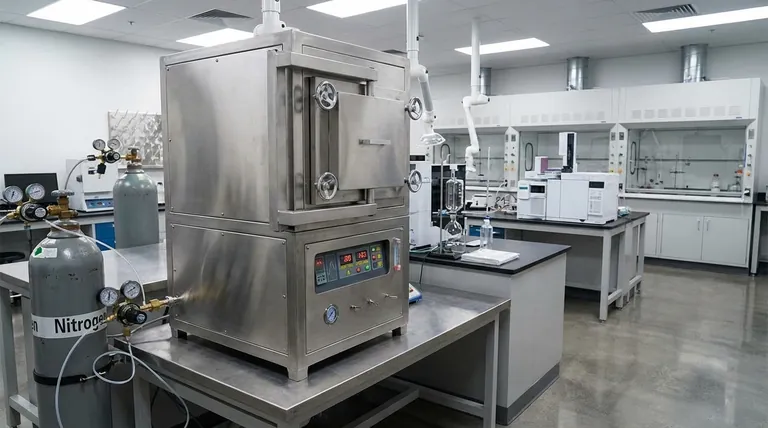
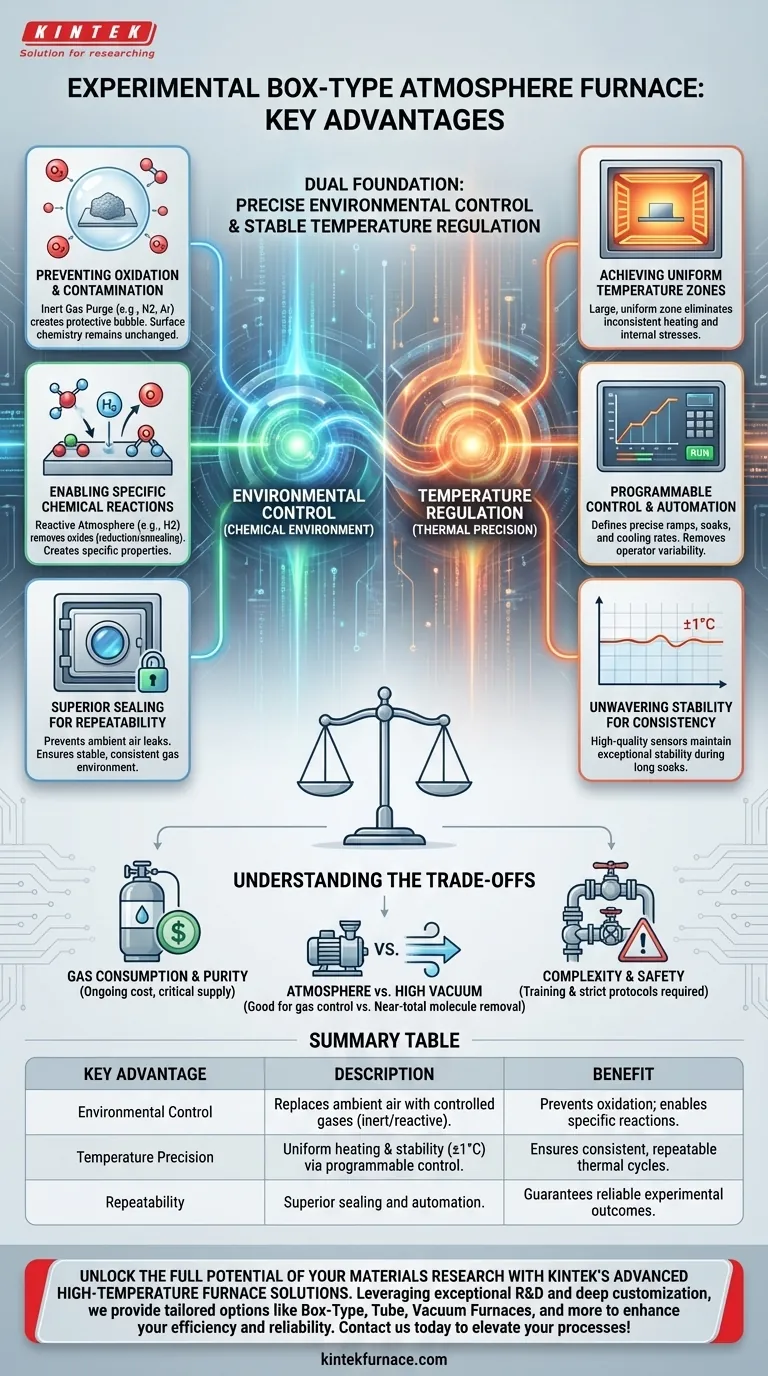
At its core, an experimental box-type atmosphere furnace provides two fundamental advantages: precise control over the chemical environment surrounding a sample and stable, uniform regulation of temperature. This combination allows for heat treatment processes that are impossible in a standard furnace, preventing oxidation, removing contaminants, and enabling specific chemical reactions required for creating advanced materials.
The true value of an atmosphere furnace is not simply heating a material, but fundamentally controlling its chemical environment while it is being heated. This capability is the key to achieving repeatable, high-purity results in modern materials research and development.

The Foundation: Absolute Environmental Control
The defining feature of this furnace is its ability to replace the ambient air with a specific, controlled gas. This capability is critical for any high-temperature process where the material's interaction with oxygen or moisture would be detrimental.
Preventing Oxidation and Contamination
Many materials, especially metals and certain ceramics, will rapidly oxidize when heated in the presence of air. An atmosphere furnace prevents this by purging the chamber and filling it with an inert gas, such as high-purity nitrogen or argon.
This creates a protective bubble around the sample, ensuring its surface chemistry remains unchanged throughout the thermal cycle.
Enabling Specific Chemical Reactions
Beyond simple protection, the furnace can create a reactive atmosphere. Introducing a reducing gas, like hydrogen, can actively remove oxides from a material's surface, a process known as reduction or annealing.
This allows for the creation of materials with specific properties or the preparation of ultra-clean surfaces for subsequent processing.
The Role of Superior Sealing
None of this would be possible without an exceptionally well-sealed furnace chamber. The integrity of the door seals and gas ports is paramount to maintaining the purity of the internal atmosphere.
A superior seal prevents ambient air from leaking in and ensures the controlled gas environment remains stable and consistent, which is essential for repeatability.
Precision and Repeatability in Thermal Processing
Controlling the atmosphere is only half the equation. The furnace must also deliver heat with exceptional precision and uniformity to produce reliable experimental outcomes.
Achieving Uniform Temperature Zones
Advanced atmosphere furnaces are designed with heating elements positioned to create a large, uniform temperature zone within the chamber. This ensures that the entire sample, regardless of its size or position, experiences the exact same thermal conditions.
Inconsistent heating can lead to internal stresses, incomplete reactions, or non-uniform material properties, all of which are eliminated by a uniform zone.
The Power of Programmable Control
Modern furnaces use sophisticated programmable controllers. Researchers can define precise multi-step thermal profiles, automating ramps, soaks at specific temperatures, and controlled cooling rates.
This automation removes operator variability and guarantees that the exact same thermal cycle is run every single time, a cornerstone of repeatable science.
Unwavering Stability for Consistent Outcomes
High-quality controllers and sensors maintain exceptional temperature stability, often holding a setpoint with a variation of as little as ±1°C.
This level of stability is critical during long soak periods, where temperature fluctuations could otherwise alter the final microstructure and properties of the material being processed, such as in the sintering of ceramics.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, an atmosphere furnace is a specialized tool with specific operational considerations. Understanding its limitations is key to using it effectively.
Atmosphere vs. High Vacuum
An atmosphere furnace is excellent for controlling the gaseous environment and is generally less expensive than a dedicated high-vacuum furnace.
However, for applications requiring the near-total removal of all gas molecules, such as in certain thin-film deposition or space simulation tests, a true vacuum furnace is irreplaceable.
Gas Consumption and Purity
Operating an atmosphere furnace requires a continuous supply of high-purity gas, which represents an ongoing operational cost. The purity of the gas source is also critical; a contaminated gas supply will contaminate the furnace and the experiment.
Complexity and Safety
While designed to be user-friendly, these furnaces are more complex than simple air-circulating ovens. Operators must be trained in purging procedures and, if using flammable gases like hydrogen, must adhere to strict safety protocols.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision to use an atmosphere furnace should be driven by the specific requirements of your material and process.
- If your primary focus is preventing oxidation of sensitive metals: An atmosphere furnace with an inert gas supply is the correct and necessary tool.
- If your primary focus is sintering advanced ceramics: The precise control over both temperature and atmosphere is essential to achieve full densification and desired mechanical properties.
- If your primary focus is synthesizing novel materials: The furnace's flexibility to create inert, reducing, or other reactive environments makes it an indispensable tool for research and development.
Ultimately, this furnace empowers you to move beyond simple heating and into the realm of precise materials engineering.
Summary Table:
| Key Advantage | Description |
|---|---|
| Environmental Control | Replaces ambient air with controlled gases (e.g., inert or reactive) to prevent oxidation and enable specific chemical reactions. |
| Temperature Precision | Ensures uniform heating and stability (±1°C) with programmable controllers for repeatable thermal cycles. |
| Repeatability | Superior sealing and automation guarantee consistent experimental outcomes in materials processing. |
Unlock the full potential of your materials research with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with tailored options like Box-Type Atmosphere Furnaces, Muffle Furnaces, Tube Furnaces, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise alignment with your unique experimental needs, enhancing efficiency and reliability. Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can elevate your processes and deliver superior results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Mesh Belt Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Controlled Inert Nitrogen Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- What does inert mean in furnace atmospheres? Protect materials from oxidation with inert gases.
- What is the main purpose of heat treatment? Transform Metal Properties for Superior Performance
- What are the benefits of inert atmosphere heat treating? Prevent Oxidation and Preserve Material Integrity
- How does a chemically inert atmosphere function in a furnace? Prevent Oxidation and Ensure Material Purity
- What is nitrogen used for in a furnace? Prevent Oxidation and Control Heat Treatment Quality



















