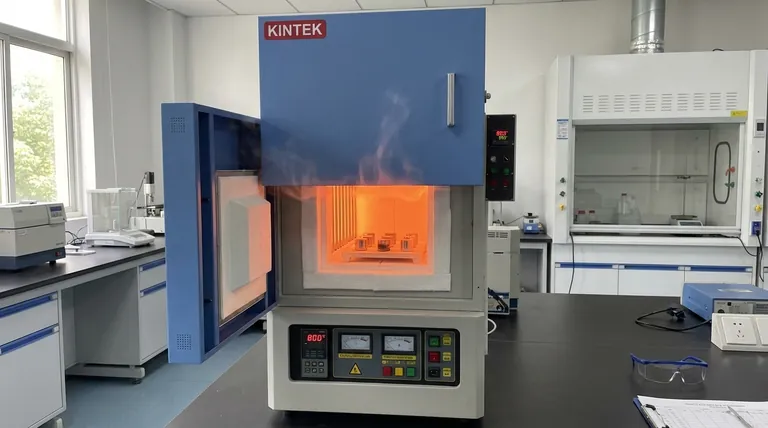
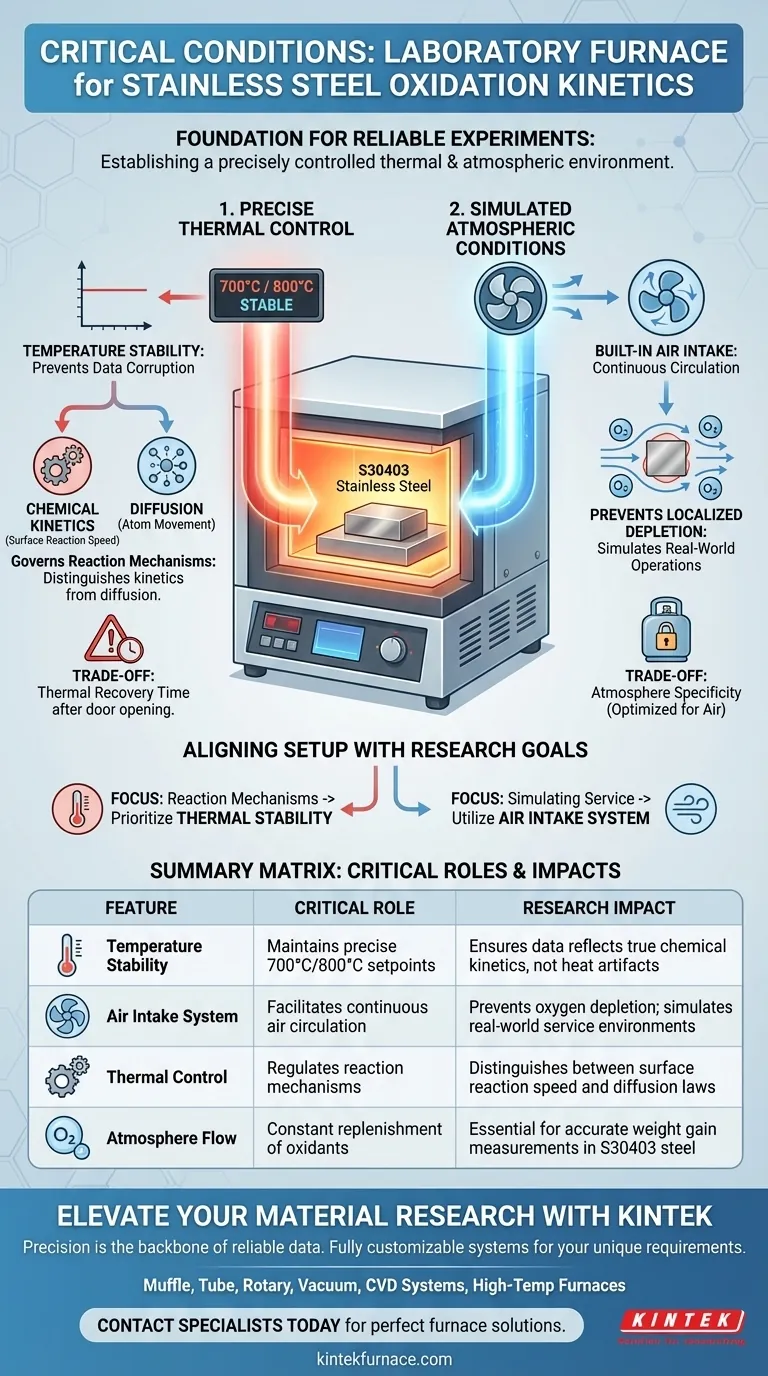
A laboratory box-type resistance furnace serves as the foundation for oxidation kinetics experiments by establishing a precisely controlled thermal and atmospheric environment. Specifically, it maintains stable high temperatures—typically at 700°C and 800°C for S30403 stainless steel—while a built-in air intake system ensures continuous air circulation. These conditions are critical for simulating real-world operations and ensuring the validity of weight gain measurements.
Reliability in oxidation kinetics testing depends on eliminating environmental variables. The box-type resistance furnace achieves this by synchronizing rigorous temperature control with consistent oxidant supply, allowing researchers to accurately map reaction rates against chemical kinetics and diffusion laws.

Establishing the Thermal Environment
Precision at Critical Temperatures
The primary function of this apparatus is to provide a stable high-temperature environment. For austenitic stainless steel (S30403), testing is frequently conducted at specific thresholds, such as 700°C and 800°C.
Ensuring Data Accuracy
Precise temperature control is not merely a feature; it is the prerequisite for accurate oxidation weight gain tests. Slight fluctuations in heat can artificially alter reaction speeds, corrupting the data used to calculate kinetic parameters.
Governing Reaction Mechanisms
Stability ensures that the observed reaction rates are true indicators of the material's behavior. This clarity allows researchers to determine if the oxidation process is governed by chemical kinetics (surface reaction speed) or diffusion (atom movement through the oxide layer).
Simulating Real-World Atmospheres
The Role of Air Circulation
Static heating environments often fail to represent actual service conditions where gases flow past the material. To address this, these furnaces are equipped with a built-in air intake system.
Preventing Localized Depletion
This intake system ensures sufficient air circulation within the chamber. By constantly replenishing the atmosphere, the furnace prevents oxygen starvation at the sample surface, which is essential for simulating real working conditions.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Thermal Recovery Times
While resistance furnaces offer excellent stability, they do not heat instantly. Researchers must be aware of the recovery time required to return to the set point (e.g., 800°C) after the door is opened to insert samples, as this can impact the initial data points of a kinetic curve.
Atmosphere Specificity
The built-in intake system is optimized for air circulation. While this is perfect for oxidation testing, it may require modification or supplementary equipment if the experiment demands a strictly inert environment or specific gas mixtures beyond standard air composition.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To maximize the utility of a box-type resistance furnace for your experiments, align your setup with your specific research objectives:
- If your primary focus is determining reaction mechanisms: Prioritize the unit's thermal stability to ensure that weight gain data reflects true chemical kinetics or diffusion rates rather than temperature artifacts.
- If your primary focus is simulating operational service: actively utilize the built-in air intake system to replicate the dynamic airflow and oxygen availability the steel will face in the field.
Rigorous control of heat and airflow turns a standard furnace into a precision instrument for material science.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Critical Role in Oxidation Kinetics | Research Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature Stability | Maintains precise 700°C/800°C setpoints | Ensures data reflects true chemical kinetics, not heat artifacts |
| Air Intake System | Facilitates continuous air circulation | Prevents oxygen depletion; simulates real-world service environments |
| Thermal Control | Regulates reaction mechanisms | Distinguishes between surface reaction speed and diffusion laws |
| Atmosphere Flow | Constant replenishment of oxidants | Essential for accurate weight gain measurements in S30403 steel |
Elevate Your Material Research with KINTEK
Precision is the backbone of reliable oxidation kinetics data. Backed by expert R&D and world-class manufacturing, KINTEK offers a comprehensive range of Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, as well as high-performance lab high-temperature furnaces.
Whether you are testing S30403 stainless steel or developing next-generation alloys, our systems are fully customizable to meet your unique temperature stability and atmospheric requirements. Ensure your experiments reflect real-world conditions with KINTEK's advanced thermal solutions.
Ready to optimize your high-temperature testing? Contact our laboratory specialists today to find the perfect furnace for your specific research needs.
Visual Guide
References
- Yaoyao Fiona Zhao, Changrong Li. Effect of V content on high temperature oxidation resistance of S30403 austenitic stainless steel. DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-17971-6
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- How does a muffle furnace with a weighing system benefit biochar research? Gain Real-Time Pyrolysis Insights
- How is a laboratory muffle furnace utilized during the debinding stage of HAp green bodies? Precision Thermal Control
- What is important about chamber size in muffle furnaces? Ensure Accurate Heating with the Right Zone
- What is a batch furnace? Maximize Flexibility and Precision for Your Heat Treatment
- What are the specific technical functions of hydrothermal autoclaves and muffle furnaces in catalyst preparation?
- What role do auxiliary equipment like fans and sprayers play in a box furnace? Enhance Precision and Efficiency in Heat Treatment
- How does the exhaust system in some muffle furnaces contribute to safety? Prevent Hazards and Ensure Safe Operation
- What are the common uses of a muffle furnace? Essential for Ashing, Sintering, and More



















