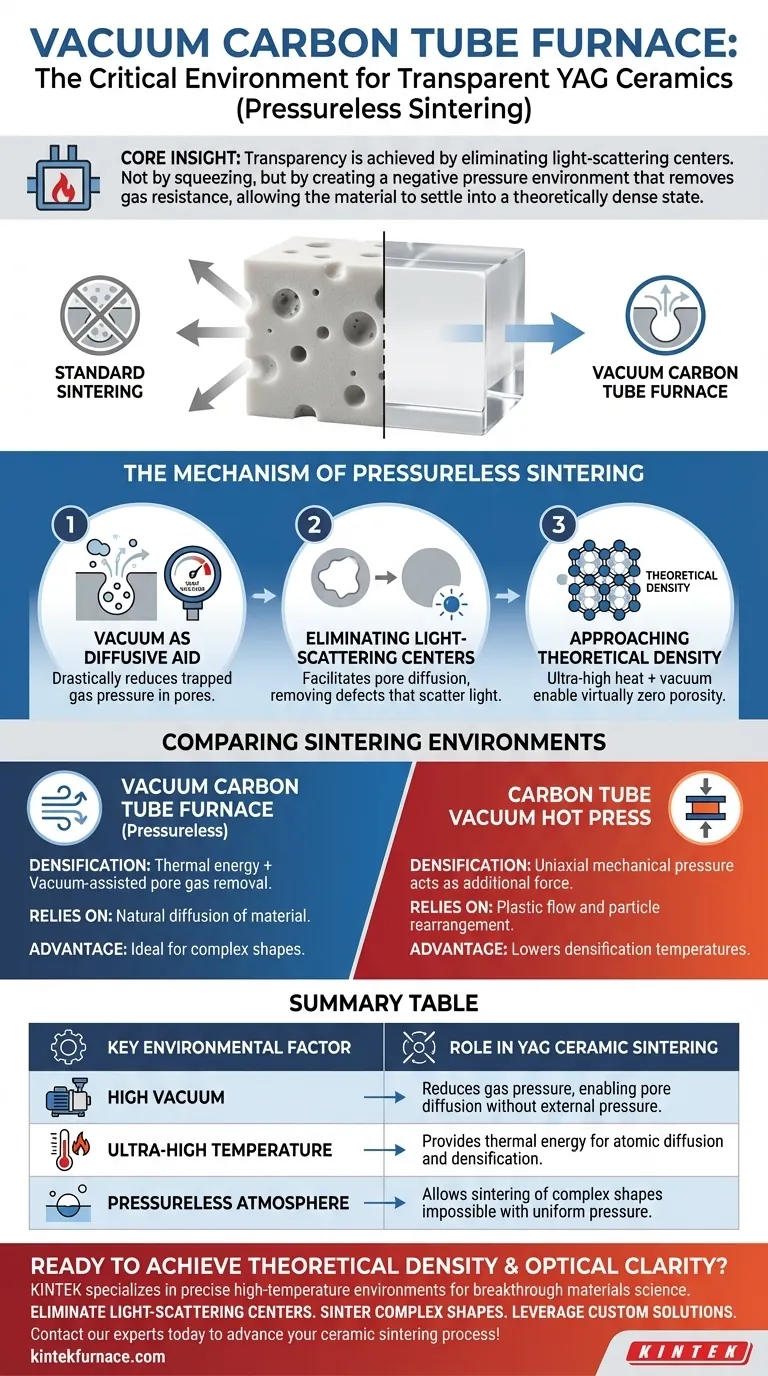
The critical environment provided by a Vacuum Carbon Tube Furnace is a combination of high-vacuum and ultra-high temperatures. This specialized atmosphere reduces the gas pressure within microscopic pores at the grain boundaries, allowing for pore diffusion and elimination without the application of external mechanical pressure.
Core Insight: The transparency of YAG ceramics depends entirely on eliminating light-scattering centers. The Vacuum Carbon Tube Furnace achieves this not by squeezing the material, but by creating a negative pressure environment that removes the gas resistance inside pores, allowing the material to naturally settle into a theoretically dense state.
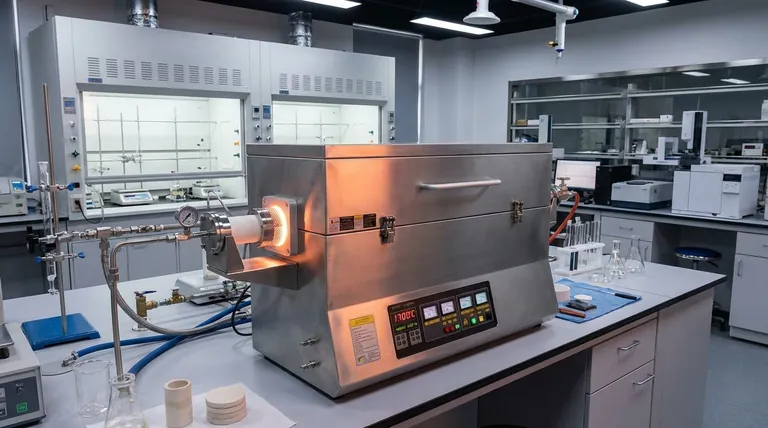

The Mechanism of Pressureless Sintering
To understand why this environment is essential for YAG transparent ceramics, you must look at how the furnace influences the microstructure of the material.
Vacuum as a Diffusive Aid
In standard sintering, trapped gas can prevent pores from closing. High-vacuum conditions drastically reduce the gas pressure inside these pores.
Eliminating Light-Scattering Centers
Transparency requires the total removal of internal defects. By facilitating pore diffusion, the furnace eliminates the voids that scatter light, transforming an opaque powder compact into a clear solid.
Approaching Theoretical Density
The combination of ultra-high heat and vacuum allows the ceramic to approach its theoretical density. This is the state where the material is solid matter with virtually no porosity.
Comparing Sintering Environments
It is vital to distinguish between the pressureless environment of a standard Vacuum Carbon Tube Furnace and alternative methods like Hot Pressing.
Thermal Diffusion vs. Mechanical Force
In a Vacuum Carbon Tube Furnace (Pressureless), densification is driven by thermal energy and the vacuum-assisted removal of pore gas. It relies on the natural diffusion of the material.
The Hot Press Contrast
Conversely, a Carbon Tube Vacuum Hot Press introduces uniaxial mechanical pressure. As noted in your references, this pressure acts as an additional driving force, promoting plastic flow and particle rearrangement.
Why Choose Pressureless?
While hot pressing lowers densification temperatures, pressureless sintering in a Vacuum Carbon Tube Furnace is often preferred for complex shapes where applying uniform uniaxial pressure is impossible. It relies on the purity of the vacuum environment to achieve density rather than brute force.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To select the correct sintering method for your YAG ceramics, consider your primary mechanism for densification.
- If your primary focus is optical transparency in complex shapes: Rely on the Vacuum Carbon Tube Furnace to evacuate pore gas and achieve density through diffusion without external pressure.
- If your primary focus is lowering densification temperature: Consider a Hot Press system to utilize mechanical force for particle rearrangement and plastic flow.
The Vacuum Carbon Tube Furnace is the definitive tool for achieving transparency when mechanical pressure is not an option, leveraging negative pressure to perfect the material's microstructure.
Summary Table:
| Key Environmental Factor | Role in YAG Ceramic Sintering |
|---|---|
| High Vacuum | Reduces gas pressure in microscopic pores, enabling pore diffusion and elimination without external pressure. |
| Ultra-High Temperature | Provides the thermal energy necessary for atomic diffusion and densification of the ceramic material. |
| Pressureless Atmosphere | Allows for the sintering of complex shapes where applying uniform mechanical pressure is not feasible. |
Ready to achieve theoretical density and optical clarity in your advanced ceramics?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the precise high-temperature environments required for breakthrough materials science. Our Vacuum Carbon Tube Furnaces are engineered to deliver the critical combination of high-vacuum and ultra-high temperatures essential for pressureless sintering of materials like YAG transparent ceramics.
Our expertise can help you:
- Eliminate Light-Scattering Centers: Achieve superior transparency by perfectly removing pores.
- Sinter Complex Shapes: Benefit from pressureless sintering for intricate component geometries.
- Leverage Custom Solutions: Our furnaces are customizable to meet your unique research and production needs.
Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, alongside lab high-temp furnaces, all tailored for unique applications.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our Vacuum Carbon Tube Furnace can advance your ceramic sintering process!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Furnace Molybdenum Wire Vacuum Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What types of heating elements are used in vacuum furnaces and what are their temperature capabilities? Optimize Your High-Temp Processes
- Why is vacuum annealing important for rare metal materials? Ensure Purity and Performance in Critical Applications
- How does a vacuum heat treatment furnace prevent contamination? Ensure Purity in High-Temperature Processes
- Why is graphite material advantageous for vacuum furnace fixturing? Boost Efficiency and Precision
- Why is uniform heating important in vacuum annealing? Ensure Consistent Material Properties and Avoid Defects
- What types of quenching methods are available in a vacuum furnace? Optimize Hardening with Oil or Gas Quenching
- Why is a high vacuum essential for Ti-6Al-4V sintering? Protect Your Alloys from Embrittlement
- What functions does a high-temperature sintering furnace perform in the preparation of porous magnesium oxide?



















