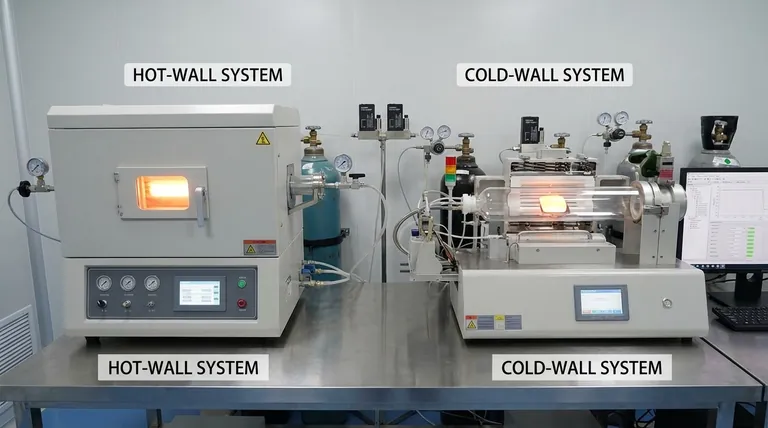
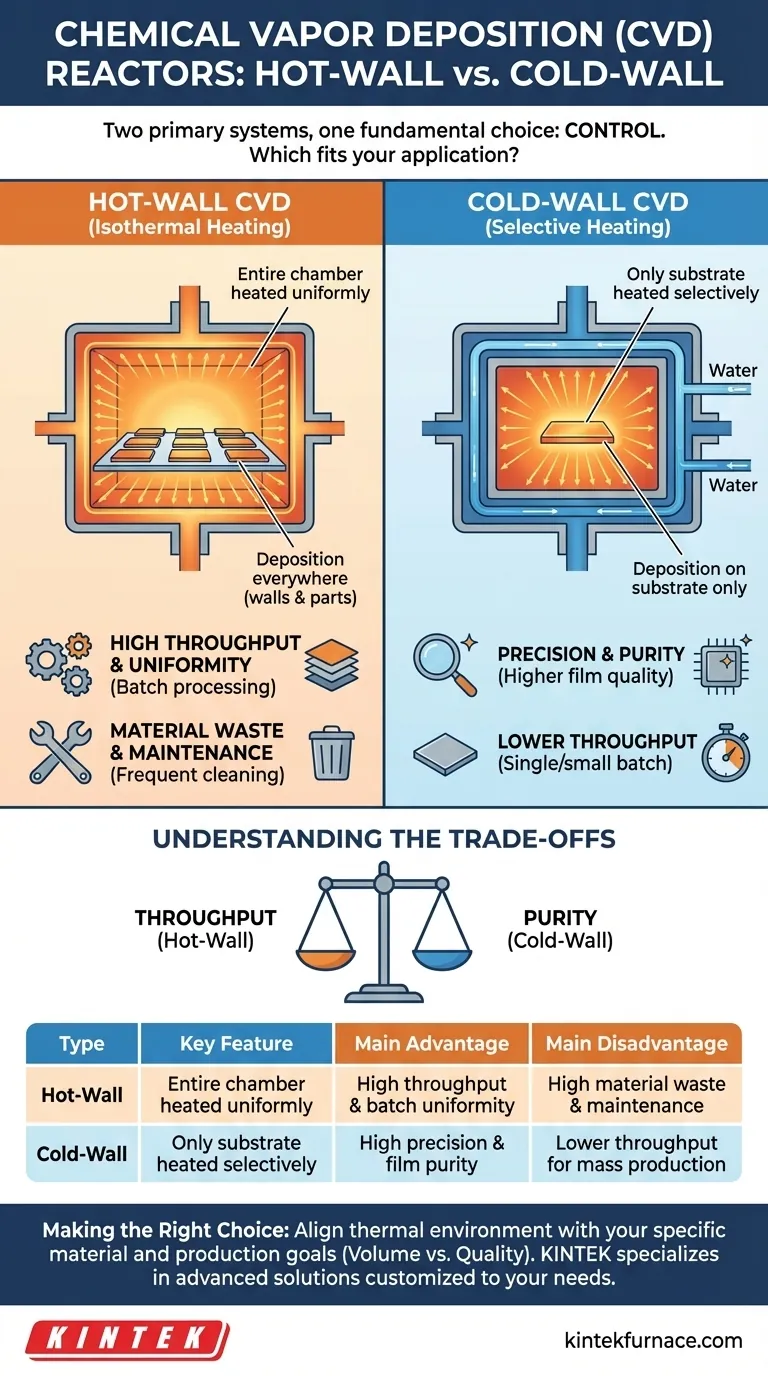
The two primary types of Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) reactors are hot-wall and cold-wall systems. A hot-wall reactor heats the entire reaction chamber, including the chamber walls and the substrates being coated. In contrast, a cold-wall reactor selectively heats only the substrate, while the chamber walls remain cool.
The fundamental choice between a hot-wall and a cold-wall CVD reactor comes down to a single principle: control. Hot-wall reactors prioritize batch uniformity and throughput, while cold-wall reactors offer precise control over the deposition process, minimizing waste and enabling higher-purity films.
How Hot-Wall CVD Works
A hot-wall reactor is conceptually straightforward. The entire system, typically a furnace, is heated to a uniform temperature, ensuring that any surface inside reaches the required temperature for the chemical reaction to occur.
The Principle of Isothermal Heating
The key characteristic is isothermal (uniform temperature) conditions. Both the substrates you want to coat and the interior walls of the reactor are held at the same high temperature.
Advantage: High Throughput and Uniformity
Because the entire space is a reactive zone, you can process a large number of parts simultaneously. This design is excellent for achieving consistent coating thickness across large batches, making it ideal for high-volume manufacturing.
Disadvantage: Unwanted Deposition
The main drawback is that the precursor gases react and deposit material everywhere, including on the chamber walls. This wastes expensive precursor materials and necessitates frequent, intensive cleaning cycles to remove the unwanted coating, leading to significant reactor downtime.
How Cold-Wall CVD Works
A cold-wall reactor creates a sharp temperature gradient. It is designed to confine the high-temperature zone exclusively to the substrate where deposition is desired.
The Principle of Selective Heating
The chamber walls are actively kept cool, often using water-cooling channels. The substrate is heated directly and independently, typically through methods like induction heating or resistive heating.
Advantage: Precision and Purity
Deposition occurs almost exclusively on the hot substrate surface. This dramatically improves material efficiency and minimizes contamination from flakes of unwanted material that can fall from the chamber walls in a hot-wall system. The result is a higher-purity film.
Disadvantage: Lower Throughput
These systems are generally designed for single-substrate or small-batch processing. The complexity of selective heating makes it more difficult to scale for the mass production volumes achievable with hot-wall reactors.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The choice between these two architectures is not about one being definitively "better" but about which is better suited for a specific application. It involves a critical balance of priorities.
Throughput vs. Purity
This is the central trade-off. Hot-wall is for volume; cold-wall is for quality. If your goal is to coat many standard parts uniformly, a hot-wall system is more efficient. If you are developing a novel material or require extremely pure films for sensitive applications (like high-end semiconductors), a cold-wall system is superior.
Material Waste and Maintenance
Hot-wall reactors consume significantly more precursor gas due to deposition on the walls. This leads to higher material costs and more frequent downtime for maintenance and cleaning, impacting overall operational cost.
Process Context
It's important to understand that "hot-wall" and "cold-wall" refer to the reactor's thermal architecture. Other specialized CVD processes, like Low-Pressure CVD (LPCVD) or Plasma-Enhanced CVD (PECVD), can be implemented within either a hot-wall or cold-wall system, depending on the desired outcome.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your application's specific requirements will determine the correct reactor architecture.
- If your primary focus is high-volume production and batch uniformity: A hot-wall reactor is typically the more efficient and cost-effective solution.
- If your primary focus is growing high-purity films, research, or complex materials: A cold-wall reactor provides the necessary precision and control over the deposition environment.
- If your primary focus is minimizing precursor material waste and operational downtime: A cold-wall reactor's efficiency can offer a lower total cost of ownership despite a potentially higher initial investment.
Ultimately, selecting the right reactor architecture is about aligning the thermal environment with your specific material and production goals.
Summary Table:
| Type | Key Feature | Main Advantage | Main Disadvantage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hot-Wall | Entire chamber heated uniformly | High throughput and batch uniformity | High material waste and maintenance |
| Cold-Wall | Only substrate heated selectively | High precision and film purity | Lower throughput for mass production |
Struggling to choose between hot-wall and cold-wall CVD reactors for your lab? KINTEK specializes in advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including CVD/PECVD systems, tailored to your unique needs. Leveraging our exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer deep customization to ensure precise control, efficiency, and cost-effectiveness for your applications. Contact us today to discuss how our expertise can optimize your deposition processes and achieve superior results!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment Machine
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What makes a CVD Tube Furnace essential for material science and nanotechnology? Unlock Precision in Material Synthesis
- Where is a CVD Tube Furnace commonly used? Essential for High-Tech Materials and Electronics
- Which industries and research fields benefit from CVD tube furnace sintering systems for 2D materials? Unlock Next-Gen Tech Innovations
- What temperature ranges can a CVD Tube Furnace achieve with different tube materials? Unlock High-Temp Precision for Your Lab
- Why are advanced materials and composites important? Unlock Next-Gen Performance in Aerospace, Auto, and More



















