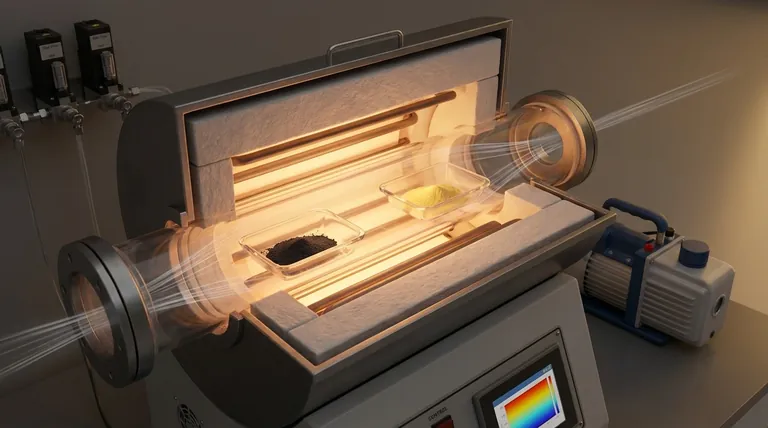
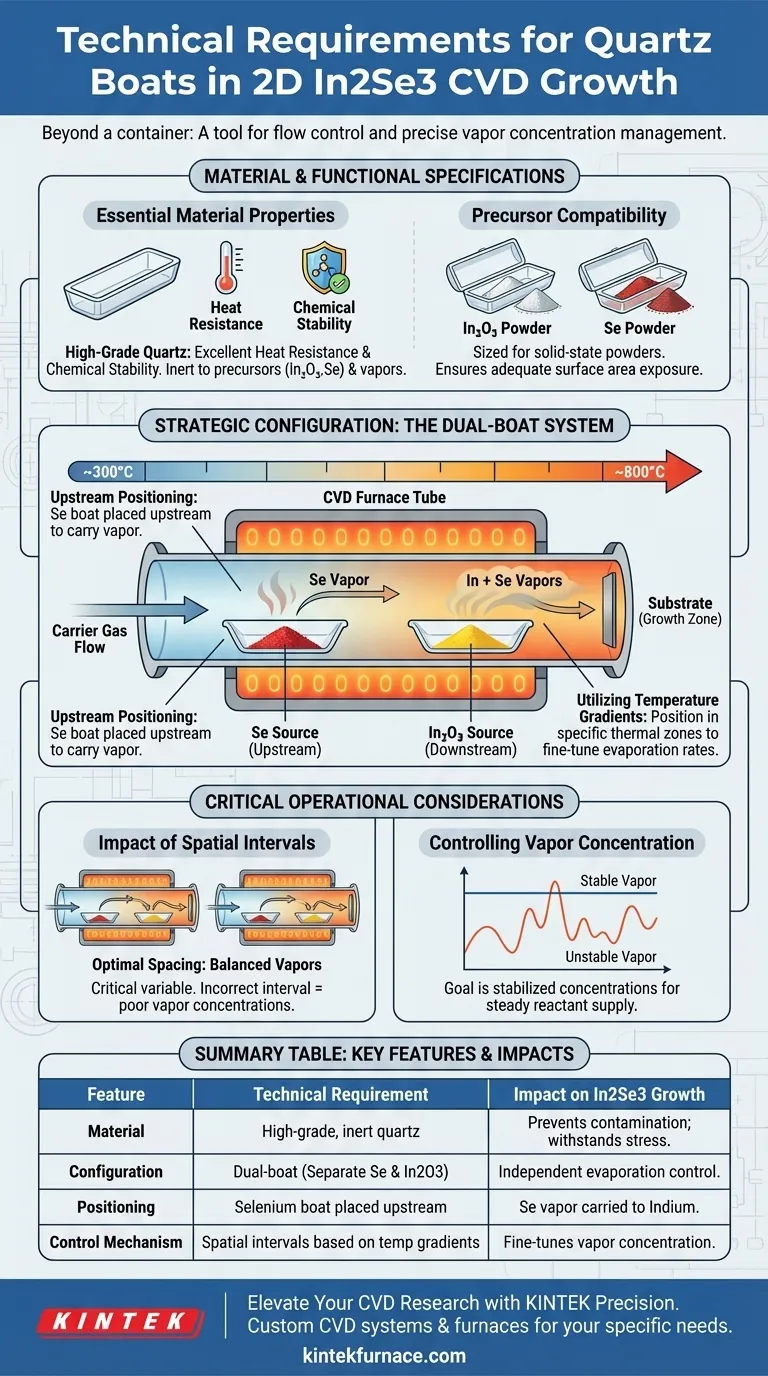
The technical requirements for a Quartz Boat in the CVD growth of 2D In2Se3 center on high-performance material properties and precise spatial configuration. Specifically, the vessel must possess exceptional heat resistance and chemical stability to safely contain Indium Oxide (In2O3) and Selenium (Se) powders without introducing contaminants during the high-temperature reaction.
In the context of 2D In2Se3 growth, the Quartz Boat is more than a passive container; it is a tool for flow control. By leveraging the boat's position within the furnace's temperature gradients, you effectively dictate the evaporation rates and vapor concentrations necessary for the reaction.

Material and Functional Specifications
Essential Material Properties
To facilitate the growth of In2Se3, the boat must be manufactured from high-grade quartz capable of withstanding significant thermal stress.
It must also demonstrate excellent chemical stability. This ensures the boat remains inert and does not react with the precursor powders or the resulting vapor.
Precursor Compatibility
The boats are specifically required to hold solid-state precursors in powder form.
For this process, the containers must be sized and shaped to accommodate Indium Oxide (In2O3) and Selenium (Se) powders, allowing for adequate surface area exposure during heating.
The Strategic Configuration of Boats
The Dual-Boat System
Successful CVD growth of this 2D material requires the use of two separate Quartz Boats.
Isolating the precursors allows for independent management of the Indium and Selenium sources, rather than mixing them in a single vessel.
Upstream Positioning
The relative position of the boats dictates the flow of reactants. The Quartz Boat containing the Selenium source must be positioned upstream.
This placement ensures that the Selenium vapor is carried downstream by the carrier gas to interact with the Indium source and the substrate effectively.
Utilizing Temperature Gradients
The physical location of the boats within the furnace tube is the primary mechanism for reaction control.
By placing the boats at specific intervals, you exploit the natural temperature gradients of the furnace. This precise spacing allows you to fine-tune the evaporation rates of the different precursors based on their specific vaporization temperatures.
Critical Operational Considerations
The Impact of Spatial Intervals
The distance between the two Quartz Boats is a critical variable, not a fixed constant.
If the interval is incorrect, the precursors may not reach their respective evaporation temperatures simultaneously or at the correct ratio. This misalignment leads to poor vapor concentrations and failed growth.
Controlling Vapor Concentration
The ultimate goal of the boat configuration is to stabilize vapor concentrations.
Using the boat's position to control evaporation rates ensures a steady supply of reactants, preventing issues where one precursor is exhausted before the growth cycle is complete.
Optimizing Your Experimental Setup
To ensure high-quality growth of 2D In2Se3, consider the following regarding your precursor containers:
- If your primary focus is Material Purity: Ensure your Quartz Boats are chemically inert and free of micro-cracks to prevent foreign element contamination during the heating phase.
- If your primary focus is Reaction Control: Meticulously measure the distance between the upstream Selenium boat and the downstream In2O3 boat to optimize their exposure to the furnace's temperature gradient.
Success in this CVD process relies not just on the quality of the quartz, but on the precision of its placement within the thermal zone.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Technical Requirement | Impact on In2Se3 Growth |
|---|---|---|
| Material | High-grade, chemically inert quartz | Prevents contamination; withstands high thermal stress. |
| Configuration | Dual-boat system (Separate Se and In2O3) | Enables independent control of precursor evaporation rates. |
| Positioning | Selenium boat placed upstream | Ensures Se vapor is carried downstream to react with Indium. |
| Control Mechanism | Spatial intervals based on temp gradients | Fine-tunes vapor concentration and ensures simultaneous evaporation. |
Elevate Your CVD Research with KINTEK Precision
High-quality 2D materials like In2Se3 demand precise thermal environments and reliable equipment. KINTEK provides expert R&D and manufacturing of high-performance CVD systems, Muffle, Tube, Rotary, and Vacuum furnaces, all of which are fully customizable to meet your specific experimental requirements.
Whether you need to optimize temperature gradients or ensure material purity, our team is ready to support your lab's unique needs.
Contact us today to find your custom lab furnace solution!
Visual Guide
References
- Dasun P. W. Guruge, Dmitri Golberg. Thermal Phase‐Modulation of Thickness‐Dependent CVD‐Grown 2D In<sub>2</sub>Se<sub>3</sub>. DOI: 10.1002/adfm.202514767
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Multi Heating Zones CVD Tube Furnace Machine for Chemical Vapor Deposition Equipment
- Custom Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment Machine
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is a U-shaped quartz reactor required for H2-TPR? Ensure Precision for Cu–Ce/HZSM-5 Analysis
- How are laboratory vacuum pumps utilized in 1T-TaS2 crystal preparation? Ensure Peak Sample Purity
- What is the key technological improvement in the circulating water vacuum pump? Discover the Self-Contained Closed-Loop System
- How does the circulating water multifunctional vacuum pump create a vacuum? Discover Its Oil-Free Mechanism
- How do B-type thermocouples contribute to temperature control in CaO-Al2O3-VOx slag processing? Achieve ±2 °C Precision
- What is the purpose of using an insulating layer in CCCM thermal conductivity tests? Ensuring 1D Heat Flow Accuracy
- Why is high-purity graphite paper typically lined on the inner walls of the mold before loading Ti-6Al-4V alloy powder?
- What is the function of the substrate heating system for WS2 thin films? Optimize Crystallinity and Adhesion



















