In essence, a lab tube furnace is a specialized type of high-temperature electric furnace used for processing small samples. Its defining characteristic is a cylindrical chamber, or tube, through which samples are heated, allowing for highly precise control over both temperature and the atmospheric environment.
The core takeaway is that a tube furnace's elongated shape is not just a design choice—it is the key to its primary function: providing exceptional temperature uniformity and enabling controlled atmospheres (like vacuum or inert gas) for sensitive material processing.

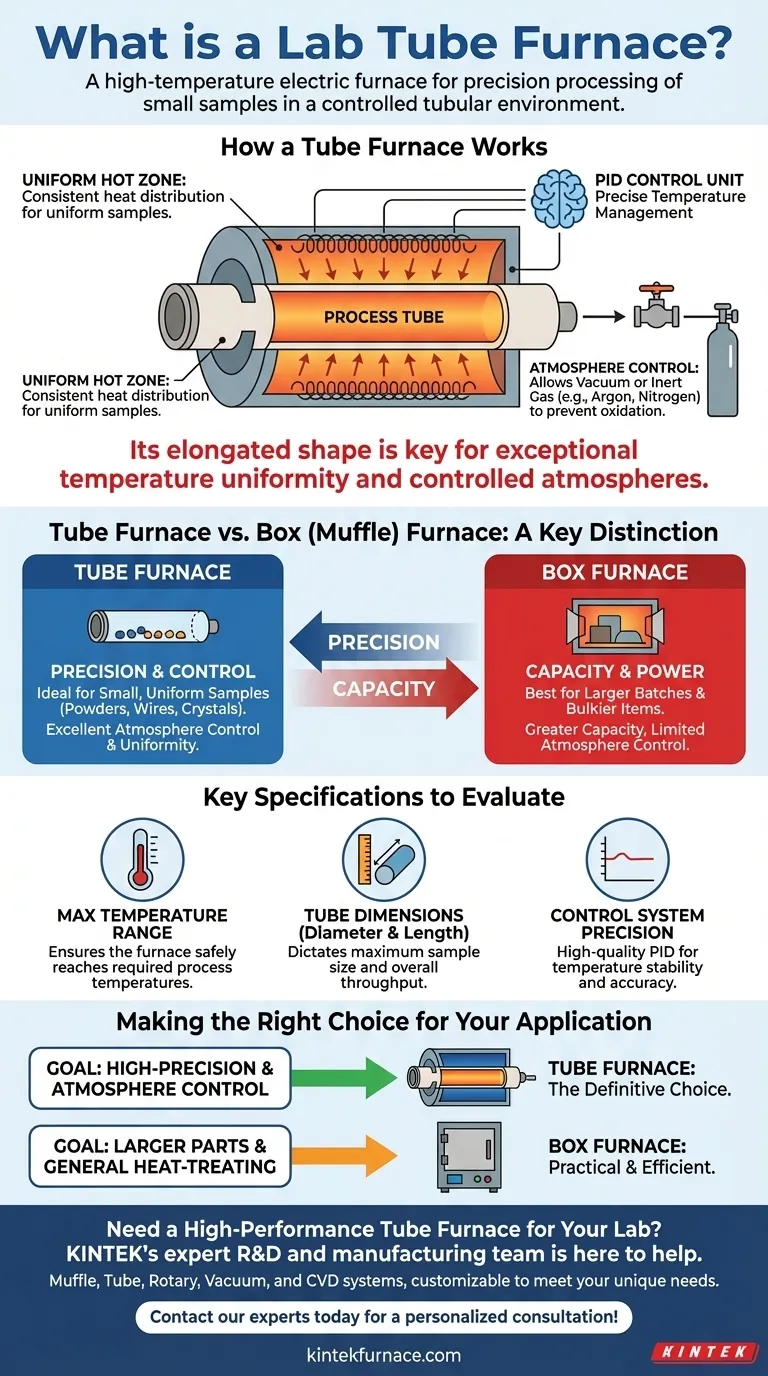
How a Tube Furnace Works
A tube furnace operates on a simple yet effective principle, leveraging a few key components to create a highly controlled heating environment.
The Core Components
The system is built around a central process tube, typically made from durable materials like ceramic or quartz to withstand extreme heat. This tube is surrounded by heating elements that radiate heat inward.
An electronic PID (Proportional-Integral-Derivative) control unit acts as the brain of the furnace, precisely managing the power sent to the heating elements to maintain a stable, accurate temperature.
Achieving Uniform Heating
The cylindrical geometry of the furnace ensures that heat is applied evenly from all sides along a specific length of the tube. This creates a "uniform hot zone" where the temperature deviation is minimal, which is critical for consistent material processing.
Atmosphere Control
The sealed nature of the tube is its most significant advantage. It allows technicians to evacuate the air to create a vacuum or introduce specific gases (like argon or nitrogen). This prevents oxidation and enables processes that are impossible in an open-air furnace.
Tube Furnace vs. Box Furnace: A Key Distinction
Choosing the right furnace depends entirely on the application's needs for precision versus capacity.
Tube Furnace: Precision and Control
The tube furnace excels in applications requiring strict control. Its design is ideal for treating small, uniform samples like powders, wires, or crystals where temperature uniformity and atmosphere management are paramount.
Box Furnace: Capacity and Power
A box furnace, also known as a muffle furnace, features a large, rectangular chamber. It is designed for processing larger batches or bulkier items, offering greater capacity and often higher heating power at the expense of precise atmospheric control.
Key Specifications to Evaluate
When selecting a tube furnace, three specifications are critical to assess for your specific application.
Maximum Temperature Range
The furnace must be able to safely and consistently reach the temperatures required for your process. This is the most fundamental specification to consider.
Tube Dimensions (Diameter and Length)
The inner diameter and heated length of the tube dictate the maximum size and volume of the sample you can process. This determines the furnace's overall throughput and sample compatibility.
Control System Precision
The quality of the PID controller determines temperature stability and accuracy. For high-sensitivity processes, a controller with low overshoot and high stability is essential to ensure repeatable results.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your final decision should be guided by the primary goal of your thermal processing task.
- If your primary focus is high-precision heating of small samples or processes requiring a specific atmosphere (vacuum or inert gas): The tube furnace is the definitive choice for its superior control.
- If your primary focus is processing larger parts, multiple samples at once, or general heat-treating that does not require atmospheric control: The greater capacity of a box furnace is the more practical and efficient solution.
Ultimately, understanding your process requirements is the key to selecting the right tool for the job.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Tube Furnace | Box (Muffle) Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Strength | Precision & Atmosphere Control | Capacity & High-Power Heating |
| Chamber Shape | Cylindrical Tube | Rectangular Box |
| Ideal For | Small samples, powders, wires, crystals | Larger batches, bulkier items |
| Atmosphere Control | Excellent (Vacuum, Inert Gas) | Limited |
| Temperature Uniformity | High in the hot zone | Good, but less uniform than tube |
Need a High-Performance Tube Furnace for Your Lab?
KINTEK's expert R&D and manufacturing team is here to help. Our tube furnaces are engineered for exceptional temperature uniformity and precise atmosphere control, perfect for your most sensitive material processing applications.
We offer a wide range of laboratory high-temperature furnaces, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, all customizable to meet your unique needs.
Let's discuss your requirements and find the perfect solution for your lab.
Contact our experts today for a personalized consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What recent improvements have been made to lab tube furnaces? Unlock Precision, Automation & Safety
- How does a vertical tube furnace achieve precise temperature control? Unlock Superior Thermal Stability for Your Lab
- What are the key operational considerations when using a lab tube furnace? Master Temperature, Atmosphere & Safety
- How is a high-temperature tube furnace utilized in the synthesis of MoO2/MWCNTs nanocomposites? Precision Guide
- How is a Vertical Tube Furnace used for fuel dust ignition studies? Model Industrial Combustion with Precision



















