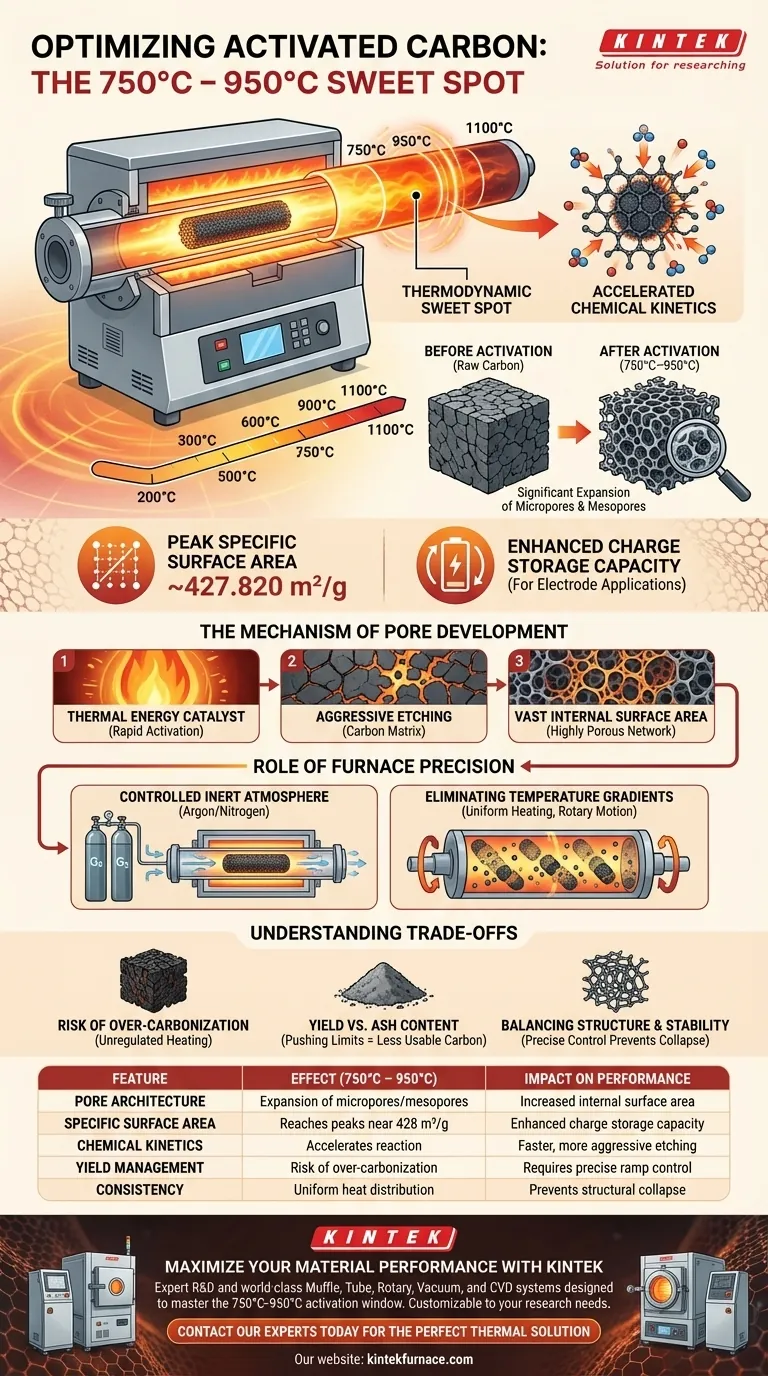
Raising the operating temperature from 750°C to 950°C serves as a critical accelerator for the activation reaction. Within a high-temperature tube furnace, this specific thermal increase energizes the interaction between chemical activators (such as potassium chloride) and the carbon framework. The direct result is a significant expansion of micropores and mesopores, leading to peak specific surface areas and enhanced charge storage capacity for electrode applications.
The temperature range of 750°C to 950°C is the thermodynamic "sweet spot" where thermal energy drives the aggressive etching of the carbon skeleton. While pushing toward 950°C maximizes surface area, this process requires precise environmental control to shape the material's internal structure effectively.

The Mechanism of Pore Development
Accelerating Chemical Kinetics
At temperatures above 750°C, the thermodynamic conditions within the furnace shift to favor rapid activation. The thermal energy acts as a catalyst, intensifying the reaction between the carbon precursor and the activating agents.
Expansion of Pore Architecture
This intensified reaction etches the carbon matrix, drastically increasing the quantity of micropores and mesopores. This transformation turns a relatively solid material into a highly porous network with a vast internal surface area.
Maximizing Specific Surface Area
The correlation between temperature and surface area is positive within this range. Materials treated at the upper limit of 950°C typically exhibit the highest specific surface areas, reaching values approximately 427.820 m²/g.
Enhancing Electrochemical Performance
The physical changes in the carbon structure have direct electrochemical benefits. The increased surface area and pore volume facilitate better ion movement and storage, directly enhancing the charge storage capacity of the resulting electrode materials.
The Role of Furnace Precision
Controlled Atmospheric Conditions
While temperature drives the reaction, the tube furnace ensures the material does not simply burn away. By maintaining a controlled inert atmosphere (such as Argon or Nitrogen), the furnace prevents oxidative consumption of the substrate during these high-heat phases.
Eliminating Temperature Gradients
For consistent activation, the heat must be applied uniformly. Advanced configurations, such as rotary tube furnaces, utilize dynamic tumbling to ensure every particle experiences the same thermal history, preventing uneven activation.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The Risk of Over-Carbonization
Higher temperatures maximize surface area, but they come with risks if the heating ramp is not controlled. Unregulated continuous heating can lead to over-carbonization, which degrades the quality of the biomass.
Yield vs. Ash Content
Pushing the temperature too high or ramping up too quickly can increase ash production. This reduces the effective char yield, meaning you produce less usable activated carbon relative to the raw material input.
Balancing Structure and Stability
While 950°C creates the most pores, it places the highest stress on the material. Precise programmable temperature control is required to ensure the carbon skeleton is etched to create pores without causing a total structural collapse.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To optimize your activated carbon production, align your furnace settings with your specific performance metrics:
- If your primary focus is maximum surface area: Target the higher end of the range (950°C) to maximize micropore creation and achieve specific surface areas near 428 m²/g.
- If your primary focus is material yield and consistency: Utilize a programmable heating ramp and slightly lower temperatures to prevent over-carbonization and minimize ash production.
Precise thermal regulation is the difference between simply burning biomass and engineering high-performance energy storage materials.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Effect at 750°C - 950°C | Impact on Performance |
|---|---|---|
| Pore Architecture | Expansion of micropores and mesopores | Increased internal surface area |
| Specific Surface Area | Reaches peaks near 427.820 m²/g | Enhanced charge storage capacity |
| Chemical Kinetics | Accelerates activator/carbon reaction | Faster, more aggressive etching |
| Yield Management | Risk of over-carbonization/ash | Requires precise ramp-rate control |
| Consistency | Uniform heat distribution needed | Prevents structural collapse |
Maximize Your Material Performance with KINTEK
Precision is the difference between simple carbonization and high-performance engineering. Backed by expert R&D and world-class manufacturing, KINTEK offers advanced Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems designed to master the 750°C–950°C activation window. Whether you need uniform tumbling in a rotary furnace or precise atmospheric control for sensitive substrates, our lab high-temp furnaces are fully customizable to meet your unique research needs.
Ready to optimize your carbon yields and surface area? Contact our experts today to find the perfect thermal solution for your lab.
Visual Guide
References
- Ria Yolanda Arundina, Bambang Subiyanto. Preparation of nitrogen-doped activated carbon from palm oil empty fruit bunches for electrodes in electric double-layer capacitance-type supercapacitors: effect of pyrolysis temperature. DOI: 10.1093/ce/zkae100
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- What is the function of the heating device in the micro-Kjeldahl method? Master Protein Analysis in Mushrooms
- Why is the intervention of precision heat treatment equipment essential for AlSi10Mg parts? Enhance LPBF Integrity
- What is the primary function of compacting PVC and metal oxide mixtures? Enhancing Dechlorination Efficiency
- What are the energy-saving advantages of using a SHS system for tungsten carbide? Cut Energy Costs by up to 90%
- Why is a N2 and SF6 gas protection system required for magnesium melting? Ensure Safety and Alloy Purity
- Why must MgO for MKPC be produced at 1600°C? Mastering Chemical Kinetics for High-Performance Modification Slurries
- Why Use a Heating Sample Stage for Si/SiO2 Interface Study? Analyze Thermal Stress & CTE Mismatch Real-Time
- What design considerations are important for custom vacuum chambers? Optimize for Performance, Cost, and Application Needs



















