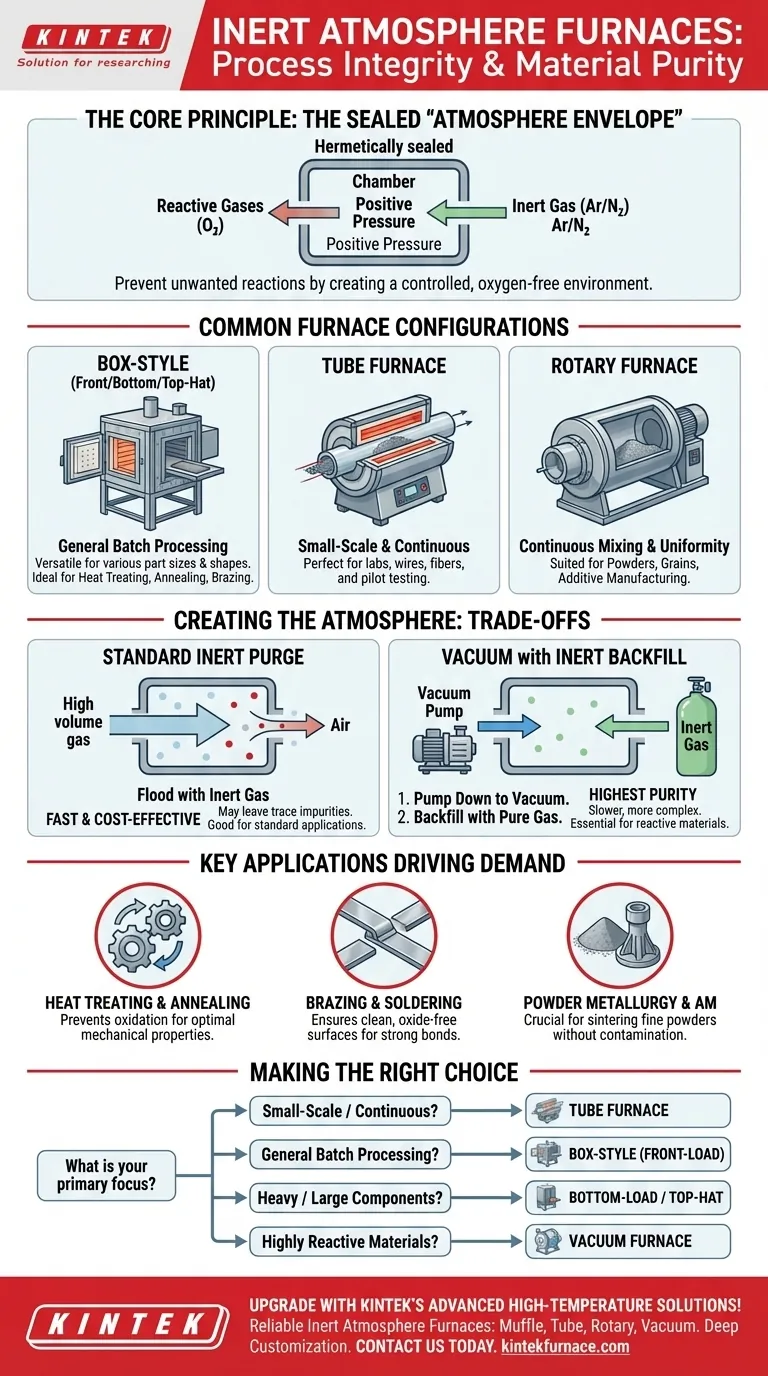
Furnaces specially designed for processing in inert atmospheres are defined by their ability to be hermetically sealed against the outside air. The most common configurations include box-style furnaces (front-load, bottom-load, and top-hat), tube furnaces, and rotary furnaces, each built around the core principle of creating an "atmosphere envelope" free of reactive gases like oxygen.
The specific shape of the furnace—whether it's a box, tube, or top-hat—is less important than its fundamental design as a sealed system. The critical factor is the ability to purge reactive gases and maintain a slight positive pressure with an inert gas, ensuring the integrity of the process environment.
The Core Principle: The Sealed Atmosphere Envelope
An inert atmosphere furnace is not merely a hot box; it is a controlled environment system designed to prevent unwanted chemical reactions at high temperatures.
What Defines an Inert Atmosphere?
An inert atmosphere is one that does not react with the material being processed. This is typically achieved by flooding the furnace chamber with a chemically inactive gas, such as argon or nitrogen, to displace the oxygen and moisture present in ambient air.
This displacement is crucial for processes where oxidation would compromise the material's structural integrity, surface finish, or chemical properties.
How a Sealed Chamber Works
To be effective, the furnace chamber must function as a sealed container, often called an "atmosphere envelope." Every potential leak point—including door seals, heating element ports, and thermocouple entries—must be hermetically sealed.
Once sealed, the inert gas is introduced. The system maintains a slight positive pressure (often around 0.022 atmospheres or higher) relative to the outside. This pressure differential ensures that if any microscopic leak exists, the inert gas will flow outward, preventing ambient air from flowing inward.
Common Furnace Configurations and Their Uses
While the sealing principle is universal, the furnace's physical configuration is chosen based on the size, shape, and quantity of the material being processed.
Box-Style Furnaces
These are the most common for general-purpose batch processing.
- Front-Load: The standard "oven" design, ideal for manually loading a wide variety of parts on shelves or trays.
- Bottom-Load: The furnace floor is an elevator that lowers for loading and then raises to seal the chamber. This is excellent for heavy or large parts that are easier to load with an overhead crane.
- Top-Hat (Bell): The furnace body (the "hat") is lifted off a stationary hearth for loading. This design is suited for processing exceptionally large or awkwardly shaped components.
Tube Furnaces
These furnaces feature a cylindrical chamber, making them ideal for small-scale laboratory experiments, pilot testing, or continuous processing of wires, fibers, or small parts that can be pushed through the tube.
Rotary Furnaces
These are specialized furnaces with a rotating cylindrical chamber. They are designed for processes that require continuous mixing to ensure uniform heat treatment, making them perfect for powders, grains, or small parts that would otherwise have inconsistent heat exposure.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Purge vs. Vacuum
Not all inert atmosphere creation methods are equal. The choice between a standard purge system and a vacuum backfill system depends on the sensitivity of your material.
Standard Inert Gas Purge
In this method, the sealed chamber is simply flooded with a high volume of inert gas to push out, or "purge," the ambient air. This is a fast, simple, and cost-effective method suitable for many applications like annealing or brazing standard metals.
However, it may not remove 100% of reactive gases, leaving trace amounts of oxygen and moisture.
Vacuum with Inert Gas Backfill
For highly sensitive or reactive materials (like titanium or certain advanced ceramics), a vacuum furnace is used. The cycle involves two steps:
- Pump Down: A vacuum pump removes nearly all the atmosphere from the sealed chamber.
- Backfill: High-purity inert gas is introduced into the near-vacuum chamber.
This method achieves a significantly higher level of atmospheric purity but comes at the cost of more expensive equipment and longer cycle times.
Key Applications Driving the Need
The demand for inert atmosphere processing is driven by a need for absolute material integrity.
Heat Treating and Annealing
Preventing surface oxidation during heat treatment preserves the intended mechanical properties and surface finish of a metal part, avoiding a brittle, oxidized outer layer.
Brazing and Soldering
For a brazing alloy to properly wet and flow into a joint, the metal surfaces must be perfectly clean and oxide-free. An inert atmosphere ensures this, creating a strong, reliable bond.
Powder Metallurgy and Additive Manufacturing
Fine metal powders have an enormous surface area-to-volume ratio, making them extremely susceptible to oxidation. Processes like powder bed fusion (3D printing) and sintering rely completely on a pure inert atmosphere to create dense, high-quality final parts.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Your selection should be guided by your material, production scale, and required atmospheric purity.
- If your primary focus is small-scale research or processing continuous materials: A tube furnace offers precise control and is highly efficient for smaller volumes.
- If your primary focus is batch processing of general parts: A front-load box furnace is the versatile workhorse for most heat treatment applications.
- If your primary focus is processing very heavy or large components: A bottom-load or top-hat furnace provides the necessary loading and capacity advantages.
- If your primary focus is processing highly reactive powders or metals: A vacuum furnace with an inert gas backfill is non-negotiable for achieving the required purity.
Ultimately, selecting the right furnace is about matching the sealing mechanism and chamber design to your material's sensitivity and your operational scale.

Summary Table:
| Furnace Type | Key Features | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Box-Style (Front-Load, Bottom-Load, Top-Hat) | Hermetically sealed, batch processing, versatile for various part sizes | Heat treating, annealing, brazing of metals and components |
| Tube Furnace | Cylindrical chamber, ideal for small-scale or continuous processing | Laboratory experiments, wire/fiber treatment, pilot testing |
| Rotary Furnace | Rotating chamber for uniform mixing, continuous operation | Powder metallurgy, grain processing, additive manufacturing |
| Vacuum Furnace | Uses vacuum backfill for high purity, suitable for sensitive materials | Processing reactive metals like titanium, advanced ceramics |
Upgrade your laboratory with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse labs with reliable inert atmosphere furnaces, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures precise alignment with your unique experimental needs, enhancing material integrity and process efficiency. Contact us today to discuss how our tailored solutions can optimize your inert atmosphere processing!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Mesh Belt Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Controlled Inert Nitrogen Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the environmental benefits of using inert gases in furnaces? Reduce Waste and Emissions for a Greener Process
- How does a chemically inert atmosphere function in a furnace? Prevent Oxidation and Ensure Material Purity
- What does inert mean in furnace atmospheres? Protect materials from oxidation with inert gases.
- How does nitrogen atmosphere heat treatment improve surface strengthening? Enhance Durability and Performance
- What is the use of nitrogen in furnace? Prevent Oxidation for Superior Heat Treatment



















