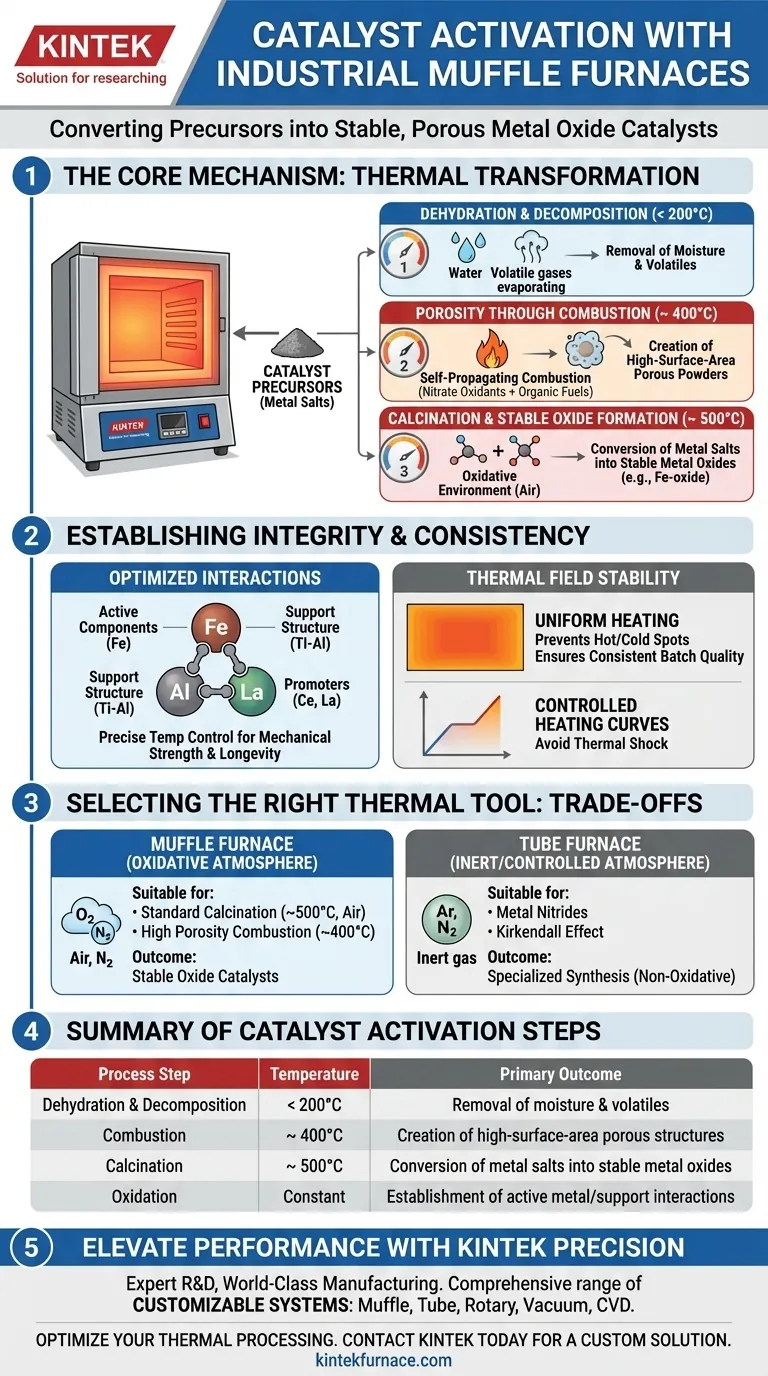
An industrial-grade muffle furnace facilitates catalyst activation by providing a stable, high-temperature oxidative environment essential for dehydrating and decomposing catalyst precursors. Typically operating around 500 °C, this equipment drives the critical chemical conversion of metal salts into stable metal oxide phases in an air atmosphere.
Core Takeaway The muffle furnace is the engine of structural transformation in catalyst preparation. By maintaining a highly precise thermal field, it ensures the uniform decomposition of precursors, fixing the active metal components onto their support structures and establishing the porosity required for high catalytic performance.

The Mechanism of Chemical Conversion
Dehydration and Decomposition
The primary function of the muffle furnace during activation is to manage the thermal breakdown of precursor materials.
As the furnace heats the material, typically to around 500 °C, it removes moisture (dehydration) and decomposes metal salts. This process effectively strips away volatile components, leaving behind the desired active phases.
Forming Stable Metal Oxides
The oxidative environment (air) within the furnace is critical for phase transformation.
It drives the conversion of unstable precursors into stable metal oxide phases. This chemical shift is the foundational step that turns a raw chemical mixture into a functional catalytic material.
Establishing Structural Integrity
Optimizing Component Interactions
High-precision temperature control allows for the development of ideal interactions between the catalyst's various ingredients.
Specifically, it manages the bonding between active components (such as Iron/Fe), the support structure (Titanium-Aluminum/Ti-Al), and promoters like Cerium or Lanthanum. These interactions determine the mechanical strength and chemical longevity of the final product.
Creating Porosity through Combustion
In specific preparation methods, the muffle furnace triggers self-propagating combustion reactions.
By heating to approximately 400 °C, the furnace initiates a reaction between nitrate oxidants and organic fuels. The uniform heating ensures this redox reaction is rapid and intense, releasing gases that create highly porous, high-surface-area powders.
Consistency and Stability
Thermal Field Stability
The quality of a catalyst is defined by its consistency across different production batches.
The muffle furnace provides excellent thermal field stability, ensuring that every part of the batch receives the exact same thermal treatment. This prevents "hot spots" or "cold spots" that could lead to uneven activation or structural defects.
Controlled Heating Curves
Laboratory and industrial muffle furnaces utilize preset temperature curves to manage the rate of change.
By following a strict heating profile, the equipment facilitates the gradual formation of specific active centers and skeletal structures. This controlled ramp-up is vital for preventing thermal shock or premature structural collapse.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Oxidative vs. Inert Atmospheres
It is vital to distinguish the muffle furnace from other thermal equipment like tube furnaces.
Muffle furnaces are designed for oxidative processes in air. If your catalyst activation requires a controlled inert atmosphere (such as Argon) to trigger specific phenomena like the Kirkendall effect or to form metal nitrides, a muffle furnace is not the correct tool. Those processes generally require the sealed environment of a tube furnace.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To ensure optimal catalyst activation, align your equipment choice with your specific chemical requirements:
- If your primary focus is standard calcination: Use a muffle furnace to convert metal salts to oxides in air at ~500 °C, ensuring stable component interaction.
- If your primary focus is high porosity via combustion: Use a muffle furnace at ~400 °C to trigger uniform redox reactions that generate high-surface-area powders.
- If your primary focus is inert atmosphere processing: Do not use a muffle furnace; switch to a tube furnace to prevent oxidation and allow for specific migration effects.
The muffle furnace is the definitive tool for ensuring the structural and chemical consistency required for high-performance oxide catalysts.
Summary Table:
| Process Step | Temperature | Primary Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Dehydration | < 200 °C | Removal of moisture and volatile components |
| Combustion | ~400 °C | Creation of high-surface-area porous structures |
| Calcination | ~500 °C | Conversion of metal salts into stable metal oxides |
| Oxidation | Constant | Establishment of active metal/support interactions |
Elevate Your Catalyst Performance with KINTEK Precision
Consistency is the hallmark of high-performance catalysts. Backed by expert R&D and world-class manufacturing, KINTEK offers a comprehensive range of Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems—all fully customizable to meet your specific activation protocols. Whether you require precise thermal fields for oxidation or controlled atmospheres for specialized synthesis, our lab high-temp furnaces provide the stability your research demands.
Ready to optimize your thermal processing? Contact KINTEK today for a custom solution.
Visual Guide
References
- Hamid Ahmed, Ahmed S. Al‐Fatesh. Methane Decomposition over a Titanium-Alumina and Iron Catalyst Assisted by Lanthanides to Produce High-Performance COx-Free H2 and Carbon Nanotubes. DOI: 10.3390/catal15010077
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- How does a high-temperature Muffle Furnace facilitate the conversion of precursors into spinel-type NiCo2O4?
- What is the mechanism for the furnace door in a muffle furnace? Discover the Double-Hinge Design for Perfect Sealing
- What role do muffle furnaces play in sintering 3D-printed beta-TCP? Optimize Your Bioceramic Results
- What is important about chamber size in muffle furnaces? Ensure Accurate Heating with the Right Zone
- Why is an automated high-temperature muffle furnace necessary for coating life assessment? Ensure Testing Precision
- How should the thermometer indicator be adjusted before using a muffle furnace? Ensure Accurate Temperature Readings
- What are the operational advantages of box type high-temperature resistance furnaces? Achieve Reliable, User-Friendly Thermal Processing
- What is the primary function of a high-temperature box resistance furnace for γ-Y1.5Yb0.5Si2O7 ceramics? Optimal Sintering & Densification



















