In short, the tube furnace is a foundational tool across a wide range of industries, most notably in materials science, metallurgy, new energy sectors like battery and LED production, and advanced ceramics. Its prevalence stems from its unique ability to create a highly controlled, high-temperature environment, which is essential for both research and specialized industrial manufacturing.
The true value of a tube furnace is not just its ability to generate heat, but its capacity to provide an extremely uniform and atmospherically controlled processing environment. This precision is why it is indispensable for developing and manufacturing advanced materials.

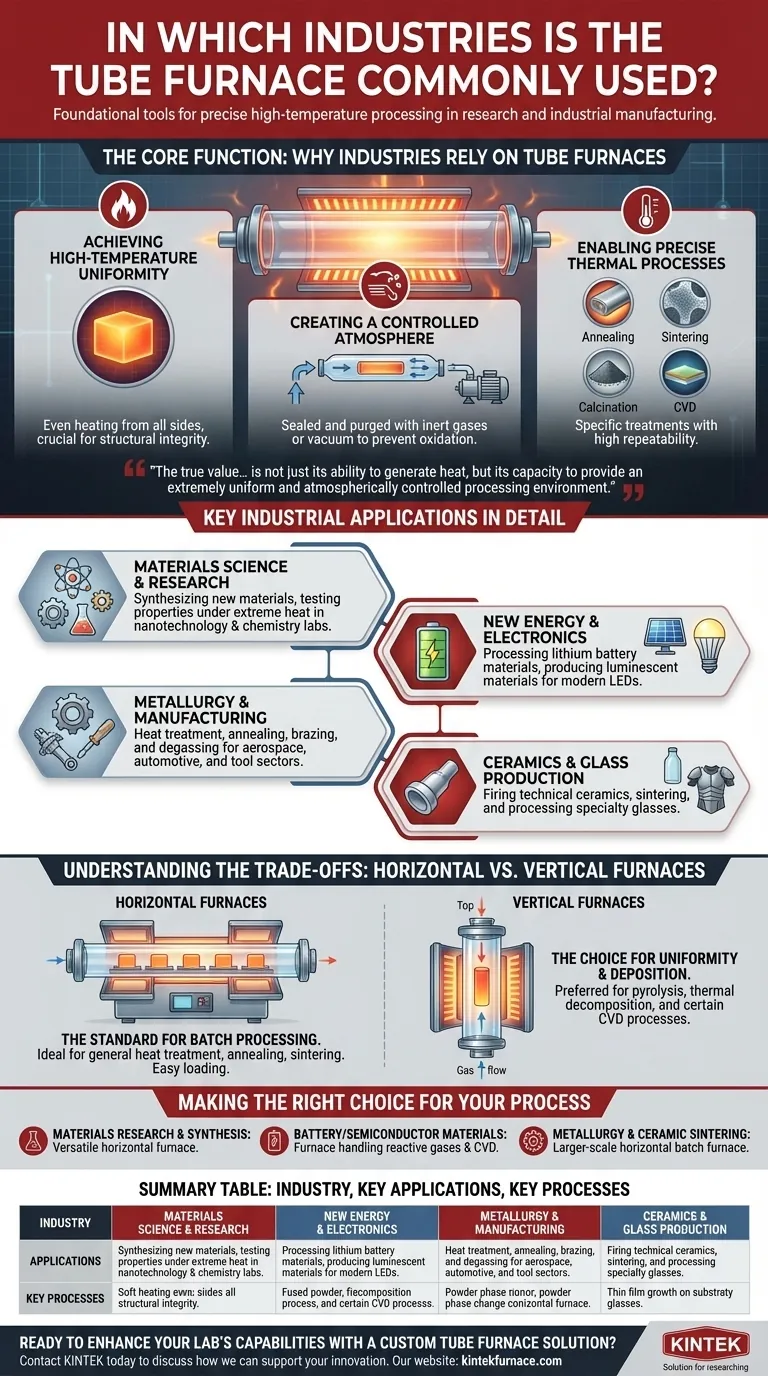
The Core Function: Why Industries Rely on Tube Furnaces
A tube furnace's design is simple but powerful. A cylindrical chamber, or tube, is surrounded by heating elements. This design is the key to its widespread adoption, as it provides three critical capabilities.
Achieving High-Temperature Uniformity
The geometry of a tube furnace ensures that the material placed inside receives exceptionally even heating from all sides. This uniformity is non-negotiable for processes where slight temperature variations could ruin the final product's structural integrity or performance.
Creating a Controlled Atmosphere
The enclosed tube can be easily sealed and purged with inert gases (like argon or nitrogen) or placed under a vacuum. This prevents oxidation and other unwanted chemical reactions, which is crucial when working with sensitive metals, semiconductors, or chemical compounds.
Enabling Precise Thermal Processes
Industries use tube furnaces to execute specific thermal treatments with high repeatability. Key processes include:
- Annealing: Softening metals or glass to improve ductility and reduce internal stresses.
- Sintering: Fusing powdered materials, such as metals or ceramics, into a solid mass just below their melting point.
- Calcination: Heating a material to drive off volatile substances or induce a phase transition, common in catalyst and cement production.
- Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD): Growing thin films of solid material onto a substrate, a fundamental process in the semiconductor and solar industries.
Key Industrial Applications in Detail
The functions of a tube furnace translate directly into applications across both cutting-edge research and high-value manufacturing.
Materials Science and Research
University labs, government research centers, and corporate R&D departments use tube furnaces for synthesizing new materials. They are essential tools in fields like chemistry, nanotechnology, and environmental protection research for testing material properties under extreme heat.
New Energy and Electronics
This is a major growth area for tube furnace use. They are critical for processing lithium battery materials, specifically for creating the precise crystalline structures needed in anodes and cathodes. They are also used to produce the luminescent materials and phosphors found in modern LEDs.
Metallurgy and Manufacturing
In the metallurgical industry, tube furnaces are workhorses for the heat treatment of metal components for the aerospace, automotive, and tool manufacturing sectors. Processes like brazing, soldering, and degassing are performed to create strong, reliable parts.
Ceramics and Glass Production
Tube furnaces are used for firing and sintering technical ceramics, which are advanced materials used in electronics, armor, and medical implants. They are also used to process specialty glasses and glass-ceramics that require precise thermal profiles.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Horizontal vs. Vertical Furnaces
The orientation of the furnace tube is not just a design choice; it dictates its ideal use case and presents specific trade-offs.
Horizontal Furnaces: The Standard for Batch Processing
Horizontal tube furnaces are the most common type. They are well-suited for processing multiple samples at once and are easy to load and unload. This makes them ideal for general-purpose heat treatment, annealing, and sintering applications in a lab or production setting.
Vertical Furnaces: The Choice for Uniformity and Deposition
In a vertical furnace, gravity can be used as an advantage. They are preferred for processes like pyrolysis and thermal decomposition where samples shouldn't touch the tube walls. Their top-loading design is also superior for certain CVD processes, ensuring a more uniform coating on substrates.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Your specific goal determines which type of furnace and process capability is most important.
- If your primary focus is fundamental materials research or synthesis: A versatile horizontal furnace offers the best flexibility for a wide range of experimental processes.
- If your primary focus is developing battery or semiconductor materials: A furnace capable of handling specific reactive gases and enabling CVD is critical for creating high-performance thin films and powders.
- If your primary focus is metallurgical heat treatment or ceramic sintering: A larger-scale horizontal batch furnace designed for high-throughput and repeatable thermal cycles is the most efficient solution.
Ultimately, the tube furnace serves as a fundamental instrument of innovation, empowering professionals to precisely control matter at high temperatures.
Summary Table:
| Industry | Key Applications | Key Processes |
|---|---|---|
| Materials Science & Research | Synthesizing new materials, nanotechnology | Annealing, sintering, calcination |
| New Energy & Electronics | Battery material processing, LED production | CVD, thermal treatments |
| Metallurgy & Manufacturing | Heat treatment of metal components | Annealing, brazing, degassing |
| Ceramics & Glass Production | Firing technical ceramics, specialty glasses | Sintering, precise thermal profiling |
Ready to enhance your lab's capabilities with a custom tube furnace solution? At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnaces tailored to your unique needs. Our product line includes Tube Furnaces, Muffle Furnaces, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, all backed by strong deep customization to meet your experimental requirements. Whether you're in materials science, new energy, metallurgy, or ceramics, we can help you achieve precise thermal processing. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your innovation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What recent improvements have been made to lab tube furnaces? Unlock Precision, Automation & Safety
- What is an example of a material prepared using a tube furnace? Master Precise Material Synthesis
- What safety measures are essential when operating a lab tube furnace? A Guide to Preventing Accidents
- What safety and reliability features are incorporated into a vertical tube furnace? Ensuring Safe, Consistent High-Temp Processing
- What are the key operational considerations when using a lab tube furnace? Master Temperature, Atmosphere & Safety



















