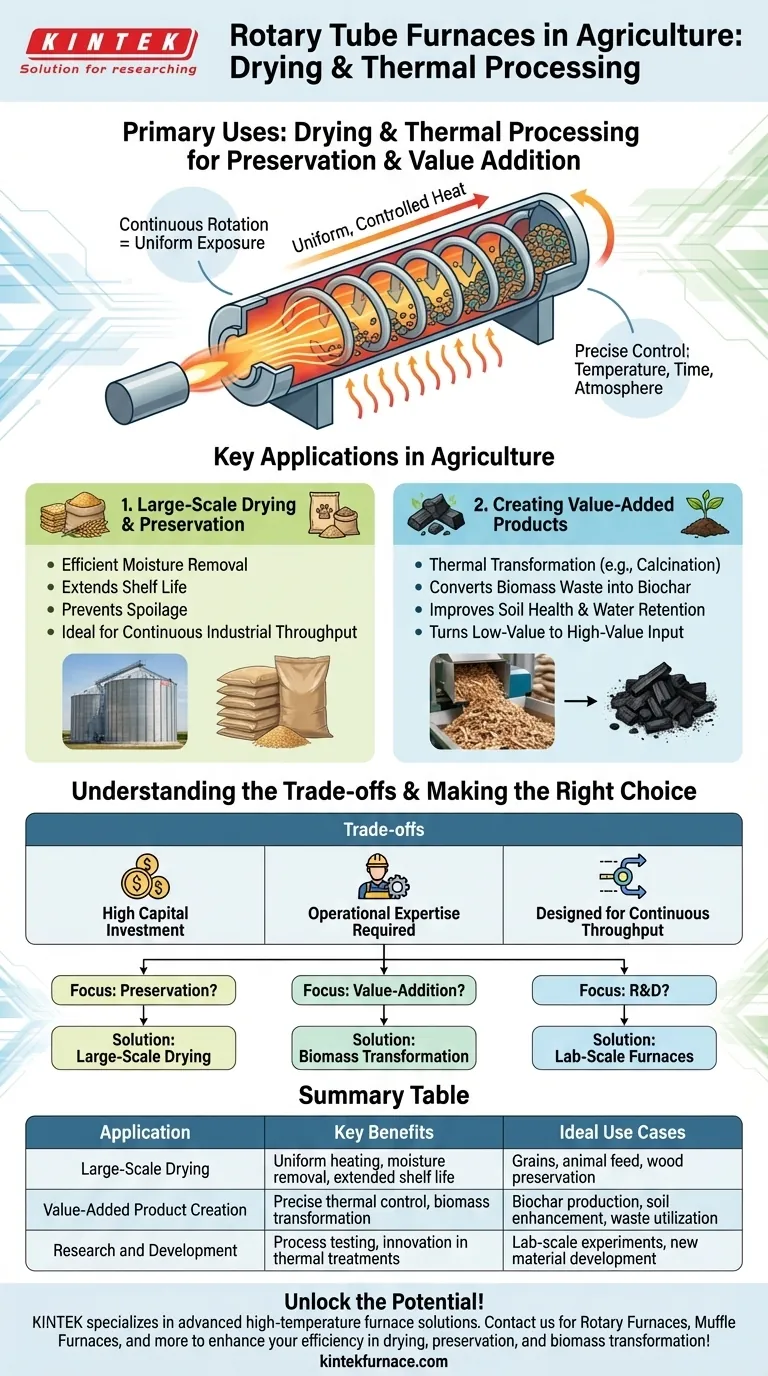
In agriculture, rotary tube furnaces are primarily used for drying and thermal processing. They are instrumental in extending the shelf life of agricultural products, animal feed, and wood by removing moisture, and for altering the physical and chemical properties of biomass to create new, value-added materials.
While often seen as industrial equipment for metallurgy or chemicals, the rotary tube furnace's core strength is its ability to apply uniform, controlled heat to loose materials. In agriculture, this translates directly to enhancing preservation and creating valuable products from raw biomass.

The Core Function: Uniform Thermal Treatment
A rotary tube furnace is, at its heart, a rotating cylindrical chamber that passes material through a heated zone. The constant, gentle tumbling is the key to its effectiveness.
Why Rotation is Critical
The rotation ensures that every particle of the material is continuously exposed to the heat source and the internal atmosphere. This prevents hot spots and guarantees a highly uniform final product, which is difficult to achieve in a static furnace.
Precise Process Control
These furnaces allow for exact control over temperature, residence time (how long the material is in the furnace), and the composition of the gas atmosphere inside the tube. This precision is essential for achieving specific outcomes, from simple drying to complex chemical transformations.
Key Applications in Agriculture
While its industrial uses are broad, the furnace's application in agriculture centers on two primary goals: preservation and transformation.
1. Large-Scale Drying and Preservation
The most direct use is for drying. By efficiently removing moisture from vast quantities of agricultural products or animal feed, the furnace prevents spoilage and dramatically extends shelf life. The continuous throughput design makes it ideal for industrial-scale processing where large volumes must be handled consistently.
2. Creating Value-Added Products
This is a more advanced application that leverages the furnace's ability to fundamentally alter materials. Through processes like calcination (thermal decomposition in the absence or limited supply of air), agricultural waste can be transformed.
A prime example is converting biomass, such as wood chips or crop residue, into biochar. Biochar is a stable, carbon-rich material that can be used to improve soil health, sequester carbon, and enhance water retention. This process turns low-value waste into a high-value agricultural input.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, a rotary tube furnace is a specialized piece of industrial equipment with specific considerations.
High Capital Investment
These are not small-scale farm implements. Rotary tube furnaces represent a significant capital investment and are typically employed by larger agricultural processors, cooperatives, or bio-refineries.
Operational Expertise Required
Achieving consistent, high-quality results requires skilled operators. Managing the temperature profiles, rotation speed, and atmospheric conditions is a technical process that demands training and experience.
Designed for Continuous Throughput
The primary advantage of a rotary furnace is its ability to process a continuous flow of material. It is less efficient for small, infrequent, or highly variable batches, which might be better served by simpler batch ovens.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To determine if this technology fits your needs, consider your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is preservation: For large-scale drying of grains, feeds, or other bulk products, a rotary furnace provides unmatched uniformity and efficiency.
- If your primary focus is value-addition: To convert agricultural biomass into new materials like biochar, the precise thermal and atmospheric control of a rotary tube furnace is essential for quality and consistency.
- If your primary focus is research and development: Lab-scale rotary tube furnaces are critical tools for testing new thermal processes and developing innovative uses for agricultural materials before scaling up.
Ultimately, the rotary tube furnace provides agriculture with a powerful method for transforming raw, perishable output into stable, durable, and more valuable products.
Summary Table:
| Application | Key Benefits | Ideal Use Cases |
|---|---|---|
| Large-Scale Drying | Uniform heating, moisture removal, extended shelf life | Grains, animal feed, wood preservation |
| Value-Added Product Creation | Precise thermal control, biomass transformation | Biochar production, soil enhancement, waste utilization |
| Research and Development | Process testing, innovation in thermal treatments | Lab-scale experiments, new material development |
Unlock the potential of rotary tube furnaces for your agricultural operations! At KINTEK, we specialize in providing advanced high-temperature furnace solutions tailored to your needs. Leveraging our exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer products like Rotary Furnaces, Muffle Furnaces, Tube Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. With strong deep customization capabilities, we ensure precise solutions for unique experimental and processing requirements. Contact us today to enhance your efficiency and innovation in drying, preservation, and biomass transformation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What types of materials are suitable for processing in rotary tube furnaces? Ideal for Free-Flowing Powders and Granules
- What supplementary features can enhance rotary tube furnace performance? Boost Efficiency with Precision Control
- What is the purpose of the rotation mechanism in a rotary tube furnace? Achieve Uniform Heating and Enhanced Process Control
- What materials can be used to make the rotating tube assembly of these furnaces? Choose the Best for Your High-Temp Needs
- What factors should be considered when selecting a tube for a rotary tube furnace? Ensure Optimal Performance and Longevity



















