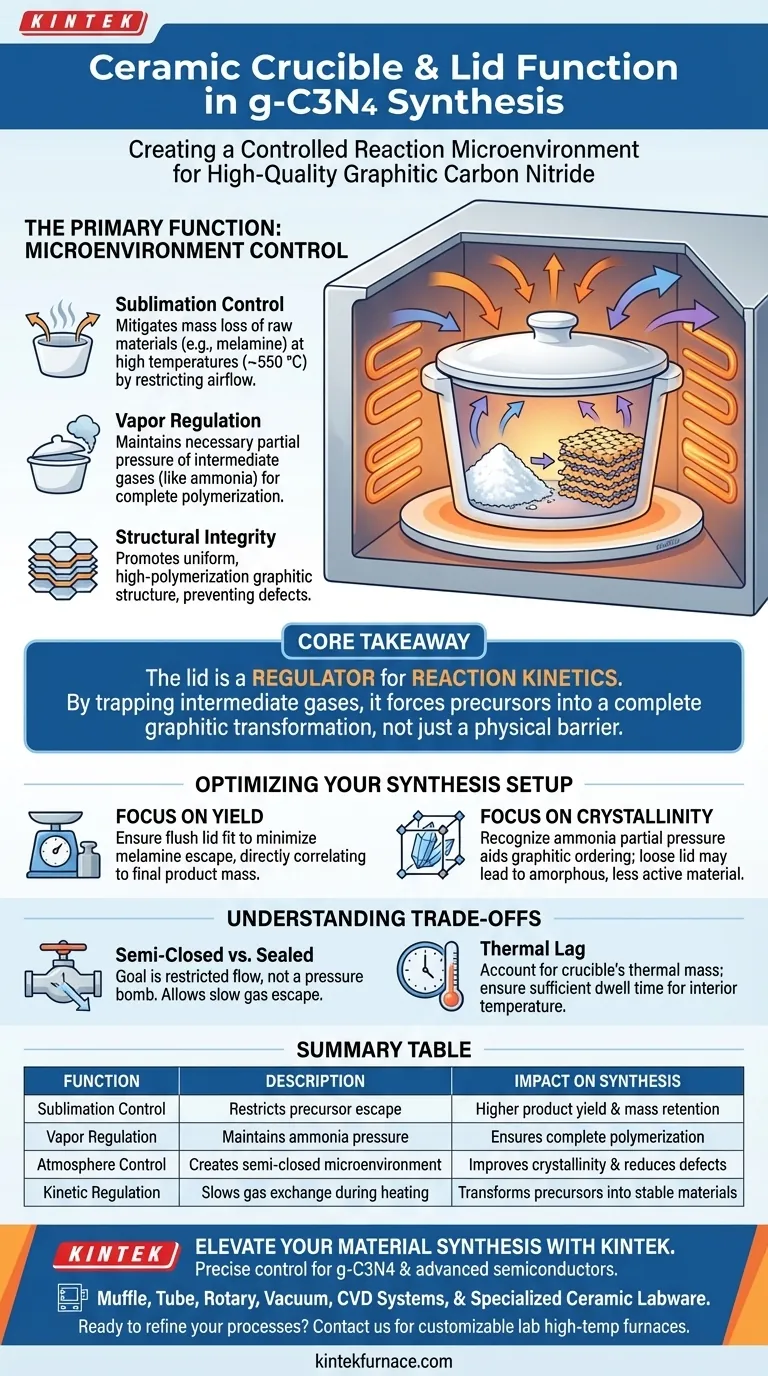
The primary function of a ceramic crucible with a lid during the synthesis of graphitic carbon nitride (g-C3N4) is to create a controlled, semi-closed reaction microenvironment. This setup significantly mitigates the mass loss of raw materials (such as melamine) caused by sublimation and maintains the necessary partial pressure of intermediate gases to ensure complete polymerization.
Core Takeaway The lid is not merely a physical barrier; it acts as a regulator for the reaction kinetics. By trapping intermediate gases like ammonia, the covered crucible forces the precursor to undergo a complete transformation into a high-polymerization graphitic structure, rather than evaporating or forming incomplete byproducts.
The Role of the Microenvironment
To understand why the lid is essential, one must look beyond simple containment. The cover alters the thermodynamic and kinetic conditions inside the crucible during the heating process in the muffle furnace.
Controlling Sublimation
precursors like melamine are prone to sublimation at the high temperatures required for synthesis (often around 550 °C).
Without a lid, a significant portion of the precursor would transition directly from solid to gas and escape the vessel before the reaction occurs.
The lid restricts this airflow, keeping the raw material within the heated zone long enough to undergo thermal polycondensation.
Regulating Vapor Pressure
The polycondensation process releases gases, specifically ammonia, as intermediate byproducts.
A covered crucible retains these gases, maintaining a specific partial pressure of ammonia within the reaction vessel.
This pressure is not a waste product; it is chemically active and influences the reaction pathway, stabilizing the transition from precursor to the final graphitic structure.
Ensuring Structural Integrity
The ultimate goal is to achieve a high-polymerization graphitic structure.
If the precursor evaporates or the intermediate gases vent too rapidly, the resulting material may suffer from low polymerization degrees or structural defects.
The containment provided by the lid promotes a more uniform and complete transformation, resulting in a higher quality semiconductor material.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While using a lid is standard practice, the "tightness" of the system introduces variables that must be managed.
Semi-Closed vs. Hermetically Sealed
The reaction environment must be relatively closed, not hermetically sealed.
The goal is to restrict flow, not to build a pressure bomb; gases must eventually escape slowly to allow the condensation to proceed.
Using a sealant or an overly heavy lid could potentially create dangerous pressure buildup or inhibit the release of byproducts necessary for the final condensation steps.
Thermal Lag
Ceramic is an insulator. Adding a heavy lid increases the thermal mass of the setup.
You must ensure your dwell time (e.g., 4 hours) accounts for the time it takes for the interior of the covered crucible to reach the target temperature of 550 °C.
Optimizing Your Synthesis Setup
When setting up your thermal polycondensation experiment, consider your specific end-goals to dictate how you manage the crucible setup.
- If your primary focus is Yield: Ensure the lid sits flush against the crucible rim to minimize the escape of sublimated melamine, which directly correlates to the final mass of the product.
- If your primary focus is Crystallinity: Recognize that the partial pressure of ammonia aids in ordering the graphitic layers; a loose lid may result in a more amorphous, less active photocatalyst.
The lid is a tool for chemical control, turning a chaotic open-air heating process into a regulated synthesis reaction.
Summary Table:
| Function | Description | Impact on Synthesis |
|---|---|---|
| Sublimation Control | Restricts precursor (melamine) from escaping as gas | Higher product yield and mass retention |
| Vapor Regulation | Maintains ammonia partial pressure | Ensures complete polymerization into graphitic structures |
| Atmosphere Control | Creates a semi-closed microenvironment | Improves crystallinity and reduces structural defects |
| Kinetic Regulation | Slows gas exchange during heating | Transforms precursors into stable semiconductor materials |
Elevate Your Material Synthesis with KINTEK
Precise control over thermal polycondensation requires more than just high temperatures—it demands the right environment. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers high-performance Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, along with specialized ceramic labware designed for your unique synthesis needs.
Whether you are optimizing g-C3N4 yield or developing advanced semiconductor materials, our customizable lab high-temp furnaces provide the thermal stability and uniformity your research deserves.
Ready to refine your laboratory processes? Contact us today to find the perfect customizable solution and experience the KINTEK advantage in precision engineering.
Visual Guide
References
- Construction of a 1D/0D/2D BiFeO <sub>3</sub> /Ag/g-C <sub>3</sub> N <sub>4</sub> Z-scheme heterojunction for enhanced visible light photocatalysis of methylene blue. DOI: 10.1039/d5ra04825g
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the role of a Teflon-lined autoclave in CeO2 synthesis? Achieve Pure, Monodisperse Nanomaterials
- Why is a platinum (Pt) crucible selected as the reaction vessel? Ensure Precision in High-Temp Molten Salt Research
- Why is an additional large alumina outer crucible required? Ensure Safety and Equipment Longevity in Steel Research
- What are the advantages of using a two-color pyrometer? Precision Sensing for Ultra-High-Temperature Furnaces
- Why Use a Capped Alumina Crucible for Glycine Pyrolysis? Optimize Your Carbon-Based Composite Synthesis
- What chemical resistance properties should be verified for alumina ceramic furnace tubes? Ensure High-Temperature Durability
- How does choosing alumina vs graphite crucibles affect Al-Si melting? Expert Guide to Data Integrity
- Alumina vs. Platinum Crucibles for Lithium Titanate (LTO) Synthesis: Which is Right for You?














