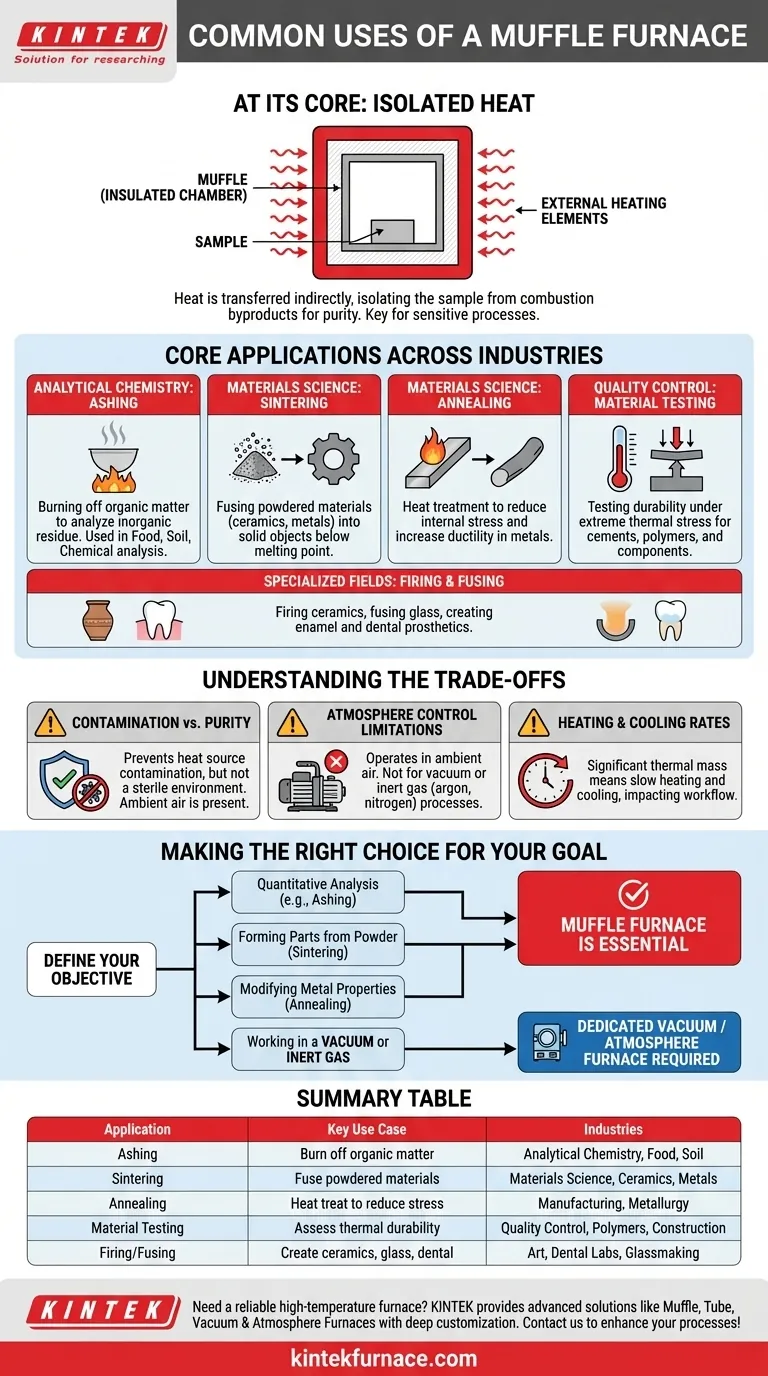
At its core, a muffle furnace is a high-temperature oven with a critical design feature: its heating elements are physically separated from the internal chamber. Its most common uses are for analytical processes like ashing, materials science applications like sintering and annealing, and rigorous material testing under extreme heat.
The defining value of a muffle furnace isn't just its high heat, but its ability to provide that heat without contaminating the sample. By isolating the material from the combustion byproducts or electrical elements, it ensures the integrity of sensitive processes.
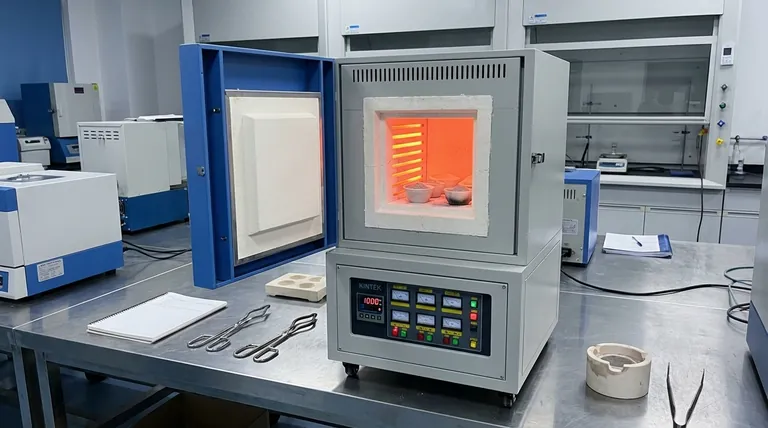

The Primary Function: Isolating the Sample
The key to understanding a muffle furnace's applications lies in its name. The internal chamber, or "muffle," acts as a barrier.
What is a "Muffle"?
A muffle is an insulated chamber that contains the sample being heated. The heating elements sit outside this chamber, heating it from the exterior.
This design ensures that heat is transferred to the sample uniformly and indirectly, typically through thermal radiation and convection.
Why Isolation Matters
In many scientific and industrial processes, direct exposure to a flame or an electrical heating element can introduce contaminants.
This isolation is crucial for applications where the chemical purity and composition of the final sample are paramount, such as burning away organic matter to weigh the inorganic residue.
Core Applications Across Industries
The muffle furnace's unique design makes it indispensable in a variety of fields, from analytical chemistry to industrial manufacturing.
Analytical Chemistry: Ashing and Gravimetric Analysis
Ashing is the most common analytical use. The process involves heating a sample at high temperatures to burn off all organic and volatile substances.
This leaves behind only the non-combustible inorganic residue, or ash, which can then be weighed and analyzed. This is a fundamental technique for determining the mineral content of food, soil, or chemical compounds.
Materials Science: Sintering and Annealing
Sintering is a process used to create solid objects from powders, particularly with ceramics and metals. The muffle furnace heats the powdered material to just below its melting point, causing the particles to fuse together.
Annealing is a heat treatment process that alters a material's physical properties. Metals are heated to a specific temperature and then cooled slowly, which removes internal stresses and increases ductility, making the metal softer and easier to work with.
Quality Control: Material and Component Testing
Industries use muffle furnaces to test how materials and components withstand extreme thermal stress.
This can involve testing the durability of cements and aggregates, the heat resistance of polymers and rubbers, or the melting point of various substances. It provides critical data for ensuring product quality and safety.
Specialized Fields: Firing and Fusing
Muffle furnaces are also used in more specialized or creative applications.
They are essential for firing ceramics and fusing glass, creating enamel coatings, and for high-temperature processes in dental labs, such as creating ceramic crowns and bridges.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While incredibly useful, a muffle furnace is not the right tool for every high-temperature job. Understanding its limitations is key.
Contamination Control vs. Purity
A muffle furnace prevents contamination from the heat source. It does not, however, create a sterile or particle-free environment. Samples are still exposed to the atmosphere inside the chamber.
Atmosphere Control Limitations
A standard muffle furnace operates in ambient air. It is not suitable for processes that require a vacuum or a specific inert gas atmosphere (like argon or nitrogen) to prevent oxidation. For those applications, a specialized vacuum or atmosphere furnace is required.
Heating and Cooling Rates
The heavy insulation that makes a muffle furnace efficient also means it has significant thermal mass. It can take a considerable amount of time to reach its target temperature and, more importantly, to cool down safely. This can impact workflow and throughput.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To select the correct heating process, you must first define your objective.
- If your primary focus is quantitative analysis (like ashing): The muffle furnace is essential for its ability to provide pure, non-contaminating heat.
- If your primary focus is forming ceramic or metal parts from powder: Sintering in a muffle furnace is the standard industrial process.
- If your primary focus is modifying metal properties (like softening): Annealing in a muffle furnace provides the controlled heating and slow cooling required.
- If your primary focus is working in a vacuum or inert gas: A standard muffle furnace is the wrong tool; you need a dedicated vacuum or atmosphere furnace.
Ultimately, choosing the right furnace depends on understanding that its purpose is to deliver controlled, isolated heat.
Summary Table:
| Application | Key Use Case | Industries |
|---|---|---|
| Ashing | Burn off organic matter for inorganic residue analysis | Analytical Chemistry, Food, Soil |
| Sintering | Fuse powdered materials to form solid objects | Materials Science, Ceramics, Metals |
| Annealing | Heat treat metals to reduce stress and increase ductility | Manufacturing, Metallurgy |
| Material Testing | Assess durability under extreme thermal stress | Quality Control, Polymers, Construction |
| Firing/Fusing | Create ceramics, glass, or dental prosthetics | Art, Dental Labs, Glassmaking |
Need a reliable high-temperature furnace for your lab? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced solutions like Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. With strong deep customization capabilities, we precisely meet unique experimental requirements for industries such as analytical chemistry, materials science, and quality control. Contact us today to enhance your processes with tailored, high-performance equipment!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What environmental conditions are critical for SiOC ceramicization? Master Precise Oxidation & Thermal Control
- Why is a high-performance muffle furnace required for the calcination of nanopowders? Achieve Pure Nanocrystals
- What metals cannot be heated by induction? Understanding Material Suitability for Efficient Heating
- What is the role of a muffle furnace in the synthesis of water-soluble Sr3Al2O6? Precision in SAO Production
- What role does a muffle furnace play in the preparation of MgO support materials? Master Catalyst Activation



















