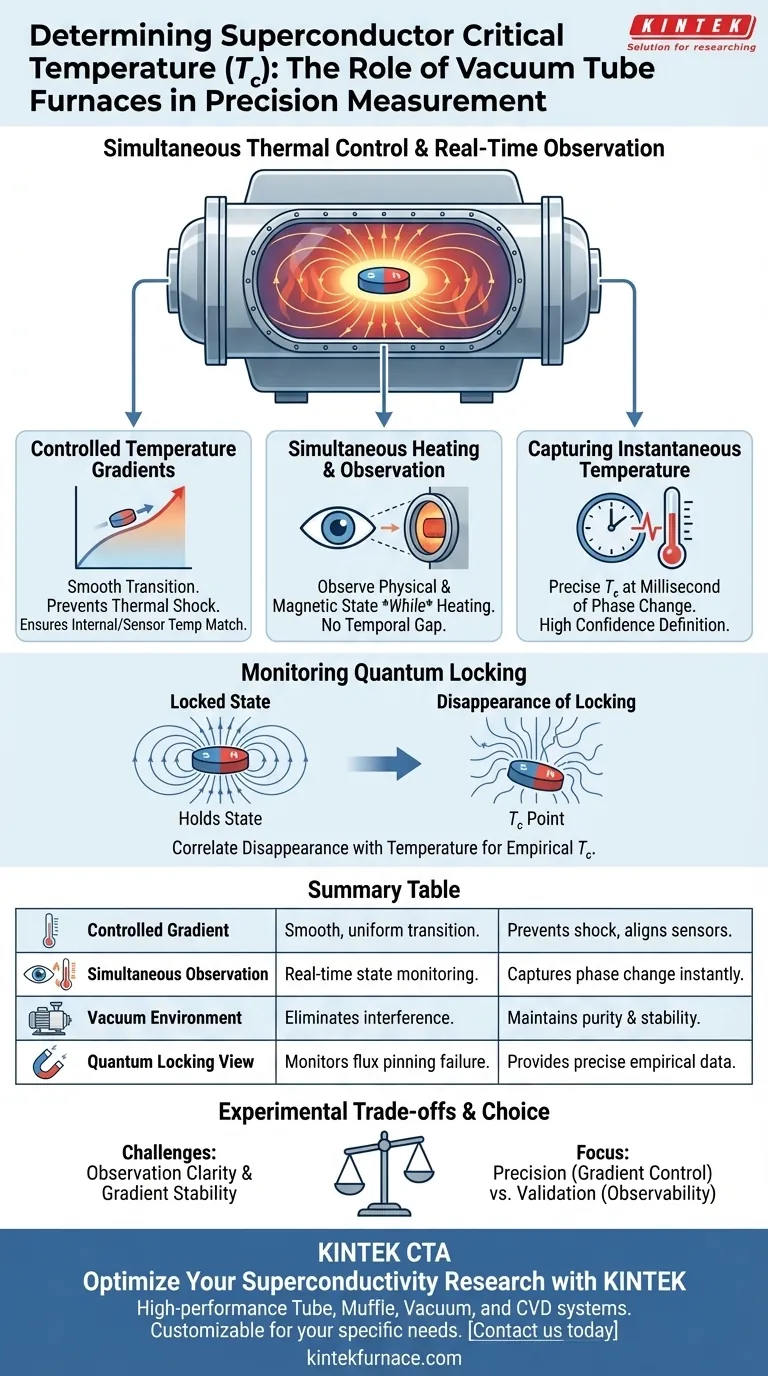
The critical contribution of a vacuum tube furnace is its ability to maintain a controlled temperature gradient while permitting the real-time observation of magnetic characteristics. This specific environment allows researchers to simultaneously heat a sample and monitor for the disappearance of quantum locking. By correlating these visual or magnetic changes directly with thermal data, you can pinpoint the exact instantaneous temperature—the critical temperature ($T_c$)—at which superconductivity ceases.
The vacuum tube furnace distinguishes itself by integrating thermal control with observational access. This ensures there is no temporal gap between a change in the material's state and the recording of its temperature.

Creating the Ideal Measurement Environment
To accurately measure the critical temperature of a superconductor, you must move beyond simple heating. You need an environment that stabilizes the relationship between temperature and magnetic behavior.
Controlled Temperature Gradients
The furnace provides a controlled temperature gradient during the heating process. This is not merely about raising the heat; it is about creating a precise, gradual thermal slope.
This gradient allows the sample to transition through temperature ranges smoothly. It prevents thermal shock and ensures that the internal temperature of the sample matches the sensor readings at the moment of measurement.
Simultaneous Heating and Observation
A defining condition provided by this setup is the ability to perform simultaneous heating and observation.
In many standard furnaces, the sample is hidden. In a vacuum tube furnace designed for this purpose, the chamber allows you to observe the sample's physical and magnetic state while the temperature changes.
Capturing the Instantaneous Temperature
The ultimate goal of these conditions is to capture the instantaneous temperature.
Because you can observe the sample in real-time, you can record the specific temperature reading the exact millisecond the material undergoes a phase change. This precision is required to define $T_c$ with high confidence.
Monitoring Quantum Locking
The determination of $T_c$ in this context relies heavily on observing specific superconducting phenomena, specifically quantum locking (flux pinning).
Observing the State Change
The furnace conditions allow researchers to watch for the quantum locking state.
As the temperature rises, the superconductor holds this state. The critical moment occurs when this locking effect disappears.
Correlating Disappearance with Temperature
The vacuum tube furnace allows you to identify the specific moment quantum locking disappears.
By syncing this visual or magnetic loss of locking with the temperature gradient, the $T_c$ is determined not by theoretical calculation, but by direct empirical observation of the failure point.
Understanding Experimental Trade-offs
While the vacuum tube furnace provides high precision for $T_c$ measurement, it introduces specific challenges that must be managed to ensure data integrity.
Dependency on Observation Quality
The accuracy of the $T_c$ measurement is entirely dependent on the clarity of the observation.
If the mechanism for observing the "disappearance" of quantum locking (visual or magnetic) is vague or obstructed, the precise thermal control becomes irrelevant. The "simultaneous" nature of the experiment requires that both the heating element and the observation window be perfectly calibrated.
Gradient Stability
maintaining a perfectly controlled gradient is difficult at extreme temperatures.
Any fluctuation in the vacuum pressure or power supply can disrupt the gradient. This can lead to a discrepancy between the recorded temperature and the actual temperature of the sample at the moment the quantum locking vanishes.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
When designing your experiment or selecting equipment, consider which variable is most critical to your specific research needs.
- If your primary focus is Precision: Prioritize a furnace with the finest control over the temperature gradient to ensure the thermal transition is slow and readable.
- If your primary focus is Validation: Ensure the furnace design maximizes the observability of the sample, allowing for unambiguous confirmation of the moment quantum locking stops.
Success in measuring $T_c$ relies on the tight synchronization of thermal control and real-time observation.
Summary Table:
| Condition Provided | Role in Tc Measurement | Research Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Controlled Gradient | Ensures slow, uniform thermal transition | Prevents thermal shock; aligns sensor with sample |
| Simultaneous Observation | Real-time monitoring of magnetic states | Captures phase change at the exact millisecond |
| Vacuum Environment | Eliminates atmospheric interference | Maintains sample purity and thermal stability |
| Quantum Locking View | Monitors the point of flux pinning failure | Provides empirical data for precise Tc definition |
Optimize Your Superconductivity Research with KINTEK
Precise $T_c$ measurement demands rigorous thermal control and specialized observation capabilities. Backed by expert R&D and world-class manufacturing, KINTEK offers high-performance Tube, Muffle, Vacuum, and CVD systems designed to meet the strictest laboratory requirements.
Whether you need custom dimensions for real-time observation or advanced temperature gradient stability, our systems are fully customizable to your unique research goals. Contact us today to find your perfect high-temp solution and see how our expertise can enhance your experimental accuracy.
Visual Guide
References
- Yong‐Jihn Kim. Superconductor Exclusion Principle for Identifying a Room Temperature Ambient Pressure Superconductor. DOI: 10.33425/2690-8077.1209
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What safety protection mechanisms are typically included in tube furnaces? Ensure Operator and Equipment Safety
- What are the specific roles of a high-temperature tube furnace during the two-stage heat treatment of BN@PyC aerogels?
- What factors determine the selection of a three-zone split tube furnace? Key Specs for Precision Thermal Processing
- What heating element is used in a multi station vacuum tube furnace and what types of furnace tubes can be used? Optimize Your High-Temp Processes
- Why is the iodine source placed at the upstream end of the tube furnace? Optimizing I-NC Chemical Vapor Deposition
- What is the function of the pre-oxidation process conducted in a tube furnace? Stabilize Lignin for Carbon Fibers.
- Why is a high-temperature tube furnace required for MoS2 and WS2 thin films? Achieve 2H Crystalline Phase Excellence
- What are the key features that ensure durability and safety in modern lab tube furnaces? Discover Reliable High-Temp Solutions



















