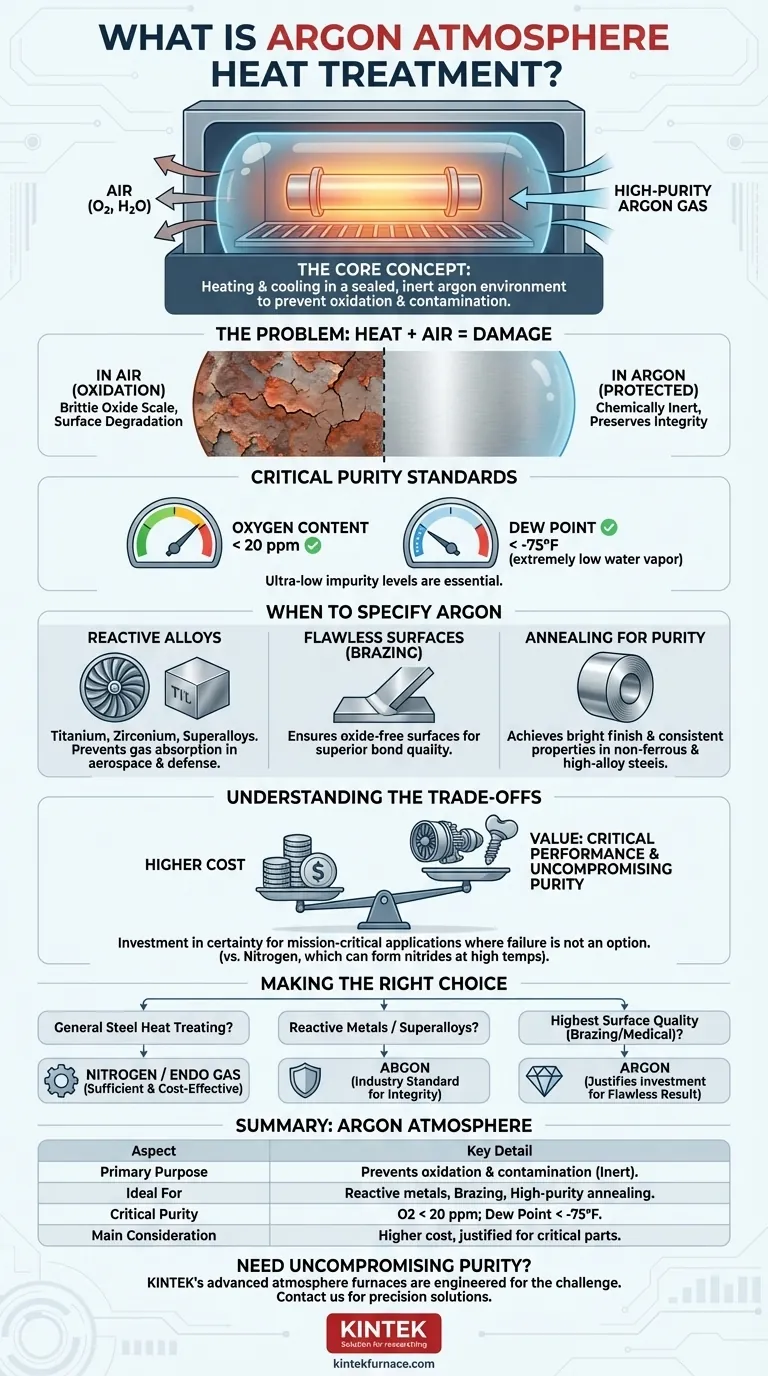
At its core, argon atmosphere heat treatment is a specialized thermal process where a material is heated and cooled within a sealed chamber filled with high-purity argon gas. This is done to prevent the material's surface and internal structure from reacting with atmospheric gases like oxygen and water vapor. By displacing these reactive elements, argon creates a chemically inert environment, protecting the part's integrity at high temperatures.
The fundamental purpose of using an argon atmosphere is to eliminate the risk of oxidation and contamination during heat treatment. While it is a costly option, it is the definitive solution for processing highly reactive metals or for applications where material purity and performance are absolutely non-negotiable.

The Core Problem: Why a Protective Atmosphere is Necessary
Heat treatment relies on precise temperature control to alter a material's physical and mechanical properties. However, introducing high heat also dramatically accelerates chemical reactions, creating a significant risk of damaging the very part you are trying to improve.
The Threat of Oxidation and Contamination
When heated in the presence of normal air, most metals will readily react with oxygen, forming a brittle, flaky layer of oxide on the surface. This process, known as oxidation or scaling, can compromise dimensional tolerances, degrade surface finish, and weaken the component. Water vapor in the air can also introduce hydrogen, leading to embrittlement in certain alloys.
The Role of an Inert Shield
Argon is a noble gas, meaning it is chemically non-reactive (inert) under almost all conditions. By flooding a heat-treating furnace with argon, you physically push out, or displace, the reactive oxygen and water vapor. The argon then acts as a stable, protective shield, ensuring the heat treatment process only affects the material's properties as intended, without any unwanted chemical side effects.
Purity is Paramount
The effectiveness of this shield depends entirely on the purity of the gas. Industrial standards for heat-treating argon typically require an oxygen content below 20 parts per million (ppm) and a dew point below -75°F. A low dew point signifies an extremely low level of water vapor, which is critical for preventing contamination.
When to Specify Argon Atmosphere Treatment
While other inert gases like nitrogen exist, argon's superior inertness makes it the necessary choice for the most demanding applications.
Heat Treating Reactive and High-Performance Alloys
Metals like titanium, zirconium, and certain superalloys are extremely reactive at elevated temperatures. They have a high affinity for oxygen and even nitrogen. For these materials, commonly used in the aerospace and defense industries, an argon atmosphere is essential to prevent gas absorption that would otherwise compromise their strength and durability.
Processes Requiring Flawless Surfaces
Applications like brazing require perfectly clean, oxide-free surfaces for the filler metal to properly wet and flow, creating a strong joint. Using an argon atmosphere ensures that no oxides form on the parent materials during the heating cycle, leading to superior bond quality.
Annealing for Maximum Purity
When annealing non-ferrous metals, stainless steel, or high-alloy steels, the goal is often to achieve a specific softness and microstructure without altering the surface chemistry. Argon provides the clean environment needed to guarantee the final product has a bright, untarnished finish and consistent properties.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a protective atmosphere is an engineering decision that balances technical requirements with economic realities. Argon is highly effective, but it comes with distinct considerations.
The Primary Factor: Cost
The most significant drawback of using argon is its high cost compared to other furnace atmospheres, particularly nitrogen. Argon is more difficult to separate from air, making its production more energy-intensive and expensive.
When Cheaper Alternatives Aren't Enough
Nitrogen is also largely inert and is widely used for heat treating common steels. However, at very high temperatures, nitrogen can react with certain alloying elements (like titanium, aluminum, and chromium) to form nitrides. These nitride formations can make the material's surface brittle. Argon, being truly inert, does not pose this risk.
The Value Proposition
The high cost of argon is justified when the cost of component failure is even higher. In critical applications like a turbine blade in a jet engine or a medical implant, the absolute guarantee of material purity and performance outweighs the expense of the processing gas.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct atmosphere is a critical decision that directly impacts the quality, performance, and cost of your final component.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose heat treating of standard carbon steels: A less expensive atmosphere like nitrogen or an endothermic gas is often sufficient and more cost-effective.
- If you are working with highly reactive metals like titanium, zirconium, or nickel-based superalloys: Argon is the industry standard to guarantee material integrity and prevent embrittlement.
- If your goal is the highest possible surface quality for brazing, medical, or electronic components: The superior protection offered by an argon atmosphere justifies the investment to ensure a flawless, oxide-free result.
Ultimately, choosing an argon atmosphere is an investment in certainty, ensuring that the material's properties are precisely controlled and protected from any external interference.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Detail |
|---|---|
| Primary Purpose | Prevents oxidation and contamination by creating an inert environment. |
| Ideal For | Reactive metals (titanium, zirconium, superalloys), brazing, high-purity annealing. |
| Critical Purity | Oxygen content < 20 ppm; Dew point < -75°F. |
| Main Consideration | Higher cost than alternatives like nitrogen, justified for critical applications. |
Need Uncompromising Purity in Your Heat Treatment Process?
When processing highly reactive metals or demanding applications where failure is not an option, standard solutions fall short. You need the certainty of a perfectly controlled, inert environment.
KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnaces are engineered for this exact challenge. Leveraging our exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with advanced furnace solutions, including our robust Atmosphere Furnaces. Our strong deep customization capability allows us to tailor systems to your unique experimental requirements, ensuring your materials are protected from oxidation and contamination.
Let us help you achieve flawless results. Contact our experts today to discuss how our precision furnace technology can safeguard your most critical components.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Mesh Belt Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Controlled Inert Nitrogen Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the key features of an atmosphere box furnace? Unlock Precise Heat Processing in Controlled Environments
- What are the primary inert gases used in vacuum furnaces? Optimize Your Heat Treatment Process
- Can box type high-temperature resistance furnaces control the atmosphere? Unlock Precision in Material Processing
- What are the development prospects of atmosphere box furnaces in the aerospace industry? Unlock Advanced Material Processing for Aerospace Innovation
- What is an atmosphere protection muffle furnace? Unlock Precise Heat Treatment in Controlled Environments



















