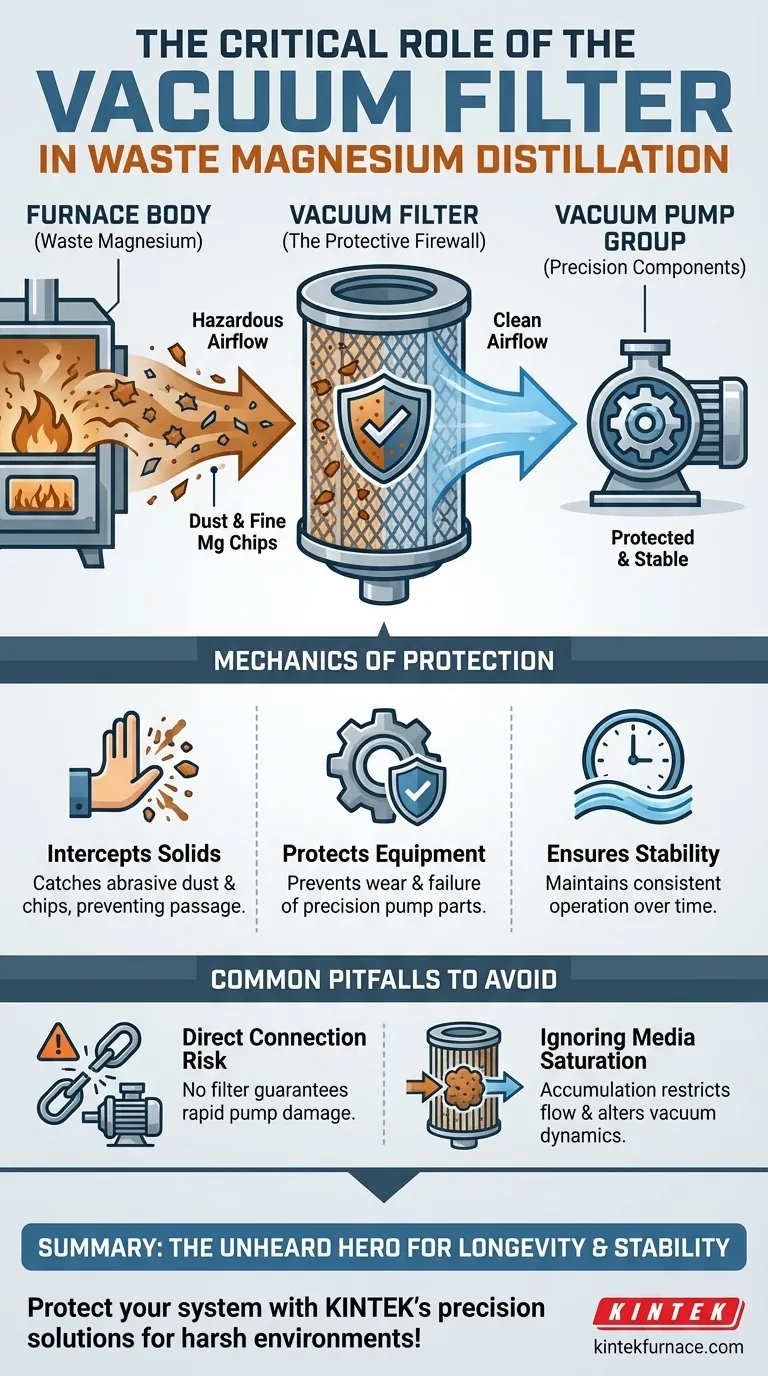
The vacuum filter serves as the critical protective barrier between your furnace body and the vacuum pump group in a magnesium distillation system. Its primary function is to physically intercept dust and fine magnesium chips carried by the airflow, preventing these abrasive contaminants from entering and destroying the precision components of your vacuum pump.
The vacuum distillation of waste magnesium generates hazardous particulate matter that inevitably travels with the process airflow. The vacuum filter is the non-negotiable safeguard that isolates the pump from these contaminants, ensuring the system’s longevity and operational stability.

The Operational Context: Why Filtration is Essential
Handling High-Hazard Raw Materials
Waste magnesium is inherently "high-hazard" raw material. It is rarely pure; it contains significant amounts of loose dust and fine magnesium chips.
The Dynamics of Airflow
During the vacuum pumping process, strong airflow is generated to depressurize the system. This airflow acts as a carrier vehicle, lifting the lightweight magnesium dust and chips from the furnace body and moving them toward the outlet.
The Mechanics of Protection
Intercepting Solid Particles
The vacuum filter is strategically installed directly in the path between the furnace and the pump. It utilizes internal media designed to catch and hold the solid particles carried by the draft, preventing them from passing further down the line.
Protecting Precision Equipment
Vacuum pumps rely on tight tolerances and precision mechanics to maintain low pressure. If magnesium chips or dust enter the pump, they cause rapid wear, mechanical binding, or total failure.
Ensuring Long-Term Stability
By preventing abrasive materials from entering the pump group, the filter allows the system to operate consistently over time. It transforms a volatile, dirty process into a stable operation by keeping the critical machinery clean.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
The Risk of Direct Connection
A common error in system design is underestimating the volume of debris generated by waste magnesium. Connecting a furnace to a pump without adequate filtration guarantees immediate wear and eventual damage to the pump group.
Ignoring Media Saturation
While the filter protects the pump, it does so by accumulating waste. If the internal media is not monitored or cleaned, the "interception" capability remains, but airflow may eventually be restricted, altering the vacuum dynamics.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To ensure your magnesium distillation system remains operational and safe, focus on the placement and integrity of your filtration.
- If your primary focus is Equipment Longevity: Prioritize a high-quality filter installation to prevent abrasive chips from ever reaching the precision pump mechanics.
- If your primary focus is Process Stability: Ensure the filter media is capable of handling the specific volume of dust your raw material generates to avoid airflow fluctuations.
The vacuum filter is not just an accessory; it is the firewall that keeps your vacuum pump functioning in a harsh environment.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Role of the Vacuum Filter |
|---|---|
| Primary Function | Acts as a protective barrier, intercepting dust and fine magnesium chips from the furnace body before they reach the vacuum pump. |
| Key Benefit | Prevents abrasive contaminants from damaging precision pump components, ensuring operational stability and longevity. |
| Operational Context | Essential for handling high-hazard waste magnesium, which generates loose dust and chips carried by process airflow. |
| Common Risk Avoided | Mitigates rapid wear, mechanical binding, or total failure of vacuum pumps due to direct exposure to contaminants. |
Protect your magnesium distillation system with precision-engineered solutions from KINTEK!
Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers robust Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, including cold tube furnaces ideal for magnesium extraction. Our lab high-temp furnaces are fully customizable to meet your unique operational needs, ensuring durability and efficiency in harsh environments.
Don't let abrasive contaminants compromise your equipment—contact us today to discuss how our tailored vacuum filtration and furnace systems can enhance your process stability and extend your system's lifespan!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace Molybdenum Wire Vacuum Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the primary function of a vacuum graphite furnace? Achieve Extreme-Temperature Material Purity
- What is the significance of vacuum in relation to graphite components in furnaces? Prevent Oxidation for Extreme Temperatures
- What is the mechanism and effect of post-annealing NiTi thin films in a vacuum furnace? Unlock Superelasticity
- Why are graphite fixtures and holders important in vacuum furnaces? Unlock Precision & Durability
- Why is graphite cost-effective for vacuum furnaces? Maximize Long-Term ROI & Efficiency



















