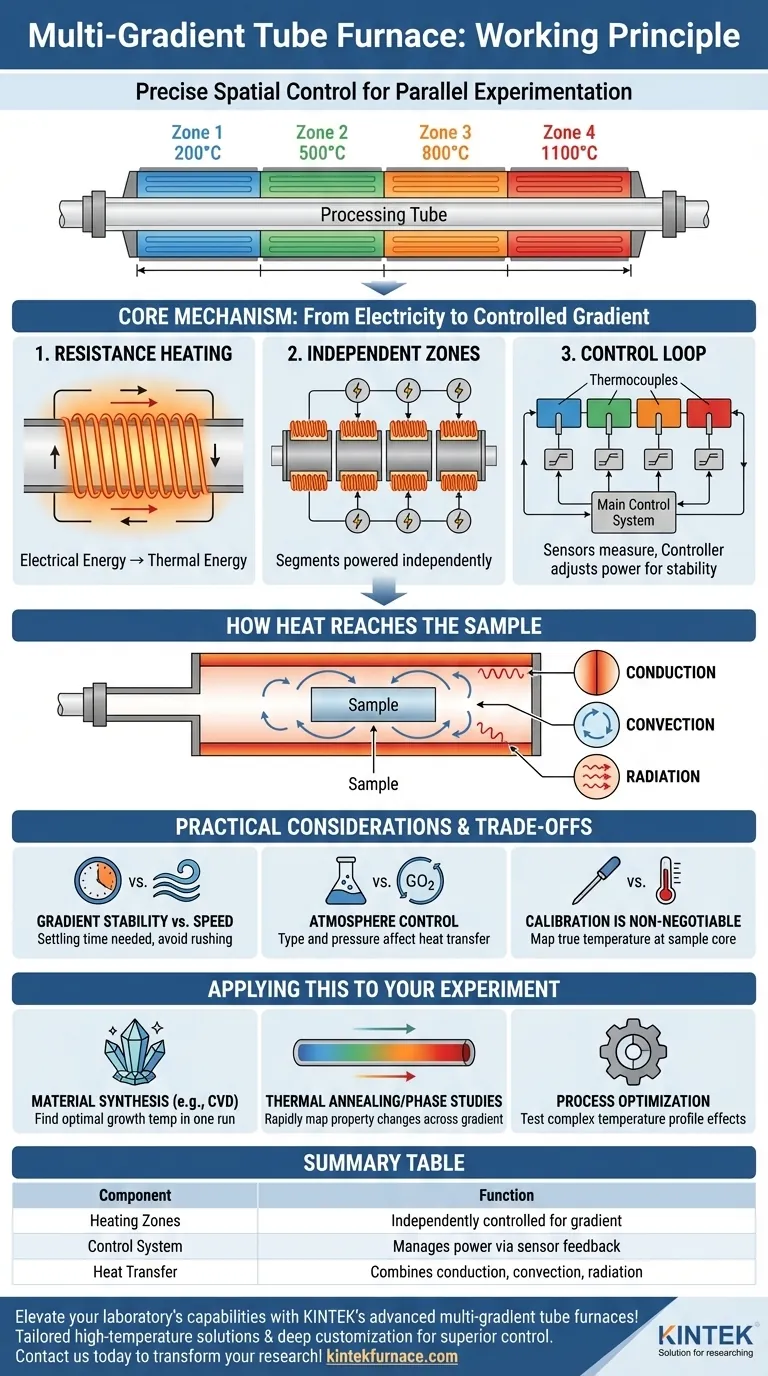
The fundamental principle of a multi-gradient tube furnace is the use of multiple, independently controlled heating zones arranged along a single processing tube. Unlike a standard furnace that strives for uniform temperature, a multi-gradient furnace intentionally creates a stable and precise temperature profile, where different sections of the tube are held at different, specific temperatures. This is achieved by linking dedicated heating elements and temperature sensors in each zone to a central control system.
The core value of a multi-gradient furnace is not just heating, but precise spatial control over temperature. It transforms a simple heating process into a sophisticated experimental platform for studying how materials and chemical reactions behave across a range of temperatures simultaneously.
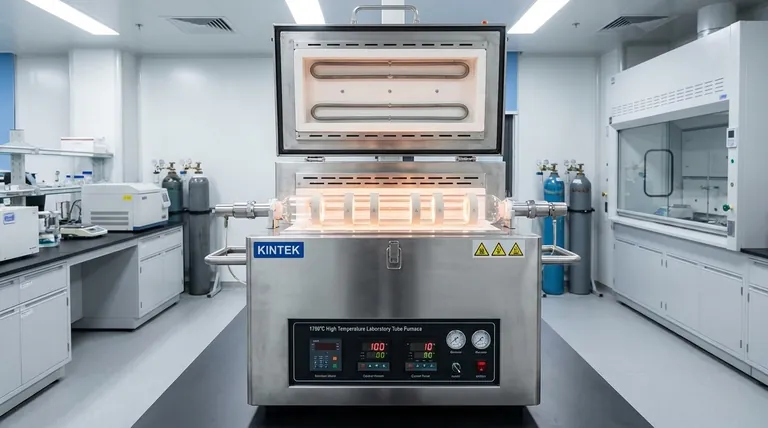

The Core Mechanism: From Electricity to a Controlled Gradient
A multi-gradient furnace's operation relies on a sophisticated interplay between heating elements, sensors, and intelligent control. It's a system designed for precision, not just brute-force heat.
The Foundation: Resistance Heating
At its heart, the furnace generates heat using the principle of electrical resistance. An electric current is passed through specialized heating elements.
These elements resist the flow of electricity, converting electrical energy directly into thermal energy. This is the same fundamental process found in most electric heating devices.
The Key Differentiator: Independent Heating Zones
The defining feature of a multi-gradient furnace is its segmented design. The furnace tube is surrounded by several distinct heating zones, often three or more.
Each zone has its own set of resistance heating elements that can be powered independently from the others. This physical separation is what makes a temperature gradient possible.
The Control Loop: Sensors and Controllers
To manage these zones, each one is equipped with a dedicated temperature sensor, typically a thermocouple. This sensor constantly measures the real-time temperature of its specific zone.
The thermocouple sends this temperature data as an electrical signal to the main control system. The controller compares the actual temperature of each zone to the target temperature you programmed. If there's a difference, the controller precisely adjusts the electrical power sent only to that zone's heating elements, ensuring each segment maintains its setpoint and the overall gradient remains stable.
How Heat Reaches the Sample
Once generated by the heating elements, thermal energy must be transferred to the sample inside the tube. This happens through three primary mechanisms working in concert.
Thermal Conduction
Heat is transferred through direct physical contact. The hot inner wall of the furnace tube conducts heat to the gas inside the tube and to any part of the sample or sample holder that is touching the wall.
Thermal Convection
If gas is present in the tube (even at low pressures), it will heat up, become less dense, and circulate. This movement of hot gas, or convection, is a significant method of heat transfer to the sample.
Thermal Radiation
All hot surfaces emit thermal energy in the form of electromagnetic waves (infrared radiation). The intensely hot inner walls of the furnace radiate heat directly to the surface of the sample, which absorbs this energy.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Practical Considerations
While powerful, a multi-gradient furnace requires a clear understanding of its operational nuances to produce reliable and repeatable results.
Gradient Stability vs. Speed
Establishing a stable, multi-zone temperature profile is not instantaneous. The system needs time to settle, as adjustments in one zone can momentarily influence adjacent zones. Rushing the heating process can lead to temperature overshoots and an unstable gradient.
The Importance of Atmosphere Control
Many experiments are conducted under vacuum or in a controlled inert gas atmosphere. The type and pressure of the gas inside the tube dramatically affect heat transfer, particularly convection. A change in atmosphere will alter the true temperature profile of the sample, even if the furnace controller's setpoints remain the same.
Calibration is Non-Negotiable
The thermocouple measures the temperature near the furnace wall, not necessarily the exact temperature at the core of your sample. For high-precision work, it is critical to perform a calibration run with a separate probe to map the true temperature profile your sample experiences.
Applying This to Your Experiment
Understanding these principles allows you to design more effective and efficient experiments. The furnace becomes more than a heater; it becomes a tool for rapid material and process discovery.
- If your primary focus is material synthesis (e.g., CVD): Use the gradient to find the optimal growth or deposition temperature for your precursors in a single experimental run.
- If your primary focus is thermal annealing or phase studies: Expose a single, long sample to the entire temperature gradient to rapidly map how its crystal structure or properties change with temperature.
- If your primary focus is process optimization: Test how a specific temperature profile—not just a single temperature—affects your final product quality, allowing for more complex process simulations.
Mastering the control of temperature gradients transforms the furnace from a simple oven into a powerful parallel-processing tool for materials science.
Summary Table:
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Heating Zones | Independently controlled sections for creating temperature gradients |
| Control System | Manages power to each zone based on sensor feedback for stability |
| Heat Transfer | Combines conduction, convection, and radiation to reach the sample |
| Applications | Material synthesis, thermal annealing, and process optimization |
Elevate your laboratory's capabilities with KINTEK's advanced multi-gradient tube furnaces! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with tailored high-temperature solutions, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise alignment with your unique experimental needs, enabling superior temperature control and efficiency. Contact us today to discuss how our furnaces can transform your research and accelerate your discoveries!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What safety and reliability features are incorporated into a vertical tube furnace? Ensuring Safe, Consistent High-Temp Processing
- How does a vertical tube furnace achieve precise temperature control? Unlock Superior Thermal Stability for Your Lab
- Why is a tube furnace utilized for the heat treatment of S/C composite cathode materials? Optimize Battery Stability
- What safety measures are essential when operating a lab tube furnace? A Guide to Preventing Accidents
- How is a high-temperature tube furnace utilized in the synthesis of MoO2/MWCNTs nanocomposites? Precision Guide



















