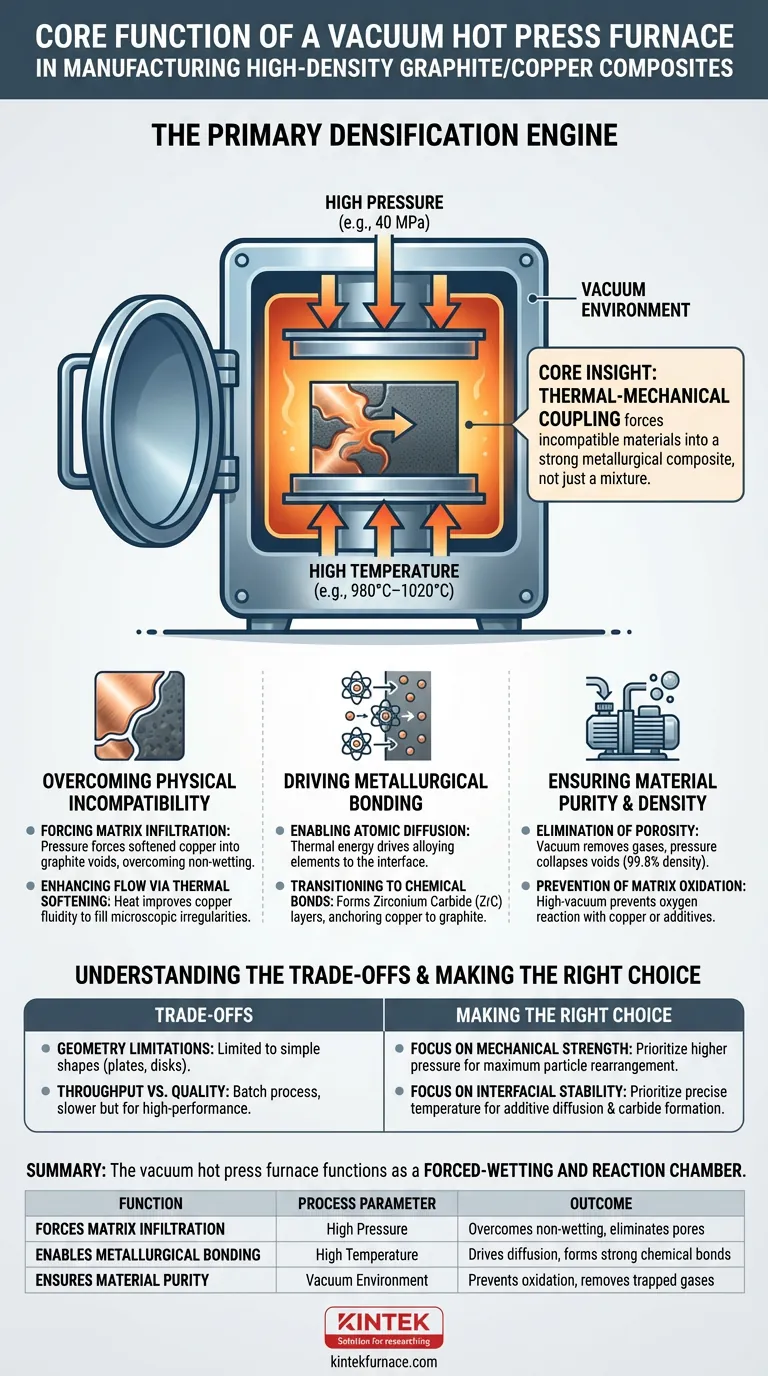
A vacuum hot press furnace acts as the primary densification engine in manufacturing graphite/copper composites. By simultaneously applying specific high temperatures (e.g., 980°C–1020°C) and substantial mechanical pressure (e.g., 40 MPa) within a vacuum, it forces the copper matrix to infiltrate the graphite structure. This process actively overcomes the natural non-wetting behavior between the two materials to eliminate internal pores and achieve near-theoretical density.
Core Insight: The furnace does not merely heat the material; it provides the thermal-mechanical coupling required to force incompatible materials (copper and graphite) into a unified state, transitioning them from a weak mechanical mixture to a strong metallurgical composite.

Overcoming Physical Incompatibility
The primary challenge in copper/graphite composites is that molten copper does not naturally "wet" or spread across graphite surfaces. The vacuum hot press furnace resolves this through mechanical force.
Forcing Matrix Infiltration
Because copper lacks affinity for graphite, it resists entering the microscopic gaps between graphite flakes.
The furnace applies high mechanical pressure (often around 40 MPa) to physically force the softened or molten copper matrix into these voids. This overcomes the capillary resistance that otherwise prevents the metal from penetrating the graphite structure.
Enhancing Flow via Thermal Softening
High temperatures (ranging from 980°C to 1020°C) soften the copper matrix or facilitate the formation of liquid phases, such as a copper-boron phase.
This thermal state improves the fluidity of the metal. When combined with pressure, the increased fluidity allows the copper to flow over rough graphite surfaces and fill microscopic irregularities that pressureless sintering would miss.
Driving Metallurgical Bonding
Achieving a high-density composite requires more than just squeezing materials together; they must chemically interact at the interface.
Enabling Atomic Diffusion
The thermal energy provided by the furnace is critical for driving atomic diffusion.
In specialized composites, this energy allows alloying elements like Zirconium to diffuse to the copper-graphite interface. Without this sustained thermal environment, these atoms would remain trapped in the matrix rather than reinforcing the weak points of the composite.
Transitioning to Chemical Bonds
The ultimate goal of this process is to shift from simple mechanical interlocking to metallurgical bonding.
For example, the furnace environment enables Zirconium to react with graphite to form a Zirconium Carbide (ZrC) layer. This chemical reaction anchors the copper to the graphite, significantly improving the material's structural integrity and thermal performance.
Ensuring Material Purity and Density
The vacuum environment is as critical as the heat and pressure, acting as a purification stage during the densification process.
Elimination of Porosity
Graphite is naturally porous, and trapped air is detrimental to thermal conductivity.
The vacuum environment removes adsorbed gases and air pockets from the interstitial spaces. Simultaneously, the mechanical pressure collapses any remaining voids, allowing the material to reach densities as high as 99.8% of the theoretical limit.
Prevention of Matrix Oxidation
Copper is highly susceptible to oxidation at sintering temperatures.
The high-vacuum environment (e.g., 10^-3 Pa) prevents oxygen from reacting with the copper or any active additives like titanium. This ensures the interface remains clean, allowing atoms to diffuse across pure surfaces rather than being blocked by oxide layers.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While vacuum hot pressing creates superior materials, it introduces specific constraints that must be managed.
Geometry Limitations
Unlike casting or pressureless sintering, hot pressing is generally limited to simple shapes (plates, disks, or cylinders) defined by the die. Complex geometries often require significant post-processing and machining, which can be difficult given the abrasive nature of graphite composites.
Throughput vs. Quality
This is a batch process that is inherently slower than continuous sintering methods. The requirement to heat, pressurize, and cool the entire thermal mass of the die and ram under vacuum increases cycle times, making it a high-cost solution reserved for high-performance applications.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The vacuum hot press furnace is a precision tool. How you utilize it depends on the specific deficiencies of your composite mixture.
- If your primary focus is mechanical strength: Prioritize higher pressure settings (e.g., 40+ MPa) to maximize particle rearrangement and ensure the elimination of all microscopic voids between the copper and graphite.
- If your primary focus is interfacial stability: Prioritize precise temperature control to drive the diffusion of additives (like Zr or B) and ensure the formation of carbide layers (like ZrC) without melting the matrix excessively.
Summary: The vacuum hot press furnace functions as a forced-wetting and reaction chamber, using pressure to solve the physical gap and heat to bridge the chemical gap between copper and graphite.
Summary Table:
| Function | Key Process Parameters | Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Forces Matrix Infiltration | High Pressure (e.g., 40 MPa) | Overcomes non-wetting, eliminates pores |
| Enables Metallurgical Bonding | High Temperature (e.g., 980°C–1020°C) | Drives diffusion, forms strong chemical bonds (e.g., ZrC) |
| Ensures Material Purity | Vacuum Environment (e.g., 10⁻³ Pa) | Prevents oxidation, removes trapped gases |
Ready to Engineer Superior Graphite/Copper Composites?
Achieving near-theoretical density and strong metallurgical bonds requires precise control over heat, pressure, and environment. The challenges of non-wetting materials and porosity are exactly what our vacuum hot press furnaces are engineered to solve.
KINTEK's high-temperature furnaces provide the essential thermal-mechanical coupling for your most demanding R&D and production goals. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, all customizable for your unique composite needs.
Let's discuss your application. Contact our experts today to explore how a KINTEK solution can enhance your material performance.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- 9MPa Air Pressure Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why are vacuum presses considered versatile tools in various industries? Achieve Perfect Lamination and Forming
- What are the processing advantages of RHS or SPS for A357 aluminum composites? Achieve Near-Full Density Faster
- What are the advantages of using vacuum hot press furnaces over traditional furnaces? Achieve Superior Material Quality and Performance
- What advantages does a vacuum hot press furnace demonstrate for Fe-Cu-Ni-Sn-VN composites? Superior Nanostructure Prep
- How does vacuum hot pressing compare to vacuum brazing and sintering? Choose the Right Process for Your Materials
- What role do high-strength graphite molds play during SPS? Boost Mo-Cr-Y Composite Densification
- Why is it necessary to treat graphite molds containing mixed powders in a vacuum drying oven before vacuum hot press sintering? Prevent Porosity and Ensure Maximum Density
- Why is 'final short-time pressing' important in vacuum hot pressing? Unlock Maximum Material Density



















