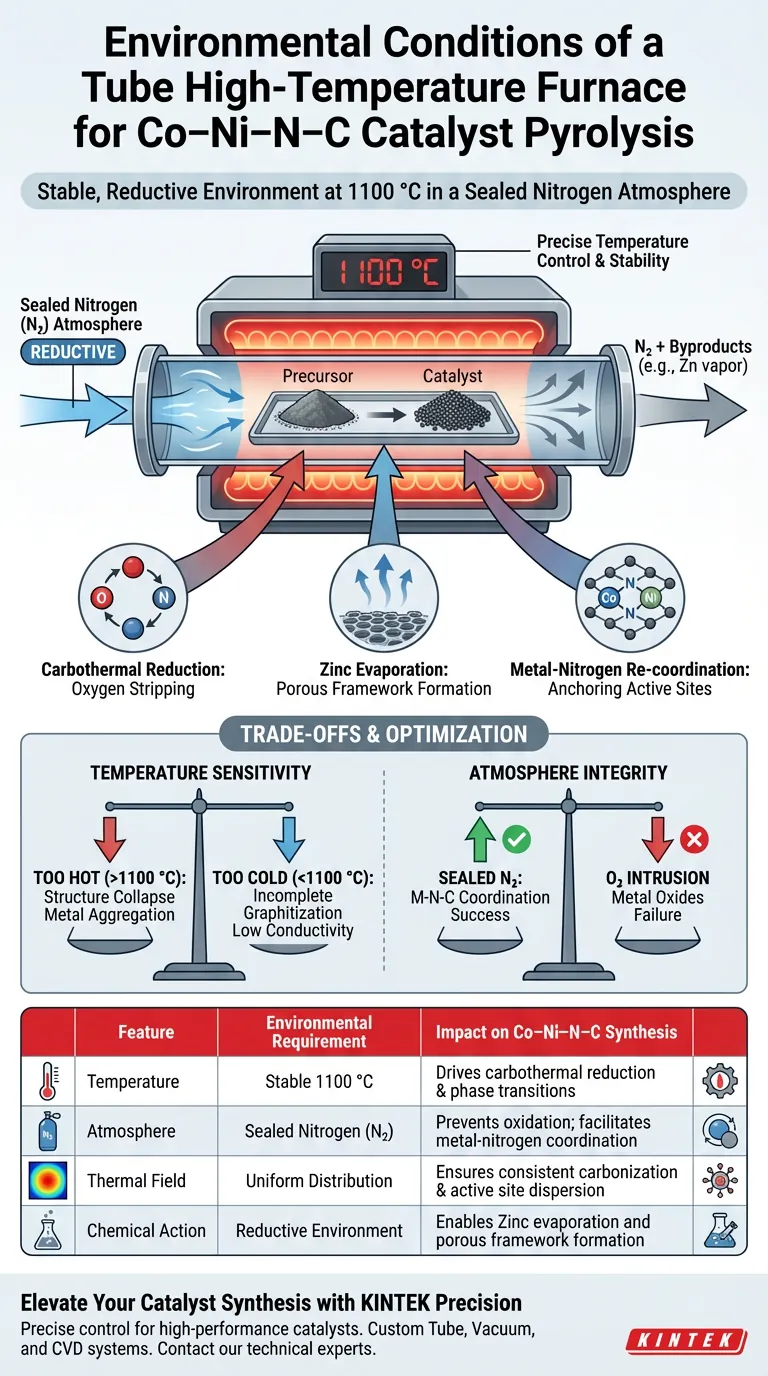
A tube high-temperature furnace provides a stable, reductive environment specifically maintained at extreme temperatures, such as 1100 °C, under a sealed nitrogen atmosphere. This precise control is the catalyst for the physicochemical changes required to synthesize Co–Ni–N–C catalysts, driving carbothermal reduction and ensuring atomic re-coordination.
Core Takeaway The tube furnace acts as a hermetically sealed reactor that balances high thermal energy with chemical inertness. This environment forces the evaporation of sacrificial components (like zinc) while simultaneously guiding Cobalt and Nickel atoms to anchor chemically into a newly formed nitrogen-doped carbon framework.
The Critical Thermal Environment
Precise Temperature Control
For Co–Ni–N–C catalysts, the furnace must maintain a rigorous temperature profile, often reaching 1100 °C. This specific high-temperature threshold is necessary to induce the phase transitions and structural rearrangements that define the final catalyst's performance.
A Reductive, Nitrogen-Rich Atmosphere
The furnace utilizes a sealed nitrogen atmosphere to create a stable, reductive environment. By excluding oxygen and other contaminants, the nitrogen blanket prevents the uncontrolled oxidation of the metal precursors during the vulnerable heating phase.
Stability of the Reaction Field
Uniform heat distribution is critical. The tube furnace ensures a stable temperature field, which prevents thermal gradients that could lead to uneven carbonization or inconsistent distribution of metal active sites across the substrate.
Chemical Transformations During Pyrolysis
Facilitating Carbothermal Reduction
The environment provided by the furnace facilitates carbothermal reduction. This process uses carbon as a reducing agent at high temperatures to strip oxygen from metal oxides, preparing the metal atoms for integration into the carbon support.
Zinc Evaporation and Framework Formation
When using ZIF (Zeolitic Imidazolate Framework) precursors, the furnace conditions drive the evaporation of the zinc component. As the zinc vaporizes, it leaves behind a porous carbon structure, effectively acting as a sacrificial template that defines the catalyst's surface area.
Metal-Nitrogen Re-coordination
Perhaps the most critical function of this environment is guiding atomic migration. The thermal energy allows Cobalt and Nickel atoms to re-coordinate with nitrogen atoms. This anchors the metals firmly within the nitrogen-doped graphitic carbon framework, preventing them from aggregating into less active metallic clusters.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Temperature Sensitivity
While 1100 °C is the target for this specific synthesis, slight deviations can be detrimental. Excessive heat can lead to the collapse of the porous carbon structure or the aggregation of Co/Ni atoms, destroying single-atom active sites. Insufficient heat will fail to fully evaporate the zinc or complete the graphitization process, resulting in low conductivity and poor catalytic activity.
Atmosphere Integrity
The term "sealed" is operational, not just descriptive. Any breach in the furnace seal that introduces oxygen will immediately disrupt the reductive nature of the environment. This leads to the formation of unwanted metal oxides rather than the desired Metal-Nitrogen-Carbon (M-N-C) coordination, rendering the synthesis a failure.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To maximize the efficacy of your pyrolysis process, align your furnace parameters with your specific structural targets:
- If your primary focus is Porosity and Surface Area: Prioritize precise temperature ramp-ups to ensure the controlled evaporation of Zinc (from ZIF precursors) without collapsing the carbon skeleton.
- If your primary focus is Active Site Density: Ensure the nitrogen atmosphere is strictly maintained to facilitate the optimal re-coordination of Cobalt and Nickel with Nitrogen.
Success in synthesizing Co–Ni–N–C catalysts relies not just on reaching 1100 °C, but on maintaining the absolute integrity of the reductive nitrogen atmosphere throughout the transition.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Environmental Requirement | Impact on Co–Ni–N–C Synthesis |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | Stable 1100 °C | Drives carbothermal reduction & phase transitions |
| Atmosphere | Sealed Nitrogen (N₂) | Prevents oxidation; facilitates metal-nitrogen coordination |
| Thermal Field | Uniform Distribution | Ensures consistent carbonization & active site dispersion |
| Chemical Action | Reductive Environment | Enables Zinc evaporation and porous framework formation |
Elevate Your Catalyst Synthesis with KINTEK Precision
Precise control over reductive atmospheres and thermal stability is the difference between a high-performance catalyst and a failed synthesis. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers specialized Tube, Vacuum, and CVD systems designed to meet the rigorous demands of Co–Ni–N–C pyrolysis.
Our laboratory high-temperature furnaces are fully customizable to your unique research needs, ensuring the integrity of your nitrogen-doped frameworks every time.
Ready to optimize your pyrolysis process? Contact our technical experts today to find the perfect furnace solution for your lab.
Visual Guide
References
- Jianping Chen, Wei‐Ning Wang. Highly efficient CO<sub>2</sub> electrochemical reduction on dual metal (Co–Ni)–nitrogen sites. DOI: 10.1039/d3ta05654f
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- What materials are used for a tube furnace heating chamber? Optimize for temperature, purity, and durability.
- In which industries is the tube furnace commonly used? Essential for Materials Science, Energy, and More
- What are the specific functions of a vertical alumina tube reactor? Key Roles in Gasification Kinetics Research
- What task is performed by industrial high-temperature tube or atmosphere furnaces? Unlock Carbon Aerogel Synthesis
- How does a tube furnace achieve energy efficiency? Optimize Heat Retention and Control
- How does a high-temperature tube furnace ensure environmental stability for SOEC? Precision Heat & Atmosphere Control
- What is the function of a high-temperature tube furnace in the preparation of Black-TiO2? Enhance Photocatalytic Power
- What is the difference between an alumina tube furnace and a quartz tube furnace? Choose the Right Tube Furnace for Your Lab



















