At its core, designing a custom vacuum chamber requires a holistic approach that balances four key areas: the physical material and geometry, the sealing mechanisms and pumping system, the functional ports needed for your application, and the specific operational environment you need to create. Neglecting any one of these areas can lead to a system that fails to reach its target pressure, compromises your experiment, or is unnecessarily expensive.
A custom vacuum chamber is not merely a container; it is an integrated system. The central challenge is understanding that every design choice—from the type of steel to the placement of a single port—has cascading effects on the chamber's ultimate performance, cost, and suitability for your specific goal.

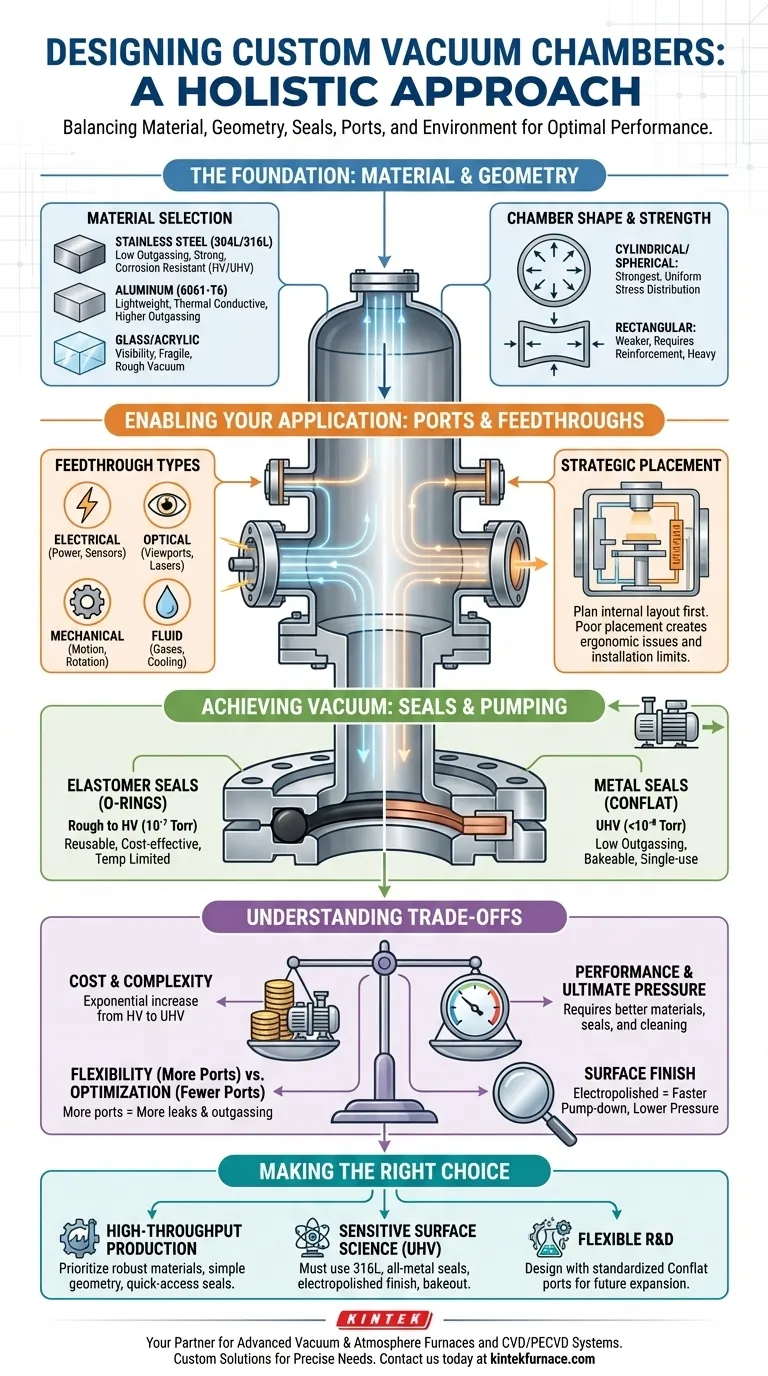
The Foundation: Material and Geometry
The physical body of the chamber is your first and most critical decision. It dictates structural integrity, the ultimate vacuum level achievable, and chemical compatibility.
Choosing the Right Material
The ideal material minimizes outgassing—the release of trapped gases from the material's surface, which is a primary obstacle to achieving high vacuum.
- Stainless Steel (304L or 316L): This is the industry standard for high vacuum (HV) and ultra-high vacuum (UHV) systems. It has low outgassing rates (especially after polishing), is strong, and is easily welded and machined. 316L offers superior corrosion resistance.
- Aluminum (6061-T6): Often used for larger chambers where weight is a concern. It's easy to machine and has excellent thermal conductivity but has higher outgassing rates than stainless steel and is more susceptible to scratches, which can trap contaminants.
- Glass or Acrylic: Typically used for rough or low vacuum applications where visibility is paramount. While glass is inert, both materials are fragile and can be difficult to seal effectively for high vacuum.
The Importance of Shape
The chamber must withstand an external pressure of one atmosphere (14.7 psi or ~1 bar) trying to crush it. Shape is the primary defense against this force.
- Cylindrical and Spherical: These are the strongest shapes for resisting uniform external pressure. They distribute stress evenly, allowing for thinner walls compared to rectangular designs.
- Rectangular or Box Chambers: These are inherently weaker. Their flat surfaces will bow inwards under vacuum and require significant reinforcement, such as external ribs or thicker walls, which adds weight and cost.
Enabling Your Application: Ports and Feedthroughs
A chamber is useless without a way to interact with the environment inside. Ports allow for pumping, venting, and mounting gauges, while feedthroughs provide access for power, signals, fluids, or mechanical motion.
Planning for Access
Think through every interaction required. A feedthrough is a purpose-built component that allows a utility to pass through the chamber wall without creating a leak.
- Electrical Feedthroughs: For powering heaters, running sensors, or creating plasma.
- Optical Feedthroughs (Viewports): For visual inspection or allowing laser access.
- Mechanical Feedthroughs: For rotating or moving samples inside the chamber.
- Fluid Feedthroughs: For introducing gases or running cooling lines.
The Impact of Port Placement
Where you put the ports is as important as what they are. Poor placement can create an ergonomic nightmare or make it impossible to install internal hardware. Always plan the layout of your internal experiment first, then design the chamber ports around it.
Achieving Vacuum: Seals and Pumping
The ability to create and hold a vacuum depends entirely on the quality of your seals and the capability of your pumping system.
Sealing Strategies: Elastomer vs. Metal
The seal is the interface between two flanges. The choice depends entirely on your target pressure and temperature.
- Elastomer Seals (O-rings): Typically made of Viton, these are used for rough to high vacuum levels (down to 10⁻⁷ Torr). They are reusable, cost-effective, and tolerant of minor flange imperfections but have higher outgassing rates and limited temperature ranges.
- Metal Seals (Conflat Flanges): These use a soft metal gasket (usually copper) crushed between two stainless steel knife-edges. They are the standard for UHV applications (below 10⁻⁸ Torr) because they have extremely low outgassing rates and can be baked to high temperatures to drive off water vapor.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Every vacuum chamber design is a compromise. Being aware of these trade-offs is key to making an informed decision.
Cost vs. Performance
The pursuit of lower pressure is a path of exponential cost. Moving from high vacuum (HV) to ultra-high vacuum (UHV) requires more expensive materials (316L vs. 304), metal seals instead of elastomers, more complex pumping systems, and specialized cleaning and handling procedures.
Flexibility vs. Optimization
A chamber designed with many extra ports offers flexibility for future experiments. However, every additional port is a potential leak point and adds to the total surface area, increasing the outgassing load and pump-down time. A chamber optimized for a single, specific task will always outperform a general-purpose one.
The Hidden Variable: Surface Finish
A smooth, electropolished internal surface has a significantly lower surface area than a rough-machined one. This directly translates to less trapped gas and water vapor, resulting in faster pump-down times and a lower ultimate pressure. This "hidden" detail is critical for HV and UHV performance.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To specify your chamber, you must first define your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is high-throughput production: Prioritize robust materials like 304 stainless steel, simple cylindrical geometry, and quick-access elastomer seals for rapid cycling.
- If your primary focus is sensitive surface science (UHV): You must use 316L stainless steel, all-metal Conflat seals, an electropolished internal finish, and carefully plan for high-temperature bakeout.
- If your primary focus is flexible R&D: Design with numerous, standardized Conflat ports for future expansion, even if you initially use them with adapter flanges for elastomer-sealed components.
Ultimately, a successful custom vacuum chamber is born from a clear and complete definition of its intended use.
Summary Table:
| Design Consideration | Key Factors | Impact on Performance |
|---|---|---|
| Material Selection | Stainless Steel (304L/316L), Aluminum, Glass/Acrylic | Affects outgassing, strength, and chemical compatibility |
| Geometry | Cylindrical, Spherical, Rectangular | Influences structural integrity and cost |
| Sealing Mechanisms | Elastomer O-rings, Metal Conflat seals | Determines vacuum level and temperature tolerance |
| Ports and Feedthroughs | Electrical, Optical, Mechanical, Fluid | Enables application-specific interactions |
| Operational Environment | Target pressure, Temperature, Application type | Guides material and seal choices for efficiency |
Ready to design a custom vacuum chamber that meets your exact needs? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures your chamber is tailored for precise experimental requirements, whether for high-throughput production, sensitive surface science, or flexible R&D. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your laboratory's performance with reliable, optimized vacuum solutions!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Ultra Vacuum Electrode Feedthrough Connector Flange Power Lead for High Precision Applications
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Ultra High Vacuum Stainless Steel KF ISO CF Flange Pipe Straight Pipe Tee Cross Fitting
- Ultra High Vacuum Observation Window Stainless Steel Flange Sapphire Glass Sight Glass for KF
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- How does a vacuum pumping system contribute to the fabrication of high-quality silicide structures? Ensure Material Purity
- What are the main technical requirements for vacuum pumps in vacuum sintering furnaces? Ensure Material Purity and Efficiency
- How does a high-vacuum pump system facilitate the synthesis of high-quality calcium-based perrhenates? Expert Synthesis
- What is the primary function of the vacuum pump system in the magnesium powder evaporation process? Ensure High Purity & Efficiency
- What materials are used for the heating elements in a vacuum furnace? Choose the Right Element for Your High-Temp Needs



















