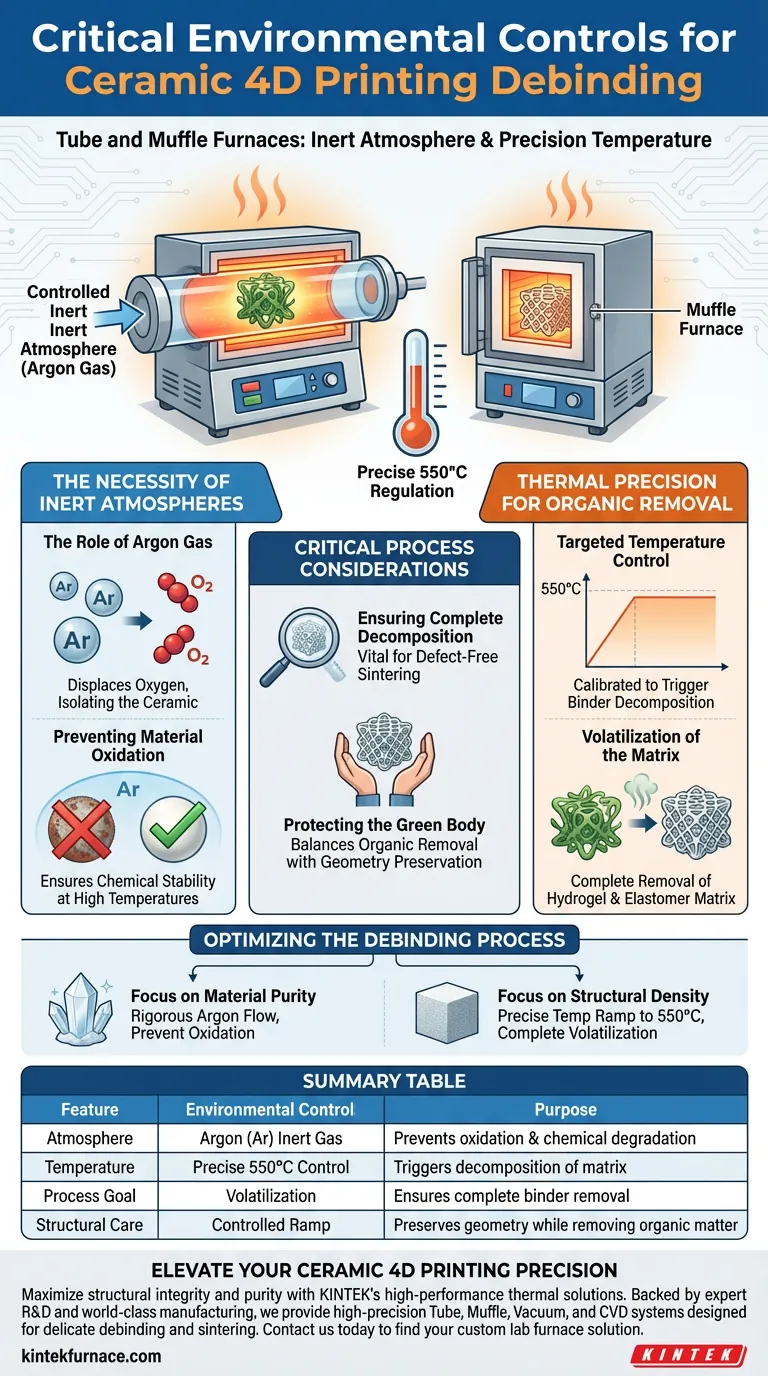
Tube furnaces and muffle furnaces provide a controlled inert atmosphere, specifically using Argon (Ar), coupled with precise temperature regulation. During the debinding stage of ceramic 4D printing, this controlled environment is critical for decomposing organic components—such as the hydrogel and elastomer matrix—while strictly preventing the oxidation of the ceramic material.
Successful debinding requires removing binders without compromising the ceramic structure. By maintaining an Argon-shielded environment at approximately 550°C, these furnaces ensure organic matter is fully volatilized while protecting the ceramic from chemical degradation.

The Necessity of Inert Atmospheres
The Role of Argon Gas
These furnaces operate by introducing a controlled Argon (Ar) atmosphere. This inert gas displaces oxygen and other reactive elements within the heating chamber.
Preventing Material Oxidation
Ceramic components are vulnerable to oxidation when exposed to high temperatures in standard air. The Argon shield effectively isolates the ceramic, ensuring it remains chemically stable during the heating process.
Thermal Precision for Organic Removal
Targeted Temperature Control
The furnace facilitates a controlled temperature rise, specifically targeting approximately 550°C. This temperature is calibrated to trigger the decomposition of the organic binders used in the printing process.
Volatilization of the Matrix
The goal is the complete removal of the hydrogel and elastomer matrix. The thermal environment ensures these organic components decompose and volatilize entirely, leaving behind a clean ceramic structure ready for densification.
Critical Process Considerations
Ensuring Complete Decomposition
It is vital that all organic matter is removed before the next phase. Any residual binder remaining after this stage can cause defects during the final sintering and densification phase.
Protecting the Green Body
The transition from a printed part to a sintered part is delicate. The environmental controls must balance the aggressive removal of organics with the gentle preservation of the ceramic geometry.
Optimizing the Debinding Process
To ensure the highest quality results in ceramic 4D printing, align your furnace settings with your specific processing goals:
- If your primary focus is material purity: Maintain a rigorous Argon flow to strictly prevent oxidation, preserving the chemical integrity of the ceramic components.
- If your primary focus is structural density: Ensure the temperature ramp to 550°C is precise to guarantee the complete volatilization of the hydrogel and elastomer matrix before sintering begins.
By mastering these environmental controls, you ensure the structural fidelity of the ceramic component is maintained throughout the critical debinding phase.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Environmental Control | Purpose in 4D Ceramic Debinding |
|---|---|---|
| Atmosphere | Argon (Ar) Inert Gas | Prevents oxidation and chemical degradation of ceramics |
| Temperature | Precise 550°C Control | Triggers decomposition of hydrogel and elastomer matrix |
| Process Goal | Volatilization | Ensures complete removal of organic binders |
| Structural Care | Controlled Ramp | Preserves geometry while removing organic matter |
Elevate Your Ceramic 4D Printing Precision
Maximize the structural integrity and purity of your advanced materials with KINTEK’s high-performance thermal solutions. Backed by expert R&D and world-class manufacturing, we provide high-precision Tube, Muffle, Vacuum, and CVD systems specifically designed to handle the delicate debinding and sintering stages of 4D printing.
Whether you need rigorous Argon-shielded environments or customizable heating profiles, KINTEK offers the thermal expertise to ensure your ceramic components are defect-free. Contact us today to find your custom lab furnace solution and take the next step in material innovation.
Visual Guide
References
- Rong Wang, Qi Ge. Direct 4D printing of ceramics driven by hydrogel dehydration. DOI: 10.1038/s41467-024-45039-y
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- Why is a high-temperature furnace with controlled gas flow required for the calcination of MCM-41? Optimize Synthesis
- What are the advantages of an atmosphere box furnace in ceramic material preparation? Unlock Precise Control for Superior Ceramics
- What types of furnaces are specially designed for processing in inert atmospheres? Explore Sealed Systems for Oxidation-Free Results
- What is the advantage of using nitrogen as a filling gas? Ensure High Yield Silica Extraction from Biomass
- What are the features of continuous annealing furnaces? Boost High-Volume Production Efficiency
- Why is temperature and atmosphere monitoring critical in furnace operations? Ensure Safety and Quality in Heat Treatment
- What are the development prospects of atmosphere box furnaces in the aerospace industry? Unlock Advanced Material Processing for Aerospace Innovation
- What is the maximum vacuum level for a low vacuum atmosphere furnace? Key Specs for Industrial Heat Treatment



















