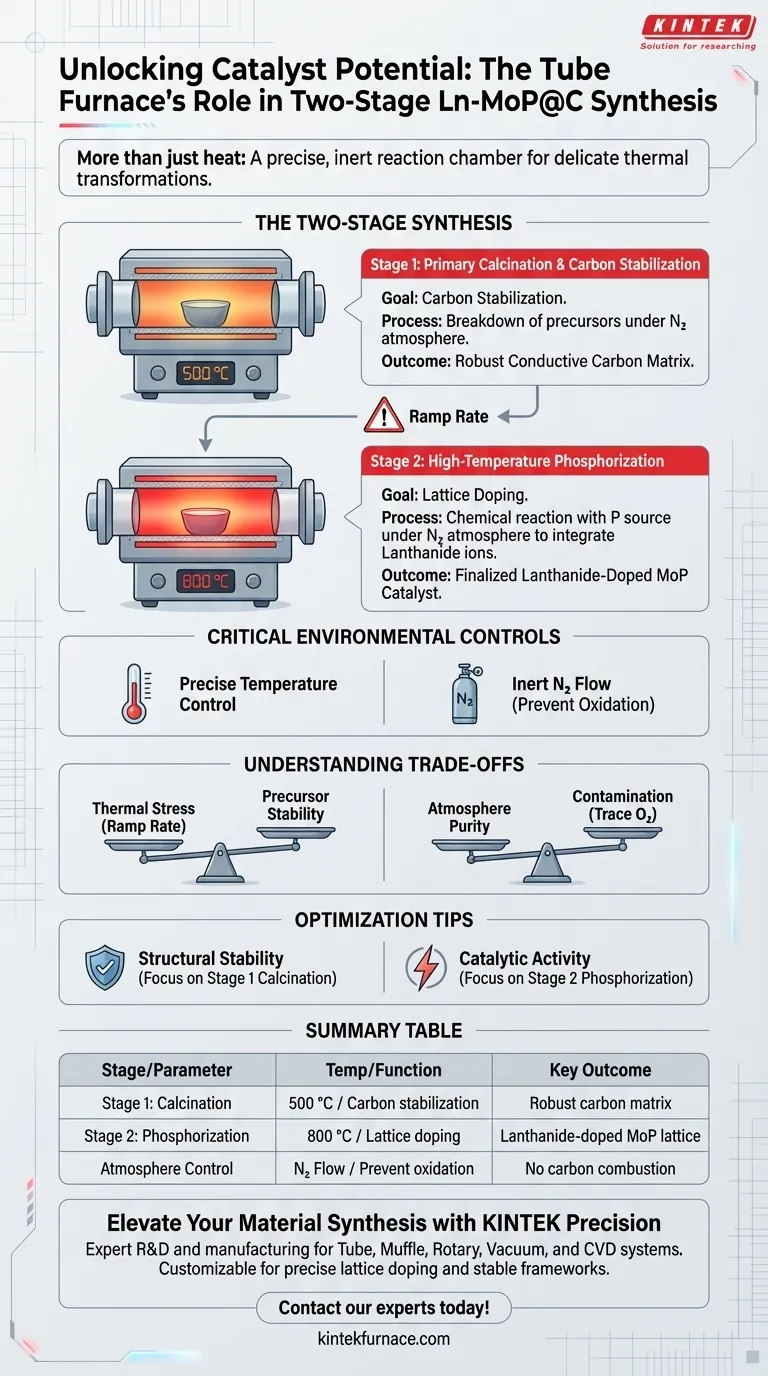
A high-performance tube furnace serves as the precise reaction chamber required to execute the delicate, two-step thermal transformation of Ln-MoP@C catalyst precursors. It primarily functions to facilitate a structural calcination at 500 °C to stabilize carbon frameworks, followed by a high-temperature phosphorization at 800 °C to integrate lanthanide ions into the molybdenum phosphide lattice.
The tube furnace provides more than just heat; it maintains the strict inert nitrogen atmosphere essential for converting organic-inorganic assemblies into stable, lanthanide-doped catalysts without uncontrolled oxidation.

The Mechanics of the Two-Stage Synthesis
The synthesis of Ln-MoP@C (Lanthanide-doped Molybdenum Phosphide encapsulated in Carbon) relies on distinct thermal environments. The tube furnace allows for the sequential execution of these stages within a controlled environment.
Stage 1: Primary Calcination and Carbon Stabilization
The first function of the furnace is to perform primary calcination at 500 °C. This stage targets the self-assembled structure composed of dopamine and molybdate precursors.
Under a protective nitrogen atmosphere, the furnace provides the thermal energy necessary to break down this assembly. The result is the conversion of the raw precursor into a carbon-stabilized, lanthanide-decorated molybdenum hybrid. This step is crucial for establishing the conductive carbon matrix that will support the catalyst.
Stage 2: High-Temperature Phosphorization
The second, more aggressive function involves ramping the temperature to 800 °C for phosphorization. This high-heat treatment is required to drive the chemical reaction between the phosphorus source and the molybdenum hybrid.
During this phase, the furnace facilitates the induction of lanthanide ions into the MoP (Molybdenum Phosphide) lattice. This doping process completes the structural transformation, finalizing the catalyst's electronic structure and active sites.
Critical Environmental Controls
Beyond temperature, the tube furnace plays a vital role in atmospheric regulation. The success of the synthesis depends on isolating the reactants from ambient air.
Atmosphere Maintenance
The furnace must maintain a continuous flow of nitrogen ($N_2$) gas throughout both heating stages. This inert environment prevents the combustion of the carbon coating derived from dopamine.
Reaction Precision
By isolating the sample, the furnace ensures that the chemical transformation is purely driven by thermal decomposition and solid-state reactions. This precision allows for the specific formation of phosphides rather than unwanted oxides.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While the tube furnace is essential for this synthesis, operating at these parameters introduces specific challenges that must be managed.
Thermal Stress and Precursor Stability
The transition from 500 °C to 800 °C represents a significant thermal leap. If the ramp rate between the calcination and phosphorization stages is uncontrolled, the carbon framework established in the first stage may degrade before the phosphide lattice fully forms.
Atmosphere Purity vs. Contamination
The effectiveness of the nitrogen atmosphere is absolute; even minor leaks can be catastrophic. At 800 °C, trace oxygen will rapidly destroy the carbon shell and oxidize the molybdenum, resulting in an inactive material rather than the desired Ln-MoP@C catalyst.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To optimize the synthesis of Ln-MoP@C catalysts, you must tailor the furnace parameters to your specific material objectives.
- If your primary focus is Structural Stability: Prioritize precise control during the 500 °C calcination stage to ensure the dopamine-derived carbon shell is fully carbonized and robust before higher heating.
- If your primary focus is Catalytic Activity: Ensure the 800 °C phosphorization stage is held long enough to fully integrate the lanthanide ions into the lattice, as this doping drives the final electrochemical performance.
Mastering these two thermal stages allows you to precisely engineer the electronic and structural properties of your final catalyst.
Summary Table:
| Synthesis Stage | Temperature | Primary Function | Key Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|
| Stage 1: Calcination | 500 °C | Carbon stabilization & breakdown of precursors | Robust conductive carbon matrix |
| Stage 2: Phosphorization | 800 °C | Chemical reaction with phosphorus source | Lanthanide-doped MoP lattice |
| Atmosphere Control | N/A | Inert Nitrogen ($N_2$) flow | Prevention of oxidation & carbon combustion |
Elevate Your Material Synthesis with KINTEK Precision
Precision in temperature and atmosphere is the difference between a high-performance catalyst and an inactive oxide. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers high-performance Tube, Muffle, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems designed to meet the rigorous demands of two-stage thermal synthesis. Our laboratory high-temperature furnaces are fully customizable to your unique research needs, ensuring stable carbon frameworks and precise lattice doping.
Ready to optimize your thermal processing? Contact our experts today to find the perfect furnace solution!
Visual Guide
References
- Jiancheng Li, Bin Liu. Balancing H <sup>*</sup> Adsorption/Desorption by Localized 4f Orbital Electrons of Lanthanide Dopants in Carbon‐Encapsulated MoP for Boosted Hydrogen Evolution. DOI: 10.1002/advs.202417583
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of resistance heating tube furnaces? Achieve Precise, Cost-Effective Thermal Processing
- How does multi-zone heating benefit the 70mm tube furnace? Unlock Precise Thermal Control for Advanced Materials
- What role does a vacuum tube furnace play in the production of rice husk biochar? Engineering High-Performance Carbon
- What are the technical advantages of using a high-temperature tube furnace? Precision Thermal Oxidation Explained
- How is a laboratory tube furnace used in materials science research? Unlock Precision in Material Synthesis and Heat Treatment
- What core task does a tubular vacuum sintering furnace perform? Optimizing Confined Carbon Chain Synthesis
- How do laboratory-scale Tube Furnaces facilitate coal gasification? Precise Simulation for Industrial Success
- How do heat treatment processes influence the configuration of a vertical tube furnace? Optimize for Quenching, Annealing, and More



















