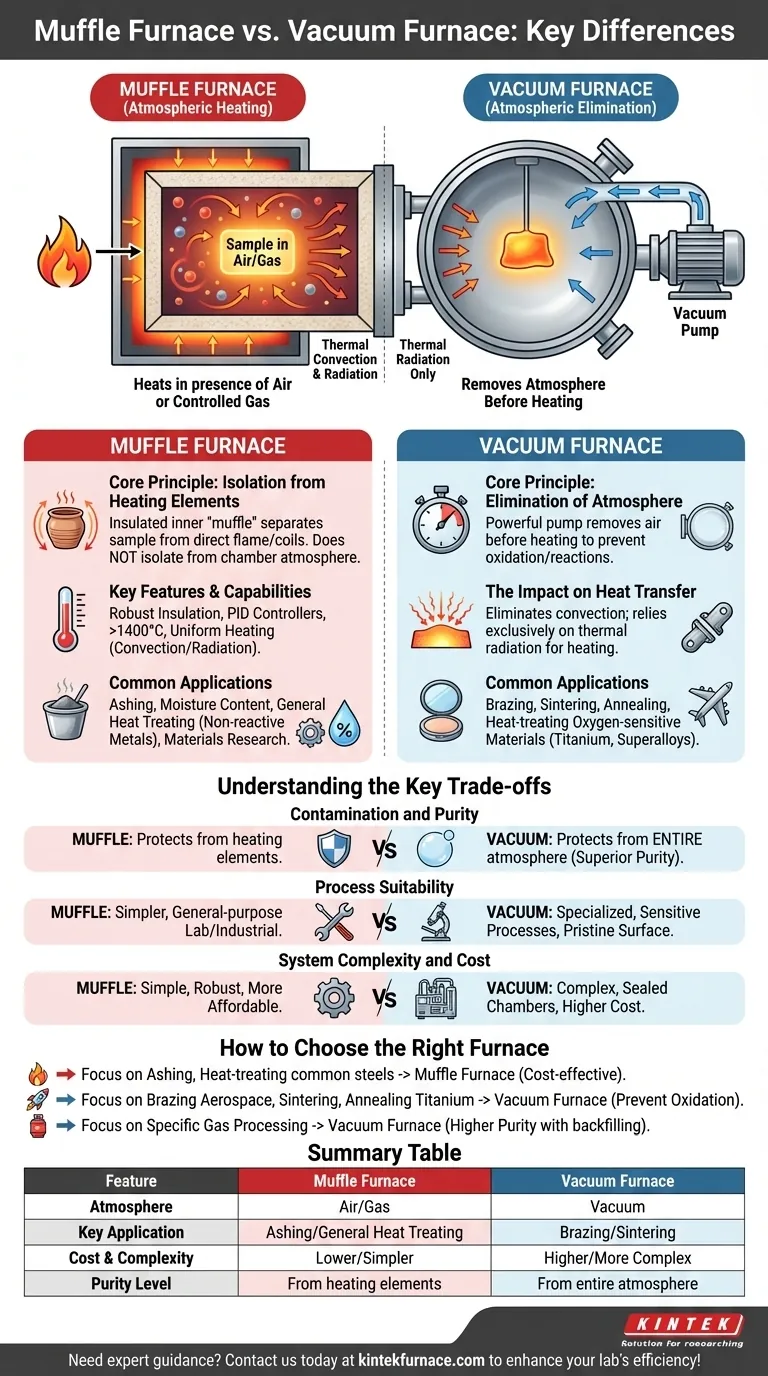
At its core, the difference between a muffle furnace and a vacuum furnace is the environment in which your material is heated. A muffle furnace heats a sample in the presence of air or a controlled gas, while a vacuum furnace first removes the atmosphere entirely before heating. This single distinction dictates their capabilities, applications, and suitability for different processes.
The choice is a function of your material's sensitivity to air. Muffle furnaces are for general, high-temperature work where atmospheric interaction is acceptable or desired. Vacuum furnaces are required for processes where any oxidation or atmospheric contamination would compromise the final product.

What Defines a Muffle Furnace?
A muffle furnace is a versatile workhorse for high-temperature applications. Its defining feature is a "muffle"—an insulated inner chamber that isolates the material from the direct flame or heating elements.
The Core Principle: Isolation from Heating Elements
The muffle, typically made of high-temperature ceramic, separates your sample from the source of heat. This prevents contamination from combustion byproducts or direct contact with the heating coils.
However, it does not inherently isolate the sample from the atmosphere inside the chamber, which is typically ambient air.
Key Features and Capabilities
Muffle furnaces are built for durability and precision in a standard atmosphere. Key features include robust insulation for thermal efficiency, PID controllers for accurate temperature regulation, and temperature ranges often exceeding 1400°C. They rely on thermal convection and radiation within the chamber to achieve uniform heating.
Common Applications
These furnaces are ideal for processes where interacting with air is not a concern, or is even part of the process itself. Common uses include ashing, determining moisture content, general heat treating of non-reactive metals, and materials research.
What Defines a Vacuum Furnace?
A vacuum furnace is a specialized system designed for processes that cannot tolerate the presence of oxygen or other atmospheric gases. Its primary function is to create a high-purity, non-reactive environment.
The Core Principle: Elimination of Atmosphere
Before the heating cycle begins, a powerful pump system removes nearly all the air from the sealed chamber. This evacuation prevents oxidation and other chemical reactions that would occur at high temperatures in a normal atmosphere.
The Impact on Heat Transfer
With almost no air molecules present, heat transfer via convection is eliminated. A vacuum furnace relies almost exclusively on thermal radiation from the heating elements to the material, which requires a different design approach to ensure temperature uniformity.
Common Applications
Vacuum furnaces are essential for high-tech manufacturing and advanced materials. They are used for brazing, sintering, annealing, and heat-treating oxygen-sensitive materials like titanium, superalloys, and specific medical-grade steels.
Understanding the Key Trade-offs
Choosing between these furnaces means weighing the need for atmospheric control against factors like cost and complexity.
Contamination and Purity
This is the most critical distinction. A muffle furnace protects against direct contamination from heating elements. A vacuum furnace protects against contamination from the entire atmosphere, offering a vastly superior level of purity.
Process Suitability
A muffle furnace is simpler and well-suited for a broad range of general-purpose lab and industrial work. A vacuum furnace is specifically designed for sensitive processes where a pristine surface finish and uncompromised material properties are non-negotiable.
System Complexity and Cost
Muffle furnaces are mechanically simple, robust, and significantly more affordable. Vacuum furnaces are complex systems involving sealed chambers, high-performance gaskets, and sophisticated pumping systems, making them more expensive to purchase, operate, and maintain.
How to Choose the Right Furnace for Your Process
Your decision should be guided by the chemical properties of your material and the desired outcome of your thermal process.
- If your primary focus is ashing, burn-off, or heat-treating common steels: A muffle furnace provides the necessary temperature control in a cost-effective and reliable package.
- If your primary focus is brazing aerospace components, sintering powdered metals, or annealing titanium: A vacuum furnace is the only choice to prevent catastrophic oxidation and ensure product integrity.
- If your primary focus is processing in a specific gas (e.g., argon or nitrogen): While a modified gas-purged muffle furnace can work, a vacuum furnace provides higher purity by first evacuating all residual air before backfilling with the desired gas.
Ultimately, selecting the right furnace begins with understanding how the atmosphere inside it will affect your material at high temperatures.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Muffle Furnace | Vacuum Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Atmosphere | Air or controlled gas | Vacuum (no atmosphere) |
| Key Application | Ashing, general heat treating | Brazing, sintering oxygen-sensitive materials |
| Cost & Complexity | Lower cost, simpler | Higher cost, more complex |
| Purity Level | Protects from heating elements | Protects from entire atmosphere |
Need expert guidance on selecting the perfect furnace for your unique needs? KINTEK leverages exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. With strong deep customization capabilities, we precisely meet your experimental requirements. Contact us today to enhance your lab's efficiency and achieve superior results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the primary function of a muffle furnace for BaTiO3? Master High-Temp Calcination for Ceramic Synthesis
- What metals cannot be heated by induction? Understanding Material Suitability for Efficient Heating
- How does a laboratory muffle furnace facilitate the biomass carbonization process? Achieve Precise Biochar Production
- Why is a high-performance muffle furnace required for the calcination of nanopowders? Achieve Pure Nanocrystals
- What is the key role of a muffle furnace in the pretreatment of boron sludge and szaibelyite? Unlock Higher Process Efficiency



















