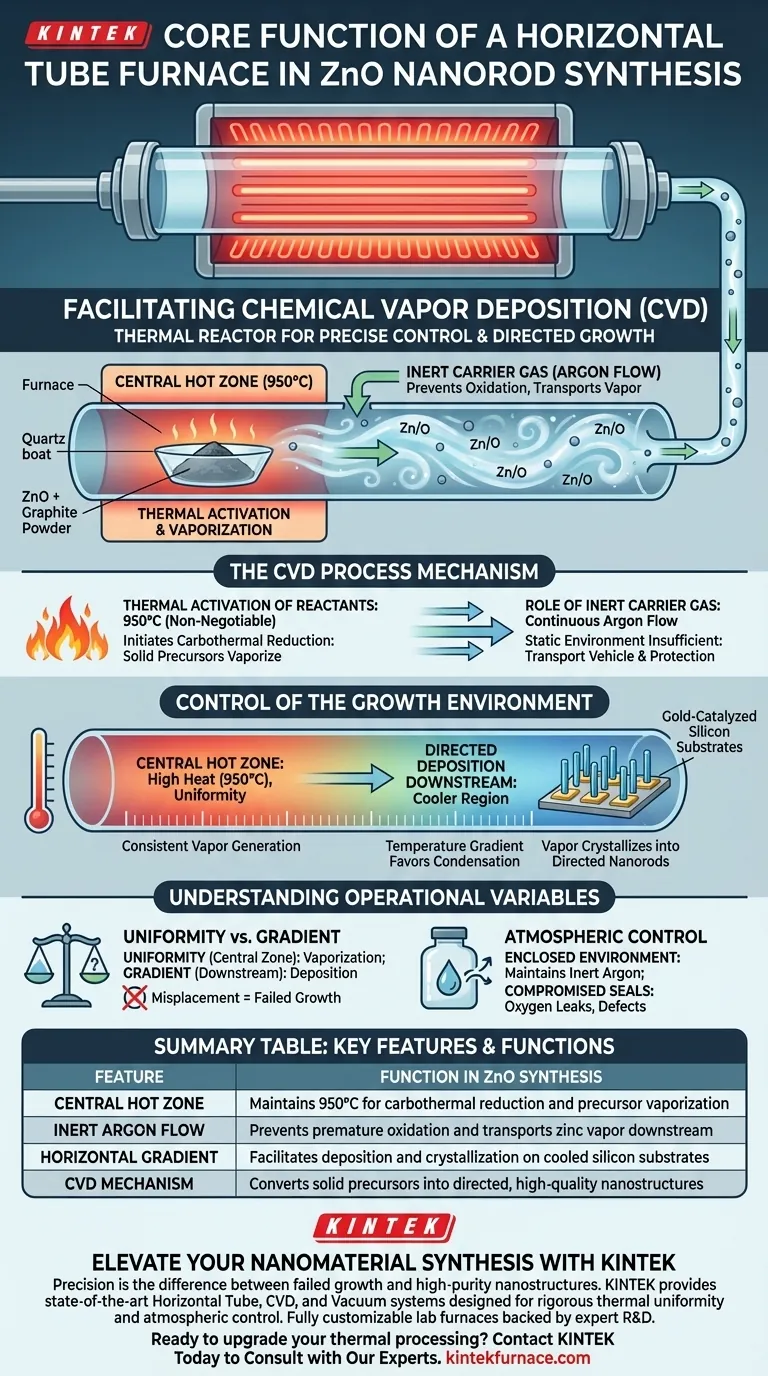
The core function of a horizontal tube furnace in this specific application is to facilitate Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) through precise thermal management. By heating a mixture of Zinc Oxide (ZnO) and graphite powder to exactly 950 degrees Celsius within a central hot zone, the furnace vaporizes the raw materials. It then maintains a constant argon gas flow to transport this vapor downstream, where it deposits onto gold-catalyzed silicon substrates to form nanorods.
Core Takeaway: The horizontal tube furnace acts as a thermal reactor that converts solid precursors into vapor and creates the necessary aerodynamic conditions for that vapor to travel and re-crystallize. It allows for the separation of the vaporization zone (high heat) and the deposition zone (downstream), which is essential for the directed growth of high-quality nanostructures.

Facilitating Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD)
To understand why a horizontal tube furnace is the standard tool for this process, you must look at the specific requirements of the CVD mechanism.
Thermal Activation of Reactants
The synthesis of ZnO nanorods requires significant thermal activation energy. The furnace's primary job is to generate this energy in a controlled manner.
By raising the temperature of the central zone to 950°C, the furnace initiates a carbothermal reduction reaction between the ZnO and graphite powder. This high heat is non-negotiable; without it, the solid precursors cannot vaporize effectively to begin the process.
The Role of Inert Carrier Gas
A static environment is insufficient for this type of synthesis. The furnace is designed to accommodate a constant flow of argon gas.
This inert gas serves two purposes: it prevents unwanted chemical reactions (such as premature oxidation) and acts as a transport vehicle. It carries the zinc-rich vapor from the hot center of the tube to the cooler downstream regions.
Control of the Growth Environment
The physical configuration of the "horizontal" tube is not arbitrary; it supports the spatial separation required for nanorod growth.
The Central Hot Zone
The furnace creates a central hot zone where the highest temperature (950°C) is maintained with high uniformity.
This is where the "source materials" (ZnO and graphite) are placed. The uniformity here ensures the phase transition from solid to vapor is consistent and efficient.
Directed Deposition Downstream
The synthesis does not happen where the heating is most intense. The furnace design allows for a temperature gradient along the length of the tube.
As the vapor moves "downstream" away from the 950°C center, it reaches the gold-catalyzed silicon substrates. The precise thermal environment at this downstream location allows the vapor to condense and crystallize into directed nanorods.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While the horizontal tube furnace is the ideal tool for this synthesis, there are operational variables that can impact success.
Temperature Uniformity vs. Gradient
A common point of confusion is the need for uniformity versus the need for a gradient.
While the supplementary references highlight the importance of temperature uniformity for phase purity, this generally applies to the central zone where vaporization occurs. However, for the actual growth, a gradient is often required so the vapor can deposit on the cooler substrate. Misunderstanding the position of your substrate relative to the central hot zone will result in failed growth.
Atmospheric Control Limitations
The furnace relies on an enclosed environment to maintain the argon atmosphere.
If the tube seals or end plugs are compromised, oxygen may leak in. This disrupts the inert environment, potentially altering the stoichiometry of the ZnO or causing defects in the nanorod crystal structure.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To maximize the effectiveness of a horizontal tube furnace for ZnO synthesis, align your setup with your specific research objectives.
- If your primary focus is Phase Purity: Ensure the central heating zone is calibrated to maintain 950°C with high uniformity to guarantee complete vaporization of the precursor mix.
- If your primary focus is Directed Growth: Pay strict attention to the placement of the gold-catalyzed substrates downstream, ensuring they are positioned where the temperature gradient favors deposition.
Success in nanorod synthesis relies not just on generating heat, but on using the furnace to strictly control the transport of mass from a solid source to a directed crystal structure.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Function in ZnO Nanorod Synthesis |
|---|---|
| Central Hot Zone | Maintains 950°C for carbothermal reduction and precursor vaporization |
| Inert Argon Flow | Prevents premature oxidation and transports zinc vapor downstream |
| Horizontal Gradient | Facilitates deposition and crystallization on cooled silicon substrates |
| CVD Mechanism | Converts solid precursors into directed, high-quality nanostructures |
Elevate Your Nanomaterial Synthesis with KINTEK
Precision is the difference between failed growth and high-purity nanostructures. KINTEK provides state-of-the-art Horizontal Tube, CVD, and Vacuum systems designed to maintain the rigorous thermal uniformity and atmospheric control required for Zinc Oxide synthesis.
Backed by expert R&D and world-class manufacturing, our lab high-temp furnaces are fully customizable to meet your unique research specifications. Whether you are optimizing phase purity or mastering directed growth, KINTEK offers the reliability your lab deserves.
Ready to upgrade your thermal processing? Contact KINTEK Today to Consult with Our Experts
Visual Guide
References
- Marion Ryan C. Sytu, Jong‐in Hahm. Individual ZnO–Ag Hybrid Nanorods for Synergistic Fluorescence Enhancement Towards Highly Sensitive and Miniaturized Biodetection. DOI: 10.3390/nano15080617
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the benefits of a high-pressure metal tube reactor for CO2 hydrogenation? Achieve Kinetic Precision
- Why is an atmosphere-protected tube furnace preferred for LMTOF1244? Ensuring Precise Chemical Stoichiometry
- What is the primary function of a tube furnace in CVD COF synthesis? Achieve Precision 2D Film Growth
- What factors influence the processing time in a rotary tube furnace? Master Control for Efficient Heat Treatment
- What critical processing conditions does a horizontal tube furnace provide for 3D porous NiO capacitors?
- How are rotary tube furnaces utilized in agriculture? Boost Efficiency in Drying and Biomass Processing
- Why is an industrial-grade tube furnace utilized for the heat treatment of TiO2 particles under an argon atmosphere?
- What is the function of a gradient temperature horizontal furnace? Expert Growth of Fe4GeTe2 Single Crystals



















