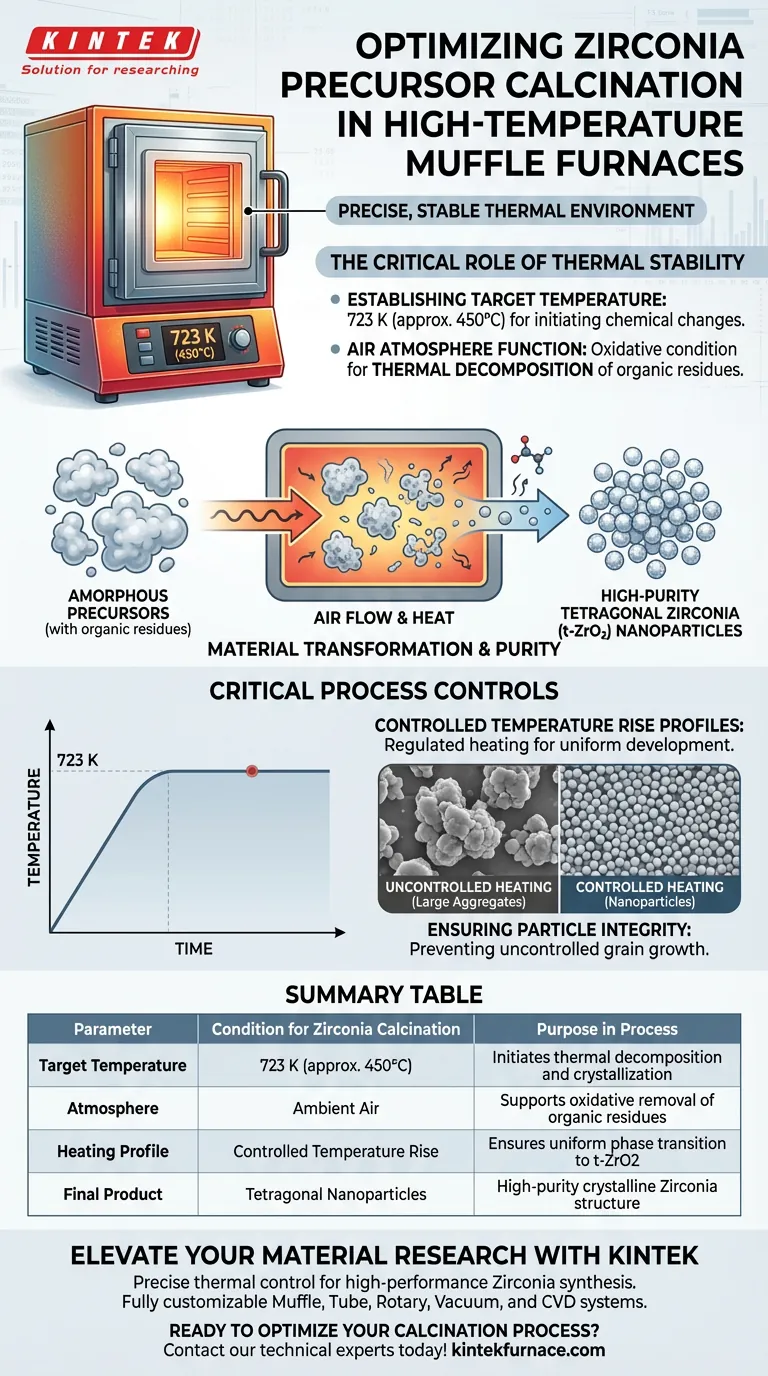
High-temperature muffle furnaces create a precise, stable thermal environment specifically tuned to 723 K (approximately 450°C) for the preliminary calcination of Zirconia precursors. In this air environment, the furnace facilitates the thermal decomposition necessary to strip away organic residues from the amorphous starting material.
By utilizing controlled temperature rise profiles, these furnaces enable the transformation of amorphous precursors into high-purity tetragonal Zirconia (t-ZrO2) nanoparticles through consistent thermal decomposition and crystallization.
The Critical Role of Thermal Stability
Establishing the Target Temperature
The primary condition provided by the muffle furnace is a stable operating temperature of 723 K. Maintaining this specific heat level is essential for initiating the chemical changes required for calcination without damaging the material structure.
The Function of the Air Atmosphere
The furnace operates in an air environment to support thermal decomposition. This oxidative condition is required to break down and remove organic residues effectively from the Zirconia precursors.
Material Transformation and Purity
Transitioning from Amorphous to Crystalline
The thermal energy supplied by the furnace drives a phase change in the material. It converts the initial amorphous precursors into a structured, crystalline form.
Achieving High Purity
The process is designed to result in tetragonal Zirconia (t-ZrO2) nanoparticles. By ensuring the complete decomposition of organic binders or additives, the furnace yields a high-purity final product.
Critical Process Controls
Controlled Temperature Rise
Success depends on more than just reaching the maximum temperature; it requires controlled temperature rise profiles. Regulating how fast the temperature increases is vital for the uniform development of the nanoparticles.
Ensuring Particle Integrity
The specific conditions of 723 K and controlled heating prevent uncontrolled grain growth. This helps maintain the material at the nanoparticle scale rather than forming large, irregular aggregates.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To optimize your calcination process for Zirconia precursors, consider your specific material requirements:
- If your primary focus is material purity: Ensure your furnace can maintain a stable 723 K in air to fully decompose all organic residues.
- If your primary focus is phase control: Prioritize furnaces that offer programmable temperature rise profiles to guarantee the formation of the tetragonal (t-ZrO2) crystalline phase.
Precise thermal control is the difference between amorphous powder and high-performance Zirconia nanoparticles.
Summary Table:
| Parameter | Condition for Zirconia Calcination | Purpose in Process |
|---|---|---|
| Target Temperature | 723 K (approx. 450°C) | Initiates thermal decomposition and crystallization |
| Atmosphere | Ambient Air | Supports oxidative removal of organic residues |
| Heating Profile | Controlled Temperature Rise | Ensures uniform phase transition to t-ZrO2 |
| Final Product | Tetragonal Nanoparticles | High-purity crystalline Zirconia structure |
Elevate Your Material Research with KINTEK
Precise thermal control is the cornerstone of high-performance Zirconia synthesis. Backed by expert R&D and world-class manufacturing, KINTEK offers a comprehensive range of Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems—all of which are fully customizable to meet your specific lab requirements. Whether you are performing preliminary calcination at 723 K or complex high-temperature sintering, our furnaces deliver the stability and programmable profiles necessary for superior material purity.
Ready to optimize your calcination process? Contact our technical experts today to find the perfect high-temperature furnace for your unique needs!
Visual Guide
References
- Maged F. Bekheet, Aleksander Gurlo. A quantitative microscopic view on the gas‐phase‐dependent phase transformation from tetragonal to monoclinic ZrO <sub>2</sub>. DOI: 10.1111/jace.19749
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
People Also Ask
- What role do muffle furnaces play in biomedical applications? Essential for Purity and Precision in Medical Research
- What are the key differences between a muffle furnace and a vacuum furnace? Choose the Right Furnace for Your Lab
- Why is a programmable temperature control furnace necessary for sintering HA? Ensure Structural Integrity & Purity
- How does a muffle furnace compare to other high-temperature furnaces in terms of cost? Discover Affordable Heat Treatment Solutions
- What are the primary functions of industrial high-temperature muffle or tube furnaces in the sintering of PCEC?
- Why is heating tube spacing critical in muffle furnace design? Master Thermal Uniformity for Superior Processing
- What are the main components of a box type resistance furnace? Unlock Precision Heating for Your Lab
- What are the modern applications of Muffle Furnaces? Essential for Clean Heat in Labs and Manufacturing



















