The primary advantages of resistance heating tube furnaces are their exceptional precision, operational simplicity, and cost-effectiveness. These furnaces provide a highly uniform and controllable heating environment within a contained atmosphere, making them a foundational and reliable tool for a wide range of material processing applications and laboratory experiments.
The true value of a resistance tube furnace is its ability to create a highly controlled and uniform thermal environment. While its low cost and ease of use are significant benefits, this precision is what enables reproducible, high-quality results in sensitive applications from academic research to industrial production.
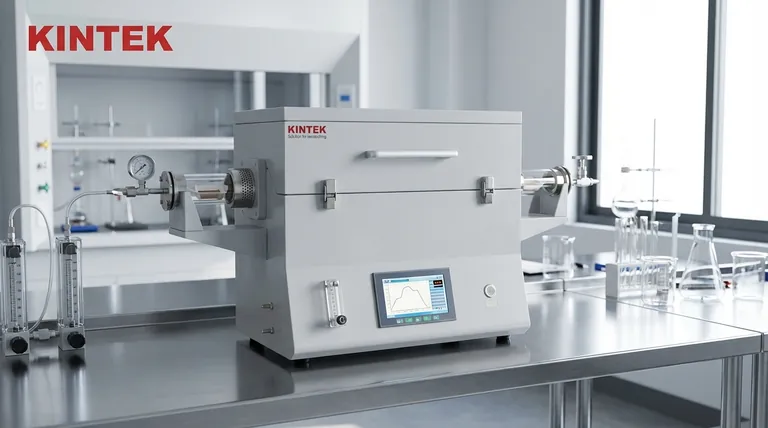

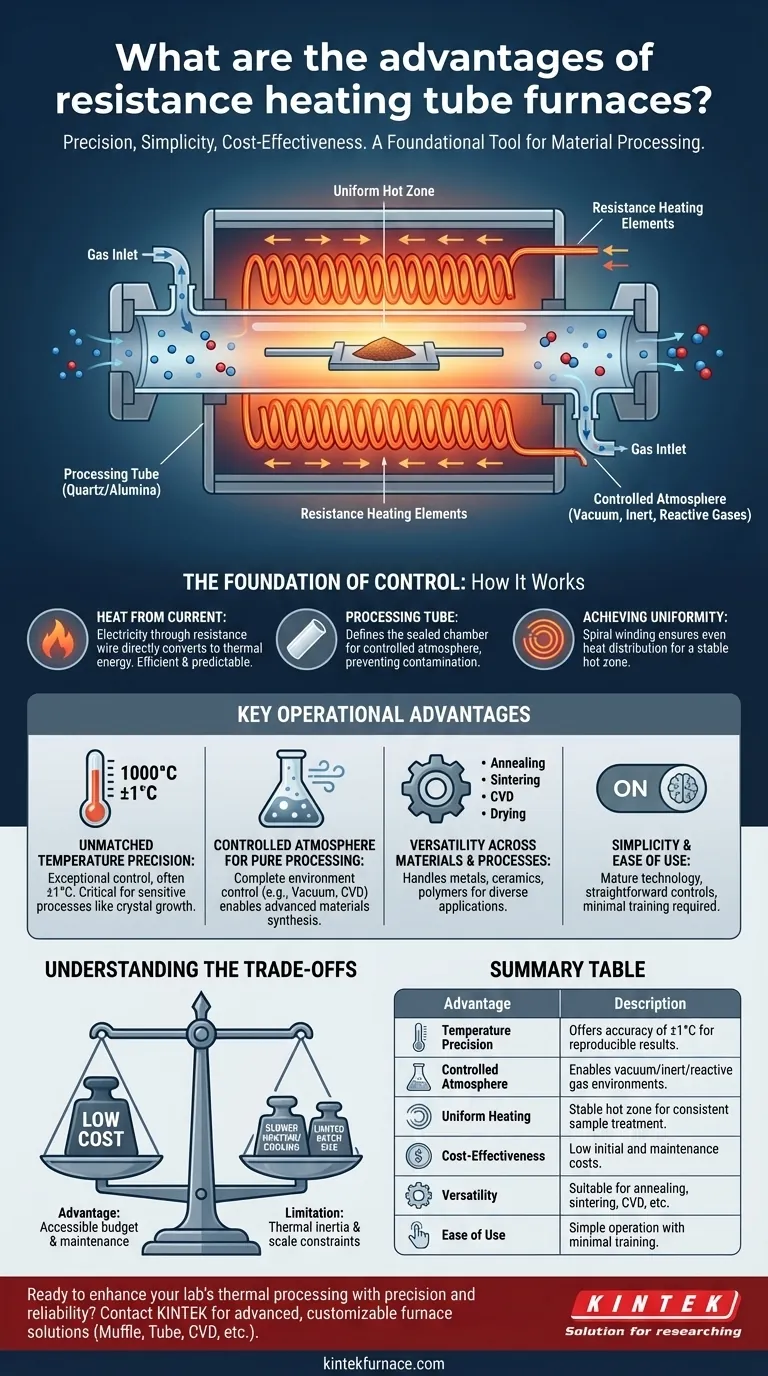
The Foundation of Control: How Resistance Heating Works
Understanding the core advantages of a resistance tube furnace begins with its simple yet effective design. Its performance is a direct result of how it generates and contains heat.
The Core Principle: Heat from Current
A resistance furnace operates on a straightforward principle: electricity is passed through a resistive heating element, typically a specialized alloy wire. As the current encounters resistance, it directly converts electrical energy into thermal energy, or heat. This method is highly efficient and predictable.
The heating elements are most often wound in a spiral pattern around the exterior of a ceramic furnace tube. This simple construction is key to the furnace's reliability and low manufacturing cost.
The Role of the Processing Tube
The tube itself—often made of quartz for lower temperatures or alumina for high-temperature applications—is more than just a sample holder. It defines the processing chamber, allowing you to maintain a specific, controlled atmosphere around your sample.
This containment is critical for preventing contamination, such as oxidation, by enabling work under a vacuum or in the presence of inert or reactive gases.
Achieving Temperature Uniformity
The spiral winding of the heating elements around the tube is not accidental. This design ensures that heat is distributed evenly along a specific length of the tube, creating a stable and uniform "hot zone."
This uniformity is essential for processes where every part of the sample must experience the exact same temperature, ensuring consistent material properties.
Key Operational Advantages
The design of a resistance tube furnace translates into several practical advantages for researchers and engineers who require high-fidelity thermal processing.
Unmatched Temperature Precision
Modern resistance tube furnaces offer exceptional temperature control, often with an accuracy of ±1°C. This precision is achieved by carefully regulating the electrical current supplied to the heating elements.
Such tight control is non-negotiable for sensitive processes like crystal growth, semiconductor annealing, or studying material phase transitions, where minor temperature deviations can ruin an experiment.
Controlled Atmosphere for Pure Processing
The sealed tube design is arguably one of its most powerful features. It allows for complete control over the gaseous environment.
This capability is vital for synthesizing advanced nanomaterials, processing air-sensitive compounds, or running applications like Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD), where specific precursor gases must be introduced without ambient contamination.
Versatility Across Materials and Processes
These furnaces are not limited to a single task. They are used across countless applications, including annealing, sintering, drying, and material synthesis.
Their ability to handle a wide range of materials—from metals and ceramics to polymers and advanced composites—makes them a versatile workhorse in almost any materials science lab.
Simplicity and Ease of Use
The technology behind resistance heating is mature and well-understood. This results in furnaces that are remarkably easy to operate, often requiring minimal training.
Their straightforward controls and reliable performance reduce the potential for user error and lower the operational overhead for a lab or production facility.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No technology is without its limitations. Being an effective advisor means acknowledging the trade-offs to ensure the tool is right for the job.
The Advantage of Low Cost
The simple structure, based on common materials and established manufacturing techniques, makes resistance tube furnaces highly cost-effective. Their initial purchase price and ongoing maintenance costs are typically lower than more complex heating technologies. This accessibility puts high-temperature processing within reach of nearly any lab budget.
The Limitation: Heating Rate and Scale
While some models boast "rapid" heating, resistance furnaces are generally slower to heat up and cool down compared to alternatives like induction or microwave furnaces. This thermal inertia can be a drawback in high-throughput environments where cycle time is critical.
Furthermore, the diameter of the tube inherently limits the size of a single sample, which can be a constraint for large-scale industrial batch processing.
Energy Consumption Considerations
Resistance furnaces are very efficient at maintaining a set temperature due to excellent insulation. However, reaching very high temperatures (above 1500°C) can be an energy-intensive process. The efficiency lies in the direct conversion of electricity to heat and its containment, but the total power draw must be considered for high-volume or extreme-temperature applications.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
To determine if a resistance tube furnace is the right investment, align its core strengths with your primary objectives.
- If your primary focus is reproducible R&D and material synthesis: The precise temperature and atmosphere control make it an ideal and cost-effective choice for achieving high-quality, reliable results.
- If your primary focus is high-throughput industrial production: Acknowledge that while scalable, the batch size is limited, and cycle times may be slower than alternative technologies.
- If your primary focus is budget and operational simplicity: The low capital cost and straightforward operation of a resistance tube furnace are unmatched for general-purpose thermal processing.
Ultimately, a resistance heating tube furnace empowers you to execute thermal processing with a high degree of confidence and control.
Summary Table:
| Advantage | Description |
|---|---|
| Temperature Precision | Offers accuracy of ±1°C for reliable, reproducible results in sensitive applications. |
| Controlled Atmosphere | Enables work under vacuum or with inert/reactive gases to prevent contamination. |
| Uniform Heating | Spiral heating elements create a stable hot zone for consistent sample treatment. |
| Cost-Effectiveness | Low initial and maintenance costs make it accessible for various budgets. |
| Versatility | Suitable for annealing, sintering, CVD, and more across diverse materials. |
| Ease of Use | Simple operation with minimal training required, reducing user error. |
Ready to enhance your lab's thermal processing with precision and reliability? Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet unique experimental requirements. Contact us today to discuss how our tailored solutions can optimize your material processing and drive your research forward!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- How is a high-temperature tube furnace utilized in the synthesis of MoO2/MWCNTs nanocomposites? Precision Guide
- What is an example of a material prepared using a tube furnace? Master Precise Material Synthesis
- What safety and reliability features are incorporated into a vertical tube furnace? Ensuring Safe, Consistent High-Temp Processing
- What recent improvements have been made to lab tube furnaces? Unlock Precision, Automation & Safety
- What safety measures are essential when operating a lab tube furnace? A Guide to Preventing Accidents



















