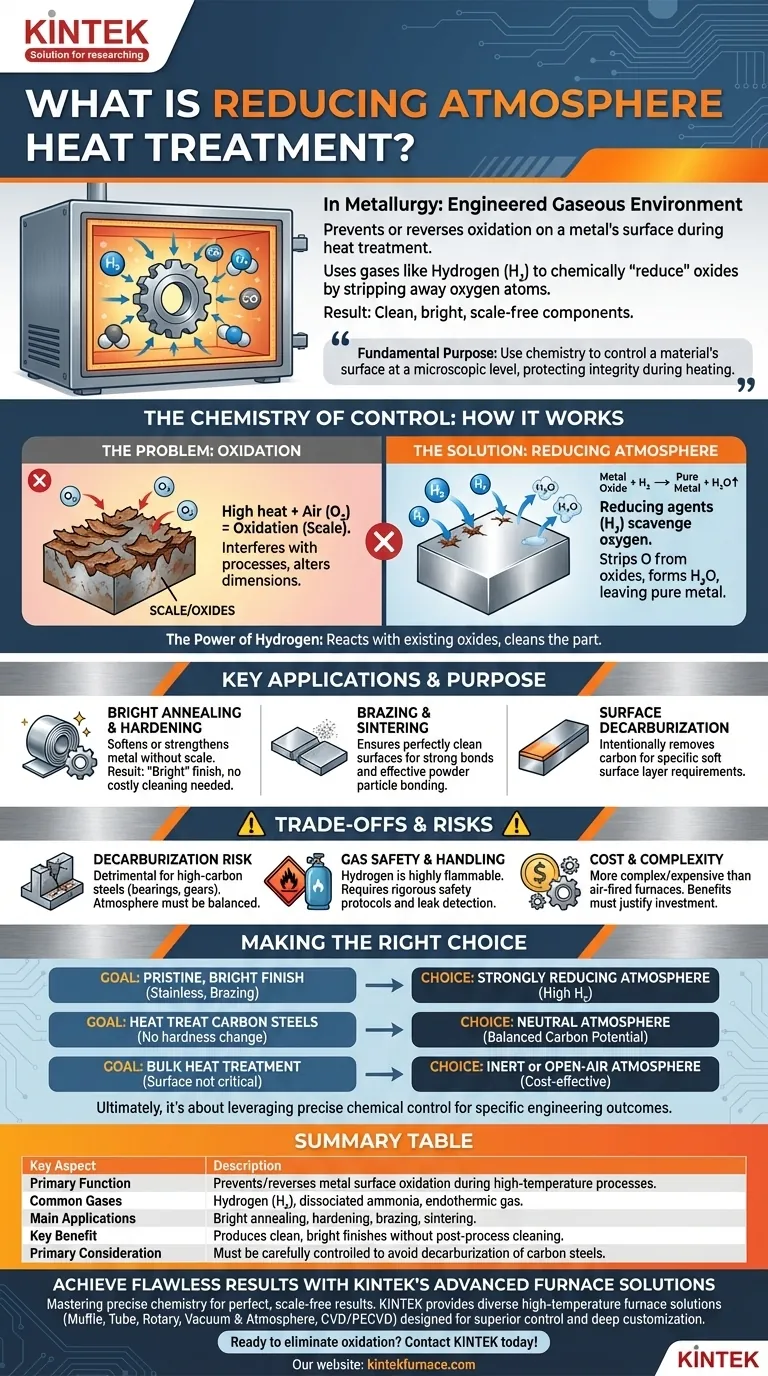
In metallurgy, a reducing atmosphere is a specially engineered gaseous environment inside a furnace that actively prevents or reverses oxidation on a metal's surface during heat treatment. By using gases rich in elements like hydrogen or carbon monoxide, it chemically "reduces" oxides by stripping away oxygen atoms. This ensures the component remains clean, bright, and free from the damaging scale that would normally form at high temperatures.
The fundamental purpose of a reducing atmosphere is to use chemistry to control a material's surface at a microscopic level. By creating an environment that is hungry for oxygen, it protects the metal's integrity during heating, enabling processes and finishes that would otherwise be impossible.

The Chemistry of Control: How Reducing Atmospheres Work
Heat treating is essential for achieving desired mechanical properties in metals, but it introduces a significant problem: oxidation. A reducing atmosphere is the solution to this chemical challenge.
The Problem: Oxidation at High Temperatures
When most metals are heated in the presence of air, the oxygen reacts with the metal's surface. This reaction, called oxidation, forms a layer of oxides, commonly known as scale.
This scale is often undesirable. It can interfere with subsequent processes like welding or painting, alter the part's dimensions, and create a rough, discolored finish.
The Solution: Removing and Preventing Oxygen
A reducing atmosphere combats oxidation by introducing gases that have a stronger affinity for oxygen than the metal being treated. These "reducing agents" effectively scavenge any free oxygen in the furnace.
The most common reducing agent is hydrogen (H₂). Other gases used to create reducing conditions include dissociated ammonia and endothermic gas (a mix of hydrogen, nitrogen, and carbon monoxide).
The Power of Hydrogen
Hydrogen is a powerful reducing agent because it readily reacts with metal oxides that have already formed on the part's surface.
This reaction strips the oxygen from the oxide, leaving behind pure metal and forming water vapor (H₂O), which is then flushed from the furnace. This not only prevents new oxidation but can also clean a lightly oxidized part.
Key Applications and Their Purpose
Controlling the furnace atmosphere enables several critical manufacturing processes that depend on a pristine metal surface.
Bright Annealing and Hardening
This is perhaps the most common application. Processes like annealing, which softens metal, and hardening, which strengthens it, can be performed without creating any surface scale.
The result is a "bright" part that retains its shiny metallic finish and requires no costly and abrasive post-process cleaning like sandblasting or acid pickling.
Brazing and Sintering
Brazing joins two pieces of metal using a filler material. For the filler to flow correctly and form a strong bond, the base metal surfaces must be perfectly clean and free of oxides. A reducing atmosphere ensures this condition is met.
Similarly, in sintering (the process of forming solid parts from metal powder), a reducing atmosphere allows the individual powder particles to bond cleanly and effectively.
Surface Decarburization
A reducing atmosphere can also be used to intentionally remove carbon from the surface of steel, a process called decarburization. While often undesirable, this is sometimes required to create a soft surface layer on a component.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Risks
While powerful, reducing atmospheres are not a universal solution and introduce their own set of complexities and potential problems.
The Unintended Risk of Decarburization
For most high-carbon steels, decarburization is a serious defect. If the atmosphere is too strongly reducing (particularly with high hydrogen and water vapor content), it can pull carbon from the steel's surface.
This leaves the surface layer softer than the core, which is detrimental for parts that require high wear resistance, such as bearings or gears. The atmosphere must be carefully balanced to be "neutral" to the steel's carbon content.
Gas Safety and Handling
The most effective reducing gas, hydrogen, is highly flammable and explosive when mixed with air. Furnaces using high concentrations of hydrogen require rigorous safety protocols, leak detection systems, and proper purging procedures to prevent accidents.
Cost and Complexity
Controlled atmosphere furnaces are significantly more complex and expensive to build, operate, and maintain than simple air-fired furnaces. The cost of the process gases and the monitoring equipment adds to the operational overhead. The benefits of a clean surface must justify this added investment.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct atmosphere is a critical decision that directly impacts the final properties and cost of the component.
- If your primary focus is a pristine, bright finish on stainless steel or for brazing: A strongly reducing atmosphere, often with a high percentage of hydrogen, is the best choice to ensure a completely oxide-free surface.
- If your primary focus is heat treating carbon steels without changing surface hardness: You need a neutral atmosphere carefully balanced to the steel's carbon potential, preventing both oxidation and decarburization.
- If your primary focus is bulk heat treatment where surface finish is not critical: A less expensive inert atmosphere (like pure nitrogen) or even open-air furnace treatment may be a more cost-effective option.
Ultimately, using a reducing atmosphere is about leveraging precise chemical control to achieve specific engineering outcomes on the surface of a material.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Primary Function | Prevents/reverses metal surface oxidation during high-temperature processes. |
| Common Gases | Hydrogen (H₂), dissociated ammonia, endothermic gas. |
| Main Applications | Bright annealing, hardening, brazing, sintering. |
| Key Benefit | Produces clean, bright finishes without post-process cleaning. |
| Primary Consideration | Must be carefully controlled to avoid decarburization of carbon steels. |
Achieve Flawless Results with KINTEK's Advanced Furnace Solutions
Mastering the precise chemistry of a reducing atmosphere is critical for achieving perfect, scale-free results in processes like bright annealing and brazing. The right furnace technology is key to maintaining this control safely and efficiently.
At KINTEK, we leverage our exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line—including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems—is designed for superior atmosphere control. Coupled with our strong deep customization capability, we can precisely engineer a solution to meet your unique experimental and production requirements, ensuring optimal outcomes for your specific metals and processes.
Ready to eliminate oxidation and achieve pristine metal surfaces? Contact KINTEK today to discuss your heat treatment challenges and discover how our tailored furnace solutions can drive your success.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Mesh Belt Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Controlled Inert Nitrogen Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- What features are important when selecting an inert atmosphere furnace or oven? Ensure Purity and Efficiency for Your Lab
- What is an inert oven? Protect Your Materials from Oxidation and Contamination
- What gases are commonly used in gas quenching applications? Optimize Cooling for Superior Metal Properties
- How do the structural designs and sealing mechanisms differ between box furnaces and atmosphere furnaces? Choose the Right Furnace for Your Lab
- How does a specialized ion nitriding furnace achieve gradient hardening on TC4 titanium? Boost Surface Wear Resistance
- What role do inert atmosphere furnaces play in the semiconductor industry? Essential for Purity and Yield
- What type of vacuum pumps are used in low vacuum atmosphere furnaces? Reliable Rotary Vane Pumps for Cost-Effective Heating
- What is the endothermic gas in heat treatment? Master Carbon Control for Superior Steel Hardening



















