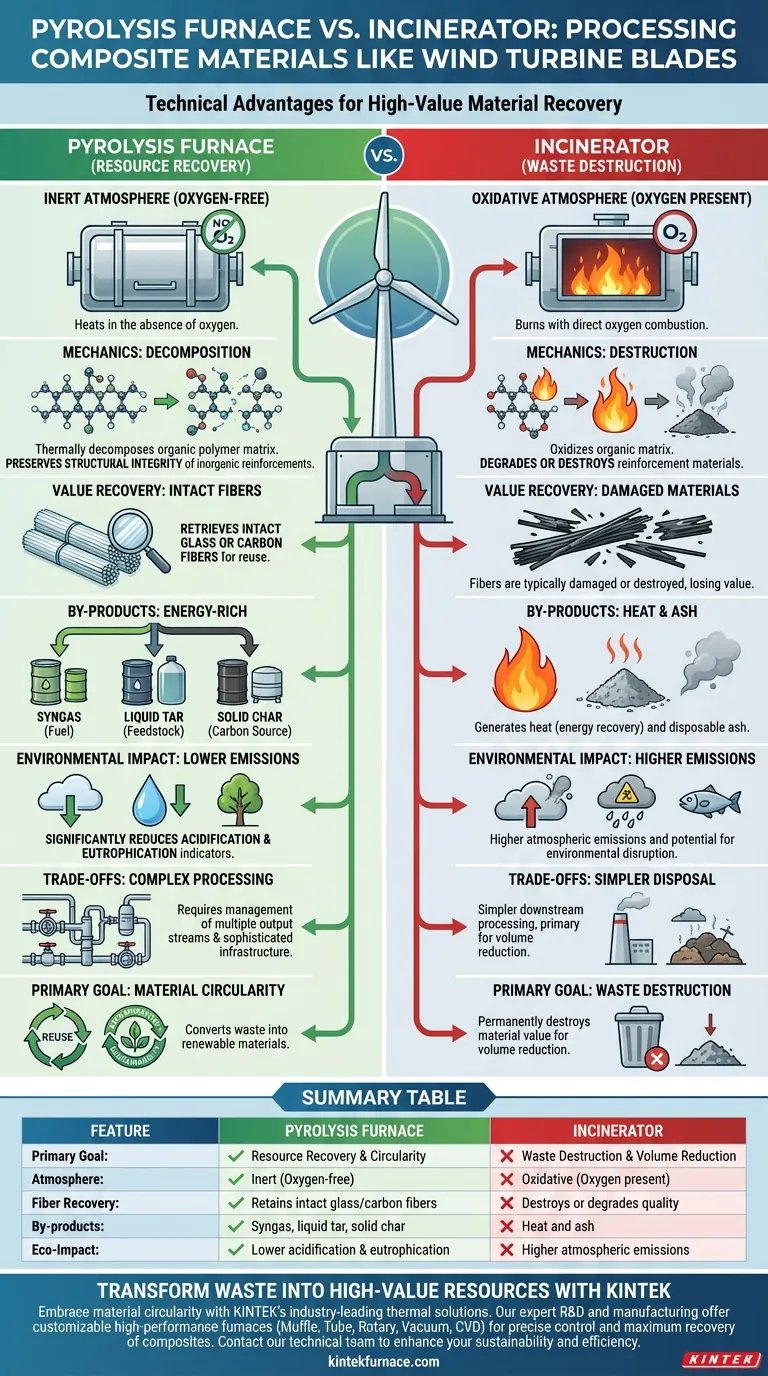
The primary technical advantage of a pyrolysis furnace is its ability to recover high-value materials rather than simply destroying them through combustion. Unlike incinerators, which burn waste in the presence of oxygen, a pyrolysis furnace heats organic components in an inert (oxygen-free) atmosphere. This process preserves the structural integrity of inorganic reinforcements, such as the glass or carbon fibers found in wind turbine blades, while converting the polymer matrix into usable energy by-products.
Core Takeaway While incineration is a volume-reduction method that destroys material to generate heat, pyrolysis is a resource-recovery method. It effectively decouples the organic polymer matrix from the inorganic fibers, allowing for the circular reuse of high-value composite materials while significantly reducing environmental impact indicators like acidification.
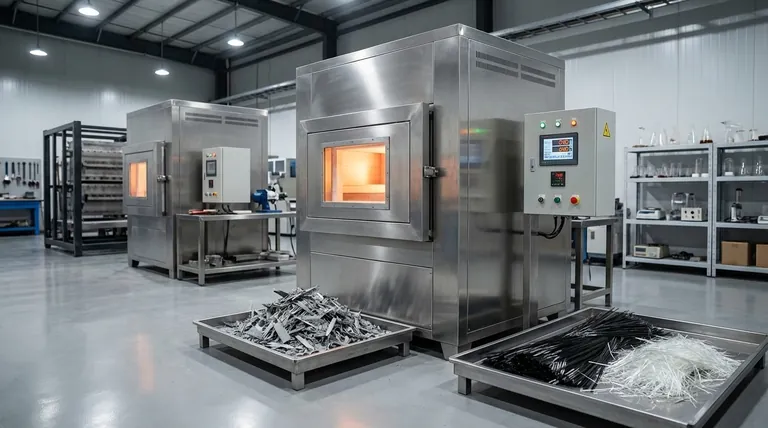

The Mechanics of Material Separation
Operating in an Inert Atmosphere
The fundamental difference lies in the processing environment. Incinerators rely on direct combustion, which requires oxygen and results in the oxidation of materials.
Pyrolysis furnaces operate in an inert atmosphere. By excluding oxygen, the system prevents combustion, forcing the organic polymer materials to decompose thermally rather than burn.
Decomposition vs. Destruction
In an incinerator, the goal is the destruction of the organic matrix to release heat. This often degrades any reinforcement materials present.
In pyrolysis, the organic components are broken down chemically. This decomposition creates a separation between the resin matrix and the structural fibers, facilitating the retrieval of the latter.
Value Recovery Capabilities
Retrieving Intact Inorganic Fibers
For composite materials like wind turbine blades, the ability to recover fibers is the most critical technical advantage.
Pyrolysis enables the retrieval of relatively intact inorganic fibers, specifically glass or carbon fibers. Because the process avoids the turbulence and oxidative stress of direct combustion, these fibers retain much of their quality and can be reused in new manufacturing applications.
Generation of Energy-Rich By-products
Instead of releasing energy immediately as heat (as incineration does), pyrolysis converts the organic polymer mass into three distinct, valuable streams.
The decomposition process yields syngas, liquid tar, and solid char. These by-products are energy-rich and can be captured and utilized as fuel sources or chemical feedstocks for other industrial processes.
Environmental Impact Profile
Reduction in Acidification
Pyrolysis offers a distinct advantage regarding atmospheric emissions.
Compared to incineration, the pyrolysis process significantly reduces acidification indicators. This suggests a lower release of acidic gases (such as sulfur dioxide or nitrogen oxides) that contribute to acid rain.
Mitigation of Eutrophication
The process also performs better regarding water and soil ecosystem impacts.
The data indicates a significant reduction in eutrophication potential compared to incineration. This means the process releases fewer excess nutrients that could disrupt aquatic ecosystems, making it a more environmentally sustainable option for processing large-scale composites.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Management of Multiple Output Streams
While incineration results in simple ash and heat, pyrolysis produces a complex set of outputs.
Operators must be prepared to handle and refine syngas, liquid tar, and solid char. This requires more sophisticated downstream processing infrastructure compared to the straightforward flue gas treatment and ash disposal of an incinerator.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To select the appropriate technology for your project, weigh your primary objectives:
- If your primary focus is Material Circularity: Choose pyrolysis to recover intact glass or carbon fibers for reuse in new composite products.
- If your primary focus is Environmental Compliance: Choose pyrolysis to minimize specific impact indicators like acidification and eutrophication.
- If your primary focus is Simple Disposal: Recognize that incineration offers volume reduction but permanently destroys the material value of the composites.
Pyrolysis transforms end-of-life composites from waste into a source of renewable materials and energy chemicals.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Pyrolysis Furnace | Incinerator |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Goal | Resource Recovery & Circularity | Waste Destruction & Volume Reduction |
| Atmosphere | Inert (Oxygen-free) | Oxidative (Oxygen present) |
| Fiber Recovery | Retains intact glass/carbon fibers | Destroys or degrades fiber quality |
| By-products | Syngas, liquid tar, and solid char | Heat and ash |
| Eco-Impact | Lower acidification & eutrophication | Higher atmospheric emissions |
Transform Waste into High-Value Resources with KINTEK
Ready to move beyond simple disposal and embrace material circularity? KINTEK provides industry-leading thermal solutions designed for the complex demands of composite recycling. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, we offer high-performance Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems—all fully customizable to your specific processing needs.
Whether you are recovering carbon fibers from wind turbine blades or processing advanced lab materials, our high-temp furnaces ensure precise control and maximum recovery. Contact our technical team today to discover how our custom furnace technology can enhance your sustainability and efficiency.
Visual Guide
References
- Guillaume Zante, Andrew P. Abbott. A toolbox for improved recycling of critical metals and materials in low-carbon technologies. DOI: 10.1039/d3su00390f
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- Why is 800 °C Required for Ln-MoP@C Phosphorization? Unlock Superior Catalyst Engineering
- What role does a reactive atmosphere like nitrogen play in PFS? Enhance Titanium Dioxide Surface Treatment
- What is the use of dental ceramic? Achieve Lifelike, Durable, and Biocompatible Restorations
- What role does high-temperature calcination play in the purification of volcanic ash? Achieve Ultra-Pure Silica Results
- What role does an infrared image furnace play in the Floating Zone Method? Mastering Nb-doped beta-Ga2O3 Crystal Growth
- What are the specific functions of a flowing 5% H2/Ar gas mixture? Master Thermal Reduction of Nanoparticles
- What is the primary function of glass matrices in HLW vitrification? Achieve Safe Radioactive Waste Immobilization
- How does the applicability of materials change with advancements in cracking technology? Unlock New Material Processing Possibilities



















