At its core, a horizontal tube furnace provides a highly controlled and uniform high-temperature environment that is exceptionally easy to access. Its primary benefits stem from this combination of precise thermal performance and practical, user-friendly design, making it a versatile workhorse for countless laboratory and industrial processes.
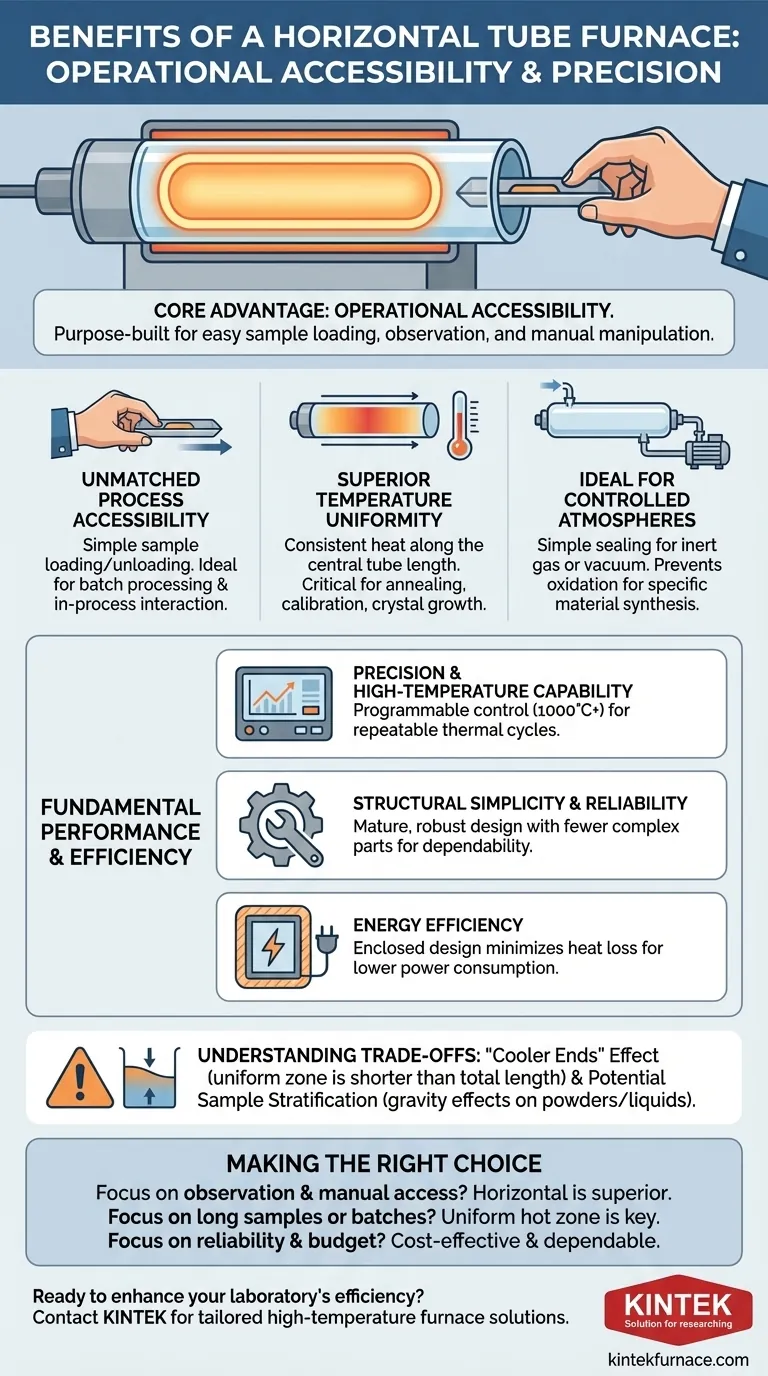
The crucial advantage of a horizontal tube furnace isn't just its ability to get hot, but its operational accessibility. The horizontal layout is purpose-built for applications requiring easy sample loading, in-process observation, or manual manipulation.
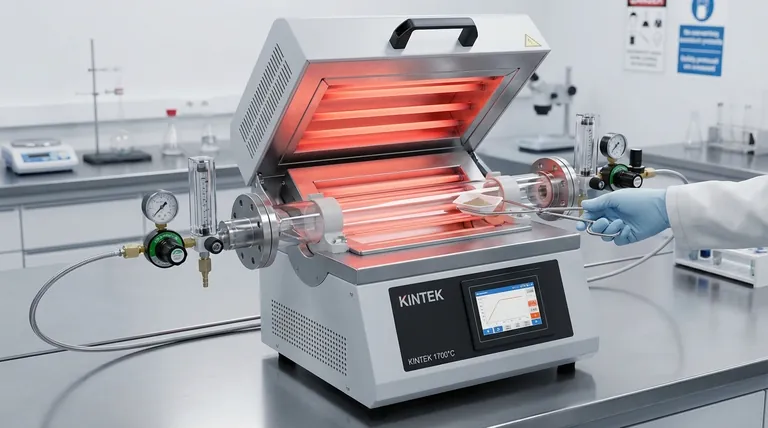

The Core Advantages of the Horizontal Design
The horizontal orientation directly influences how you interact with your process, offering distinct benefits over other furnace configurations.
Unmatched Process Accessibility
The most significant benefit is the ease of placing and removing samples. The horizontal tube allows operators to simply slide sample boats, crucibles, or substrates in and out.
This straightforward access is ideal for batch processing and for experiments where samples must be observed or manipulated during the heating cycle.
Superior Temperature Uniformity
Horizontal furnaces are engineered to provide an exceptionally uniform temperature zone along the central length of the tube. Heating elements are distributed to ensure consistent heat.
This uniformity is critical for applications like annealing, calibration, or crystal growth, where even minor temperature variations across the sample can compromise results.
Ideal for Controlled Atmospheres
Sealing the ends of a horizontal tube with flanges is a simple and reliable process. This makes it highly suitable for creating a controlled atmosphere.
Whether you need to flow inert gas (like argon or nitrogen) to prevent oxidation or pull a vacuum for specific material synthesis, the horizontal configuration is easy to adapt and maintain.
Fundamental Performance and Efficiency
Beyond its layout, a horizontal tube furnace is built on mature technology that delivers reliable and efficient performance.
Precision and High-Temperature Capability
These furnaces offer precise, programmable temperature control, allowing for repeatable thermal cycles. Most models are capable of reaching high temperatures, often well above 1000°C.
This combination of precision and high heat is essential for materials research, semiconductor fabrication, and various quality control tests.
Structural Simplicity and Reliability
The design of a horizontal tube furnace is fundamentally simple and robust. This mature technology translates to high reliability, ease of operation, and straightforward maintenance.
Fewer complex parts mean fewer points of failure, making it a cost-effective and dependable choice for continuous or long-duration use.
Energy Efficiency
By enclosing the heating chamber within a well-insulated case, tube furnaces inherently minimize heat loss to the surrounding environment. This enclosed design leads to higher thermal efficiency and lower power consumption compared to open-air furnaces.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While highly versatile, the horizontal design is not universally optimal. Understanding its limitations is key to making an informed decision.
The "Cooler Ends" Effect
A tube furnace is naturally cooler at the ends where heat escapes. This means the uniform hot zone is always shorter than the total heated length of the furnace.
It is critical to know the specified length of the uniform zone for your furnace to ensure your entire sample is processed at the target temperature.
Potential for Sample Stratification
For processes involving loose powders or liquids that may melt, gravity can cause some stratification or uneven distribution within a horizontal crucible. The sample may not have a perfectly uniform depth.
In these specific cases, a vertical furnace, where gravity aids in sample containment and uniformity, may be a better alternative.
Sample Containment Requirements
Working with a horizontal tube requires appropriate sample holders, such as ceramic or quartz "boats," to contain the material. While simple, this is an operational step that must be considered, especially when dealing with fine powders or materials that could spill during loading.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the right furnace depends entirely on the demands of your specific process.
- If your primary focus is process observation and manual sample manipulation: The horizontal furnace is the superior choice due to its unparalleled ease of access.
- If your primary focus is treating long samples or multiple small samples in a single batch: The extended, uniform hot zone of a horizontal furnace is highly effective.
- If your primary focus is melting materials or processing powders where gravity-induced uniformity is critical: You should carefully evaluate whether a vertical furnace might better suit your needs.
- If your primary focus is reliability, budget, and operational simplicity: The mature, simple design of a horizontal tube furnace often makes it the most cost-effective and dependable option.
By understanding these core principles of design and performance, you can confidently select the right tool for your scientific or industrial goal.
Summary Table:
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Unmatched Process Accessibility | Easy sliding of samples in and out, ideal for batch processing and in-process observation. |
| Superior Temperature Uniformity | Consistent heat along the tube length, crucial for annealing and crystal growth. |
| Ideal for Controlled Atmospheres | Simple sealing for inert gas or vacuum use, preventing oxidation in material synthesis. |
| Precision and High-Temperature Capability | Programmable control up to 1000°C+, ensuring repeatable thermal cycles for research. |
| Structural Simplicity and Reliability | Robust design with fewer parts, leading to ease of maintenance and long-term dependability. |
| Energy Efficiency | Insulated enclosure reduces heat loss, lowering power consumption compared to open-air furnaces. |
Ready to enhance your laboratory's efficiency with a tailored high-temperature furnace solution? Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced horizontal tube furnaces and other products like Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental requirements. Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can benefit your specific applications and drive your research forward!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- How is a Vertical Tube Furnace used for fuel dust ignition studies? Model Industrial Combustion with Precision
- Why is a tube furnace utilized for the heat treatment of S/C composite cathode materials? Optimize Battery Stability
- What are the key operational considerations when using a lab tube furnace? Master Temperature, Atmosphere & Safety
- What recent improvements have been made to lab tube furnaces? Unlock Precision, Automation & Safety
- How is a high-temperature tube furnace utilized in the synthesis of MoO2/MWCNTs nanocomposites? Precision Guide



















