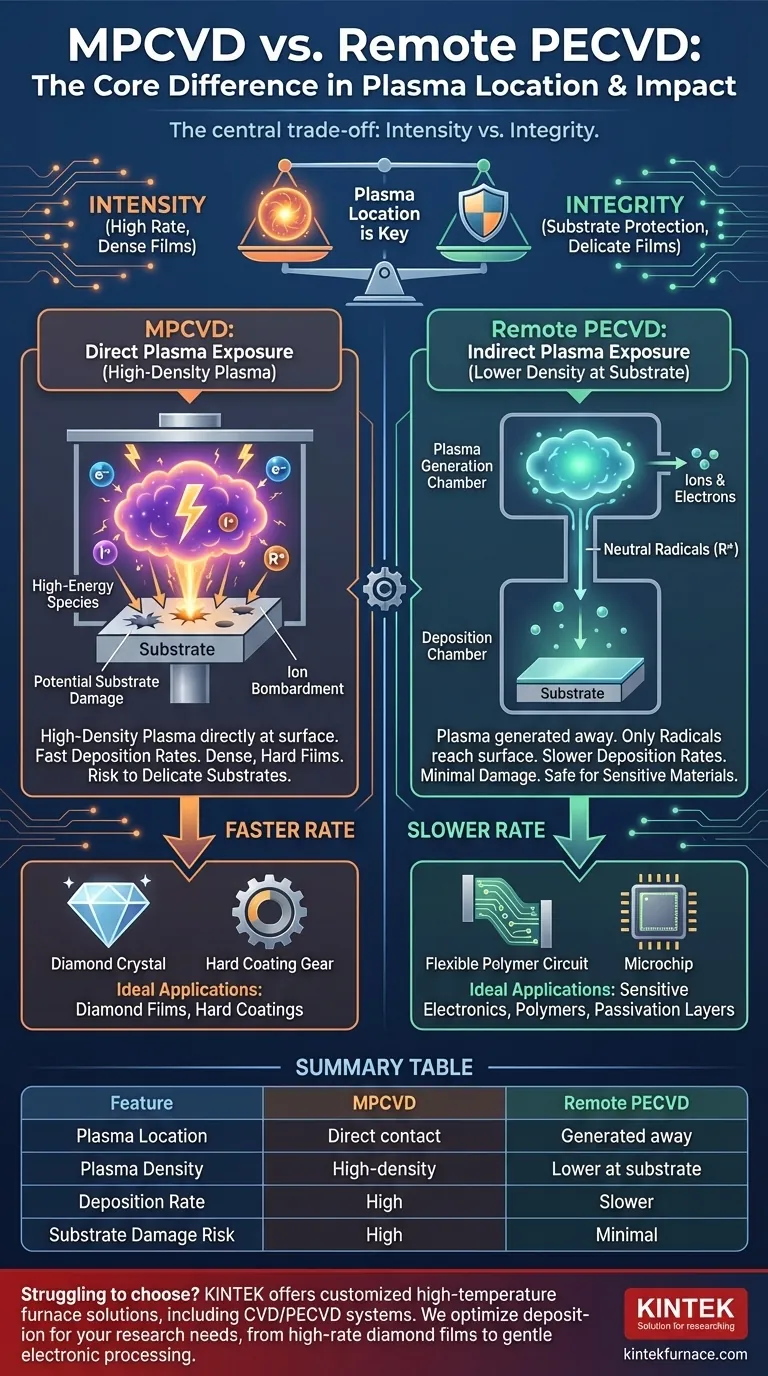
At its core, the difference between MPCVD (Microwave Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition) and remote PECVD lies in the location of the plasma relative to the substrate. In remote PECVD, the plasma is intentionally generated away from the substrate to minimize damage, while in a typical MPCVD setup, the plasma is generated in direct contact with or very near the substrate to maximize plasma density and reaction rates.
The central trade-off is one of intensity versus integrity. MPCVD offers high-density plasma for potentially faster deposition and higher-quality films, but at the risk of damaging the substrate. Remote PECVD prioritizes protecting the substrate from plasma-induced damage, often at the cost of lower deposition rates.

The Fundamental Difference: Plasma Location
The placement of the plasma source dictates the fundamental characteristics of each deposition process, influencing everything from substrate compatibility to the final properties of the film.
MPCVD: Direct Plasma Exposure
In a typical MPCVD system, microwaves are used to generate a very high-density plasma directly within the reaction chamber. This means the substrate is immersed in an environment rich with high-energy electrons, ions, and reactive free radicals.
This direct exposure is highly effective at breaking down precursor gases and driving chemical reactions. The high concentration of reactive species can lead to very high deposition rates and the formation of dense, high-quality films.
Remote PECVD: Indirect Plasma Exposure
Remote PECVD systems are designed with two distinct regions: a plasma generation chamber and a deposition chamber. The plasma is created in the first chamber, physically separated from the substrate.
Only specific, longer-lived reactive species—primarily neutral radicals—are transported into the deposition chamber to react at the substrate surface. Energetic ions and electrons are largely filtered out or recombine before they can reach the substrate, creating a plasma-free deposition environment.
The Impact on Deposition and Film Quality
This difference in plasma location creates a cascade of effects that determine the ideal application for each method.
Plasma Density and Deposition Rate
MPCVD is a form of High-Density Plasma (HDP) deposition. The intense plasma directly at the surface typically results in a higher degree of ionization and a greater flux of reactive species.
This often translates to significantly higher deposition rates, making it efficient for growing thick films.
Remote PECVD, by contrast, may have a lower effective concentration of reactive species at the substrate. Some species inevitably recombine during transport from the plasma zone, which can lead to slower deposition rates.
Substrate Damage and Surface Integrity
The primary advantage of remote PECVD is the dramatic reduction in plasma-induced damage. By keeping energetic ions away from the substrate, it prevents physical sputtering and unwanted charge-related defects on the surface.
This makes it the superior method for depositing films on temperature-sensitive or electronically delicate substrates, such as polymers, organic electronics, or the gate layers in advanced microprocessors.
MPCVD's direct plasma exposure carries a significant risk of ion bombardment. While this can sometimes be beneficial for densifying a film, it is often detrimental, compromising the performance of sensitive devices.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Rate vs. Integrity
Choosing between these methods requires a clear understanding of your project's primary goal: are you prioritizing speed and film robustness, or is substrate preservation paramount?
The Case for MPCVD
This method excels when the goal is to create exceptionally hard or dense films and the substrate can withstand the intense plasma environment. Its high plasma density is ideal for applications like growing high-quality synthetic diamond films or other hard coatings where throughput and material properties are key.
The Case for Remote PECVD
This method is essential when the substrate itself is the most valuable or delicate part of the equation. It enables the deposition of high-quality dielectric or passivation layers on finished electronic devices without damaging the underlying circuitry. It is the go-to technique for low-temperature applications on plastics or other soft materials.
Navigating the Terminology
The lines between these terms can sometimes blur. It's helpful to see them as part of a larger family of techniques.
- PECVD is the broad umbrella term for any CVD process enhanced by a plasma.
- MPCVD is a specific type of PECVD that uses microwaves as its power source, typically in a direct, high-density configuration.
- HDP-CVD (High-Density Plasma CVD) is a category focused on achieving high plasma density. MPCVD is one type of HDP-CVD, but some HDP systems can also be configured with remote plasma sources.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your application's specific requirements will dictate the correct technology choice.
- If your primary focus is maximizing deposition rate and creating dense, robust films (like diamond or hard coatings): MPCVD is often the superior choice due to its high plasma density and direct reactant activation.
- If your primary focus is protecting a sensitive substrate (like a polymer, organic material, or advanced semiconductor device): Remote PECVD is the necessary choice to prevent destructive ion bombardment and plasma damage.
- If your primary focus is depositing a standard film (like silicon nitride or oxide) on a robust substrate (like a silicon wafer): Both methods may be viable, and the choice could depend on the specific film property requirements and equipment availability.
Ultimately, understanding where the plasma is created is the key to selecting the right tool for your material deposition challenge.
Summary Table:
| Feature | MPCVD | Remote PECVD |
|---|---|---|
| Plasma Location | Direct contact with substrate | Generated away from substrate |
| Plasma Density | High-density plasma | Lower plasma density at substrate |
| Deposition Rate | High | Slower |
| Substrate Damage Risk | High risk of ion bombardment | Minimal plasma-induced damage |
| Ideal Applications | Diamond films, hard coatings | Sensitive substrates, electronics, polymers |
Struggling to choose between MPCVD and remote PECVD for your lab's unique needs? KINTEK specializes in advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including CVD/PECVD systems. With our exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer deep customization to precisely match your experimental requirements—whether you need high deposition rates for diamond films or gentle processing for sensitive electronics. Contact us today to discuss how our tailored solutions can optimize your deposition processes and enhance your research outcomes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Cylindrical Resonator MPCVD Machine System for Lab Diamond Growth
- MPCVD Machine System Reactor Bell-jar Resonator for Lab and Diamond Growth
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano Diamond Coating
People Also Ask
- Why is the temperature control system important in MPCVD equipment? Ensure Precise Diamond Growth and Process Stability
- What is the basic principle of operation for the microwave plasma chemical vapor deposition system? Unlock High-Purity Material Growth
- What are some challenges associated with MPCVD? Overcome High Costs and Complexity for Diamond Synthesis
- How is CVD classified based on physical characteristics of vapor? Explore AACVD and DLICVD Methods
- Why is maintaining gas pipelines important in MPCVD equipment? Ensure Purity and Safety in Crystal Growth



















