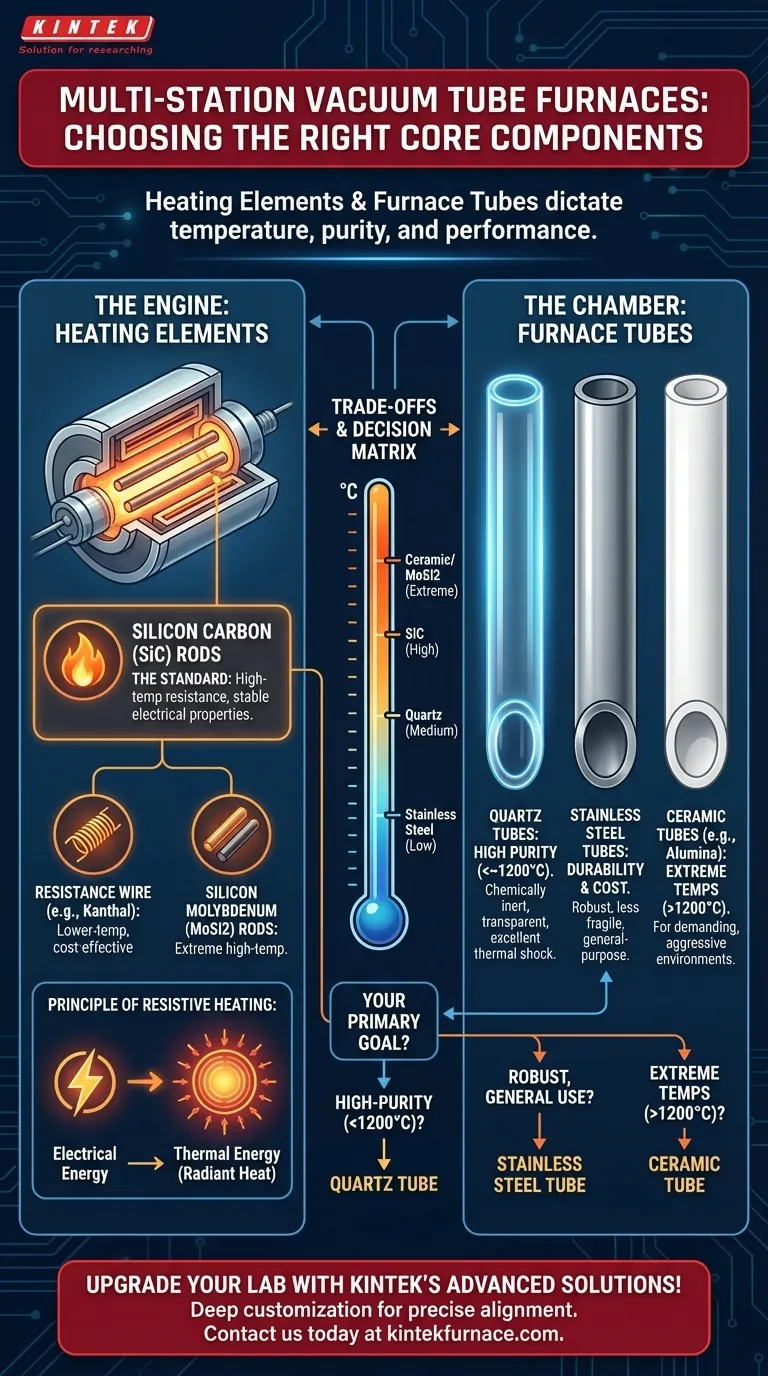
In a multi-station vacuum tube furnace, the most common heating element is a silicon carbon (SiC) rod, prized for its ability to reach high temperatures reliably. The furnace tube, which contains the sample, is typically made of either high-purity quartz or durable stainless steel, with the choice depending on the specific temperature and chemical requirements of the process.
The selection of a heating element and furnace tube is not a minor detail—it is the central engineering choice that dictates the furnace's maximum temperature, chemical compatibility, and overall performance envelope. Understanding the properties of these materials is crucial for matching the equipment to your specific application.

The Core Component: The Heating Element
The heating element is the engine of the furnace. Its job is to convert electrical energy into thermal energy efficiently and stably at extreme temperatures.
The Standard: Silicon Carbon (SiC) Rods
A silicon carbon rod is the most frequently used heating element in these systems. Its selection is based on excellent high-temperature resistance and stable electrical properties, allowing it to operate under high current loads without rapid degradation.
Alternative Heating Materials
While SiC is common, other materials are also used. Resistance wire (like Kanthal) is often found in lower-temperature furnaces, while silicon molybdenum (MoSi2) rods are used for applications requiring even higher temperatures than SiC can provide.
The Principle of Operation
These elements work on the principle of resistive heating. They possess good electrical conductivity, but enough resistance that when a high current is passed through them, they heat up intensely. This radiant heat is what warms the furnace tube and the sample inside.
Choosing the Right Furnace Tube
The furnace tube is the sealed environment for your process. It must withstand high temperatures, steep thermal gradients, high vacuum, and the specific chemical atmospheres being used.
Quartz Tubes: For High Purity
High-purity quartz is a superior choice for processes where contamination is a concern. It is chemically inert to most substances and offers excellent thermal shock resistance. Its transparency is also an advantage for visually monitoring a process.
Stainless Steel Tubes: For Durability
Stainless steel tubes are a robust and often more cost-effective option. They are mechanically strong and less fragile than quartz, making them suitable for general-purpose applications where minor metallic interaction with the sample is not a critical issue.
Ceramic Tubes: For Extreme Temperatures
For processes that must exceed the limits of quartz (typically around 1200°C), ceramic tubes (such as Alumina) are required. These materials are designed for the most demanding high-temperature and chemically aggressive environments.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Material vs. Application
The ideal combination of heating element and tube material is entirely dependent on your goal. Making the wrong choice can lead to failed experiments, damaged equipment, or contaminated samples.
Temperature Limitations are Critical
The materials create a clear temperature hierarchy. Stainless steel is generally limited to the lowest temperatures, followed by quartz, then silicon carbon elements, and finally ceramic tubes with silicon molybdenum elements at the highest end.
Chemical Compatibility and Atmosphere
In a furnace designed for multiple atmospheres and vacuum, chemical inertness is key. Quartz is highly inert. Stainless steel, however, can react with certain process gases or sample materials at high temperatures, potentially introducing contaminants.
Vacuum Integrity and Durability
Both quartz and stainless steel can hold a high vacuum. The primary trade-off is fragility versus robustness. Quartz can crack from mechanical or severe thermal shock, while stainless steel is far more durable but can warp or degrade after many thermal cycles.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Your specific experimental goal dictates the correct material configuration. Consider the following guidelines to make an informed decision.
- If your primary focus is high-purity processing below ~1200°C: A quartz tube is the standard choice for its exceptional chemical inertness.
- If your primary focus is robust, general-purpose heating where budget is a concern: A stainless steel tube provides excellent durability and cost-effectiveness.
- If your primary focus is reaching the highest possible temperatures (above 1200°C): A high-purity ceramic tube (e.g., Alumina) is essential to withstand the extreme conditions.
Matching the furnace materials to your specific process parameters is the foundation for achieving reliable and repeatable results.
Summary Table:
| Component | Material Options | Key Characteristics | Typical Use Cases |
|---|---|---|---|
| Heating Element | Silicon Carbon (SiC) Rods | High-temperature resistance, stable electrical properties | Standard high-temp applications |
| Heating Element | Resistance Wire (e.g., Kanthal) | Lower temperature capability, cost-effective | Low-temp processes |
| Heating Element | Silicon Molybdenum (MoSi2) Rods | Higher temperature than SiC, robust | Extreme high-temp applications |
| Furnace Tube | Quartz | High purity, chemically inert, transparent | High-purity processes below ~1200°C |
| Furnace Tube | Stainless Steel | Durable, cost-effective, less fragile | General-purpose, budget-conscious applications |
| Furnace Tube | Ceramic (e.g., Alumina) | Extreme temperature resistance, chemically robust | Processes above 1200°C, aggressive environments |
Upgrade your laboratory with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with tailored options like Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise alignment with your unique experimental needs, whether you require high-purity quartz tubes, durable stainless steel, or extreme-temperature ceramic components. Contact us today to discuss how our expertise can optimize your processes and deliver reliable, repeatable results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
People Also Ask
- What role does a laboratory tube furnace perform during the carbonization of LCNSs? Achieve 83.8% Efficiency
- What safety and reliability features are incorporated into a vertical tube furnace? Ensuring Safe, Consistent High-Temp Processing
- What are the key operational considerations when using a lab tube furnace? Master Temperature, Atmosphere & Safety
- How is a high-temperature tube furnace utilized in the synthesis of MoO2/MWCNTs nanocomposites? Precision Guide
- What is an example of a material prepared using a tube furnace? Master Precise Material Synthesis



















