A laboratory muffle furnace acts as a high-precision thermal reactor during the debinding stage. It is utilized to apply a strictly controlled temperature profile—often reaching final temperatures around 1050°C—to pyrolyze and volatilize organic resin binders within hydroxyapatite (HAp) green bodies.
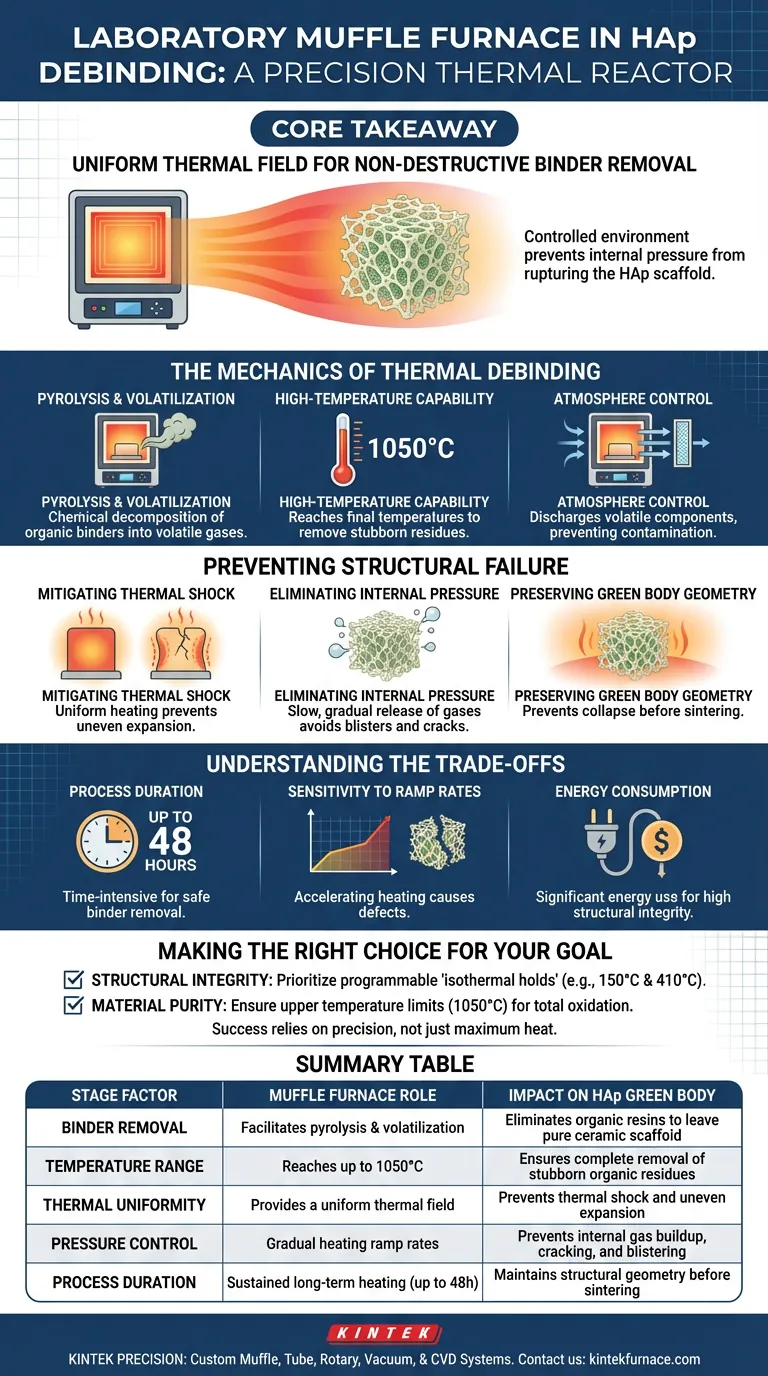
Core Takeaway The muffle furnace’s primary function during debinding is not just heating, but providing a uniform thermal field for the slow, non-destructive removal of organic material. This controlled environment is the only way to prevent internal pressure from rupturing the fragile HAp scaffold before it is sintered.

The Mechanics of Thermal Debinding
Pyrolysis and Volatilization
The muffle furnace is employed to facilitate the chemical decomposition of organic binders. By raising the temperature, the furnace converts the solid resin binders holding the HAp powder together into volatile gases.
High-Temperature Capability
While debinding often begins at lower temperatures, the furnace must be capable of reaching significant highs, such as 1050°C. This ensures the complete removal of stubborn organic residues that could contaminate the final biomaterial.
Atmosphere Control
The furnace creates a contained environment where these volatile components can be discharged safely. This prevents the re-deposition of carbon or other impurities onto the porous HAp structure.
Preventing Structural Failure
Mitigating Thermal Shock
The most critical role of the muffle furnace is generating a uniform thermal field. If the temperature varies significantly across the furnace chamber, the HAp green body will experience uneven expansion.
Eliminating Internal Pressure
If binders decompose too quickly, gas pressure builds up inside the ceramic body. The muffle furnace allows for a slow, gradual release of these gases, preventing the formation of blisters, cracks, or delamination.
Preserving Green Body Geometry
During this stage, the HAp structure is fragile because the binder—which provides its shape—is being removed. The gentle, even heating of the muffle furnace prevents structural collapse before the ceramic particles begin to sinter and bond.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Process Duration
Effective debinding in a muffle furnace is time-intensive. Complex debinding programs can last up to 48 hours to ensure safe binder removal without damaging the part.
Sensitivity to Ramp Rates
The process requires rigorous patience. Accelerating the heating rate to save time almost invariably leads to defects, as the internal stresses caused by temperature gradients will fracture thick-walled structures.
Energy Consumption
Maintained high temperatures over long durations result in significant energy use. This is an unavoidable cost of achieving high structural integrity in HAp ceramics.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To maximize the effectiveness of a muffle furnace for HAp debinding, tailor your approach to your specific constraints:
- If your primary focus is Structural Integrity: Prioritize a furnace with programmable "isothermal holds" (e.g., at 150°C and 410°C) to allow gases to escape fully before increasing heat.
- If your primary focus is Material Purity: Ensure your furnace can sustain the upper temperature limits (1050°C) to guarantee the total oxidation of all organic residues.
Success in debinding hydroxyapatite relies less on maximum heat and more on the precision of the thermal profile.
Summary Table:
| Stage Factor | Muffle Furnace Role | Impact on HAp Green Body |
|---|---|---|
| Binder Removal | Facilitates pyrolysis & volatilization | Eliminates organic resins to leave pure ceramic scaffold |
| Temperature Range | Reaches up to 1050°C | Ensures complete removal of stubborn organic residues |
| Thermal Uniformity | Provides a uniform thermal field | Prevents thermal shock and uneven expansion |
| Pressure Control | Gradual heating ramp rates | Prevents internal gas buildup, cracking, and blistering |
| Process Duration | Sustained long-term heating (up to 48h) | Maintains structural geometry before sintering |
Elevate Your Material Research with KINTEK Precision
Don't let internal cracks or impurities ruin your hydroxyapatite scaffolds. KINTEK provides industry-leading muffle furnaces designed for the rigorous demands of thermal debinding. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, we offer customizable Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems tailored to your specific lab requirements.
Whether you need precise ramp rates for delicate green bodies or high-temp capabilities for total purity, our high-temp furnaces ensure consistent results every time.
Contact us today to find the perfect furnace for your HAp processing needs.
Visual Guide
References
- Ali Arab, Chunwei Zhang. Influence of Cell Geometry on the Mechanical and Failure Characteristics of 3D Voronoi Hydroxyapatite Through the Stereolithography Technique. DOI: 10.3390/ceramics8010004
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What are the design features of a muffle furnace? Key Components for Precision and Purity
- What role does a muffle furnace play in TiO2 sol-gel transformation? Achieve High-Performance Photocatalytic Coatings
- How does an industrial-grade muffle furnace contribute to the catalyst activation process? Maximize Catalyst Efficiency
- What is the purpose of using a muffle furnace to fire Al2O3 ceramic shells at 1050°C? Enhance Strength and Purity
- What scientific processes can a muffle furnace assist with? Unlock Precise, Contaminant-Free Heat Treatment
- Why are muffle furnaces important in laboratories? Essential for Contamination-Free High-Temperature Processing
- What is a muffle furnace and what are its primary uses? Unlock Precise High-Temp Solutions
- What is the purpose of a muffle furnace in microbiological analysis? Achieve Absolute Sterility and Precise Sample Preparation



















