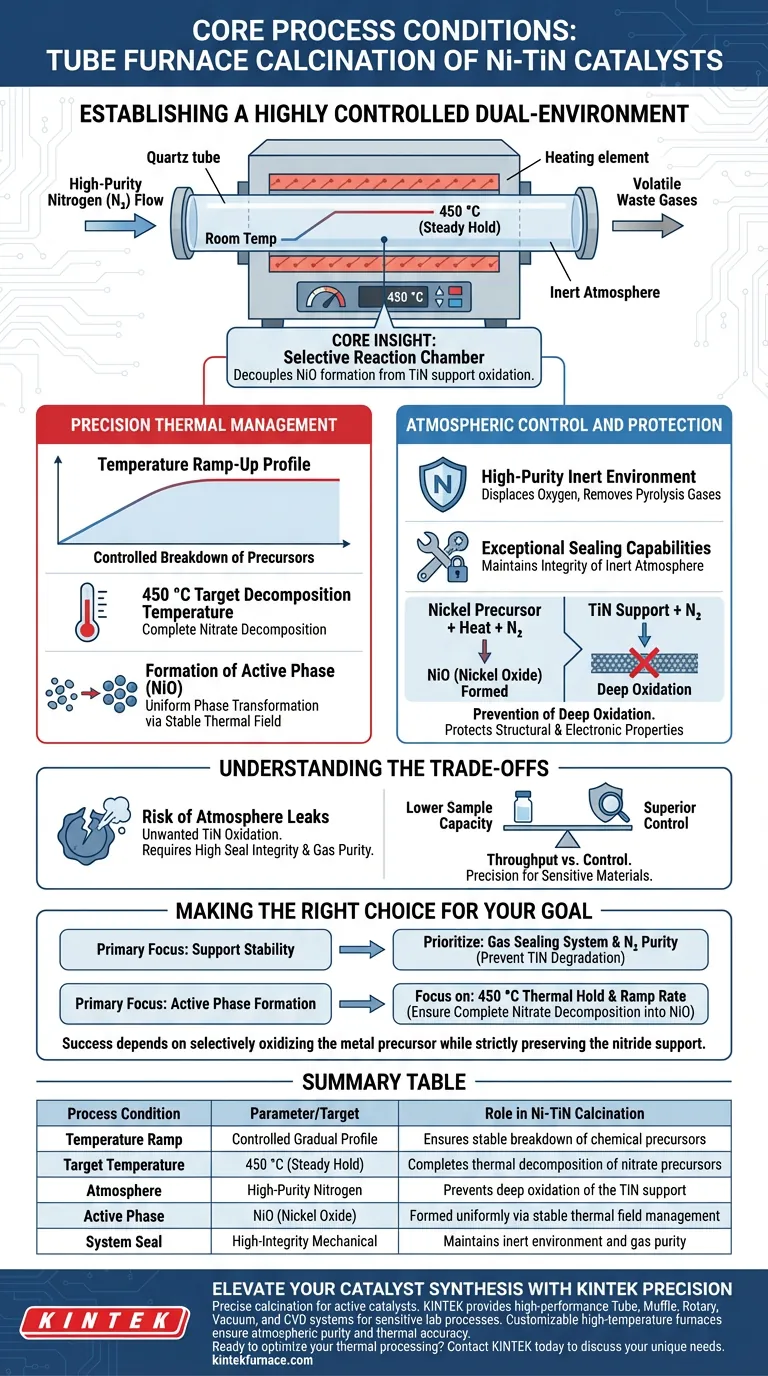
A tube furnace establishes a highly controlled dual-environment characterized by a precise temperature ramp-up profile and a high-purity nitrogen atmosphere. During the calcination of Ni-TiN catalysts, specifically at temperatures around 450 °C, this equipment manages the delicate balance of thermally decomposing nitrate precursors while simultaneously shielding the substrate from unwanted chemical changes.
Core Insight: The tube furnace is not merely a heat source; it is a selective reaction chamber. Its primary function in this context is to decouple the formation of the active Nickel Oxide (NiO) phase from the oxidation of the support, ensuring the sensitive Titanium Nitride (TiN) remains intact.
Precision Thermal Management
Controlled Temperature Ramp-Up
The tube furnace provides a specific temperature ramp-up profile rather than a sudden application of heat. This gradual increase is critical for the controlled breakdown of chemical precursors.
Target Decomposition Temperature
For Ni-TiN catalysts, the process typically targets a steady holding temperature of 450 °C. At this specific thermal plateau, the furnace ensures the complete thermal decomposition of nitrate precursors loaded onto the support.
Formation of the Active Phase
This thermal treatment drives the conversion of the precursor materials into the desired NiO (Nickel Oxide) phase. The stability of the temperature field ensures that this phase transformation occurs uniformly across the catalyst batch.
Atmospheric Control and Protection
High-Purity Inert Environment
Unlike open-air muffle furnaces, a tube furnace utilizes a continuous flow of high-purity nitrogen. This creates an inert environment that effectively displaces oxygen and removes volatile waste gases generated during pyrolysis.
Sealing Capabilities
The physical design of the tube furnace allows for exceptional sealing. This mechanical feature is vital for maintaining the integrity of the inert atmosphere throughout the duration of the calcination process.
Prevention of Deep Oxidation
The most critical role of the nitrogen atmosphere is to protect the TiN (Titanium Nitride) support. While the nickel precursor must oxidize to become NiO, the TiN support must not undergo deep oxidation, which would degrade its structural and electronic properties.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The Risk of Atmosphere Leaks
The success of this process relies entirely on the integrity of the tube seal and the purity of the nitrogen gas. Even minor leaks or contaminants in the gas line can introduce oxygen, leading to the unwanted oxidation of the TiN support, rendering the catalyst ineffective.
Throughput vs. Control
While a tube furnace offers superior atmospheric control compared to a muffle furnace, it often has a lower sample capacity. You trade the ability to process large bulk volumes for the precision required to protect sensitive materials like nitrides.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To maximize the performance of your Ni-TiN catalyst, align your process parameters with your specific structural requirements:
- If your primary focus is Support Stability: Prioritize the integrity of the gas sealing system and nitrogen purity to prevent the degradation of the TiN phase.
- If your primary focus is Active Phase Formation: Focus on the precision of the 450 °C thermal hold and ramp rate to ensure complete nitrate decomposition into NiO.
Success in Ni-TiN calcination depends on using the tube furnace to selectively oxidize the metal precursor while strictly preserving the nitride support.
Summary Table:
| Process Condition | Parameter/Target | Role in Ni-TiN Calcination |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature Ramp | Controlled Gradual Profile | Ensures stable breakdown of chemical precursors |
| Target Temperature | 450 °C (Steady Hold) | Completes thermal decomposition of nitrate precursors |
| Atmosphere | High-Purity Nitrogen | Prevents deep oxidation of the TiN support |
| Active Phase | NiO (Nickel Oxide) | Formed uniformly via stable thermal field management |
| System Seal | High-Integrity Mechanical | Maintains inert environment and gas purity |
Elevate Your Catalyst Synthesis with KINTEK Precision
Precise calcination is the difference between an active catalyst and a degraded support. Backed by expert R&D and world-class manufacturing, KINTEK provides high-performance Tube, Muffle, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems tailored for the most sensitive lab processes.
Whether you are developing Ni-TiN catalysts or advanced nitrides, our customizable high-temperature furnaces ensure the atmospheric purity and thermal accuracy your research demands.
Ready to optimize your thermal processing? Contact KINTEK today to discuss your unique needs.
Visual Guide
References
- Yi Zhu, Xunyu Lu. Making light work: designing plasmonic structures for the selective photothermal methanation of carbon dioxide. DOI: 10.1039/d3ey00315a
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What are the critical functions of a laboratory tube furnace in biomass synthesis? Optimize Your Carbonization Process
- What role do laboratory tube or muffle furnaces play in simulating SCM435 steel behavior? Optimize Material Research
- What types of reactions can tube furnaces be used for besides synthesis and purification? Explore Versatile Thermal Processing Applications
- What are common uses of tube furnaces? Precision Heating for Material Synthesis and Control
- What role does a high-temperature tube furnace play in Silicon/Hard Carbon synthesis? Master Battery Anode Production
- What is the function of autoclaves and tube reactors in hydrometallurgical leaching? Unlock Refractory Ore Potential
- Why is a tube furnace essential for Ru-TiO2/PC catalyst synthesis? Master Complex Atmosphere Control
- What factors determine the selection of a three-zone split tube furnace? Key Specs for Precision Thermal Processing



















