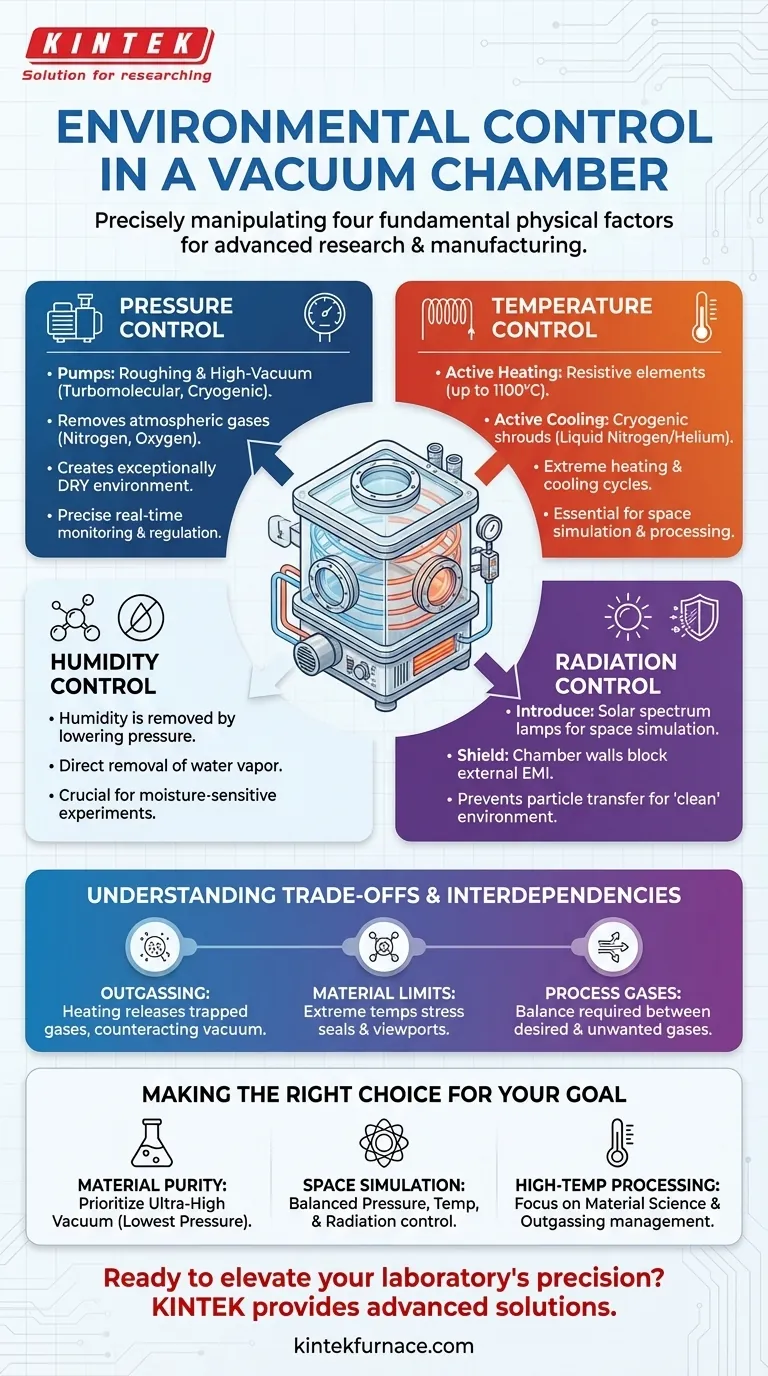
At its core, a vacuum chamber is an environment where you can precisely control four fundamental physical factors. These are pressure, temperature, humidity, and specific forms of radiation. By manipulating these variables, you can create highly specialized conditions that are impossible to achieve in a normal atmosphere, enabling advanced scientific experiments and manufacturing processes.
A vacuum chamber is not merely a box with the air removed. It is a sophisticated tool for creating a bespoke, artificial environment by giving you independent and precise control over the fundamental variables that define a physical space.

The Foundation: Pressure Control
Pressure is the primary variable controlled in any vacuum system. The entire purpose is to reduce the density of gas molecules far below that of the surrounding atmosphere.
How Pressure is Lowered
Achieving a vacuum is a multi-step process. First, a roughing pump removes the bulk of the air. Then, high-vacuum pumps, like turbomolecular or cryogenic pumps, take over to remove the remaining molecules and achieve much lower pressures.
The Impact of Low Pressure
Reducing pressure directly removes atmospheric gases like nitrogen and oxygen. Crucially, it also removes water vapor, which is the mechanism by which a vacuum chamber controls humidity. A deep vacuum is an exceptionally dry environment.
Monitoring and Regulation
Pressure isn't just lowered; it's precisely managed. A system of vacuum gauges provides real-time pressure readings, allowing automated or manual control of the pumps and gas inlets to maintain a specific, stable pressure level required for a process.
Managing Thermal Energy: Temperature Control
Controlling temperature is often as critical as controlling pressure. This can involve both extreme heating and cooling, depending on the application.
Active Heating Systems
Heating is typically accomplished with resistive heating elements integrated into the chamber walls or placed around the sample. For the extreme temperatures mentioned in research, such as 1100°C, specialized materials like ceramics and refractory metals are required for both the chamber and the heating elements.
Active Cooling Systems
Cooling a chamber to cryogenic temperatures is often done using shrouds or platens through which liquid nitrogen or helium flows. This is essential for simulating deep space conditions or for processes where heat must be rapidly drawn away from a sample.
Introducing and Shielding Radiation
Vacuum chambers are also used to control a sample's exposure to radiation, a critical factor in space simulation, materials science, and electronics testing.
Simulating Space Environments
For testing satellites and components, chambers can be equipped with specialized lamps that replicate the sun's full electromagnetic spectrum. This allows engineers to test how materials and electronics withstand the harsh radiation environment of space.
Shielding from Contamination
Conversely, the chamber itself acts as a shield. The steel walls block most external electromagnetic interference, and the vacuum prevents particle transfer, creating a "clean" environment for highly sensitive measurements where outside influence must be eliminated.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Interdependencies
Controlling one factor in a vacuum chamber inevitably affects the others. Understanding these interactions is critical for success and safety.
The Challenge of Outgassing
Heating any material, including the chamber walls themselves, causes it to release trapped gases and moisture in a process called outgassing. This directly counteracts the vacuum, increasing the pressure. Your vacuum pumps must be powerful enough to overcome the outgassing from your sample and the chamber at your target temperature.
Material Limitations at Extremes
Pushing a chamber to very high temperatures (e.g., 1100°C) places immense stress on every component. Seals can fail, metal walls can deform, and viewports can crack. Designing for such conditions requires careful selection of exotic materials and an understanding of thermal expansion to prevent catastrophic failure.
Process Gases vs. Chamber Pressure
Many processes, like chemical vapor deposition (CVD), involve intentionally introducing specific gases into the chamber. The control system must be sophisticated enough to maintain the desired low pressure of unwanted atmospheric gases while managing the precise flow and pressure of the desired process gas.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your primary objective dictates which environmental factor you will prioritize.
- If your primary focus is material purity or deposition: Your main goal is achieving the lowest possible pressure (ultra-high vacuum) to minimize any molecular contamination.
- If your primary focus is space simulation: You need a balanced and dynamic control system to precisely mimic the low pressure, extreme temperature cycles, and solar radiation of an orbital environment.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature processing: Your central challenge is material science—ensuring your chamber, seals, and sample holder can withstand the heat while your pumps manage the significant outgassing.
Mastering these environmental controls is what transforms a vacuum chamber from a simple container into a powerful instrument for discovery and innovation.
Summary Table:
| Environmental Factor | Key Control Methods | Primary Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Pressure | Roughing and high-vacuum pumps, gauges | Material purity, deposition processes |
| Temperature | Resistive heating, cryogenic cooling | High-temperature processing, space simulation |
| Humidity | Removal via vacuum pumps | Dry environments for sensitive experiments |
| Radiation | Specialized lamps, chamber shielding | Space testing, materials science |
Ready to elevate your laboratory's precision? Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet unique experimental requirements. Contact us today to discuss how our tailored solutions can optimize your environmental control and drive innovation in your projects!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine Heated Vacuum Press Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace with Pressure for Vacuum Sintering
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the process of hot pressing? A Guide to Achieving Superior Material Density
- What are the advantages of vacuum hot press furnaces? Achieve Superior Material Density & Purity
- What is a vacuum hot press furnace? Unlock Superior Material Performance
- How does precise temperature control affect Ti-6Al-4V microstructure? Master Titanium Hot Pressing Accuracy
- What are the primary components of a vacuum hot press furnace? Master the Core Systems for Precise Material Processing



















