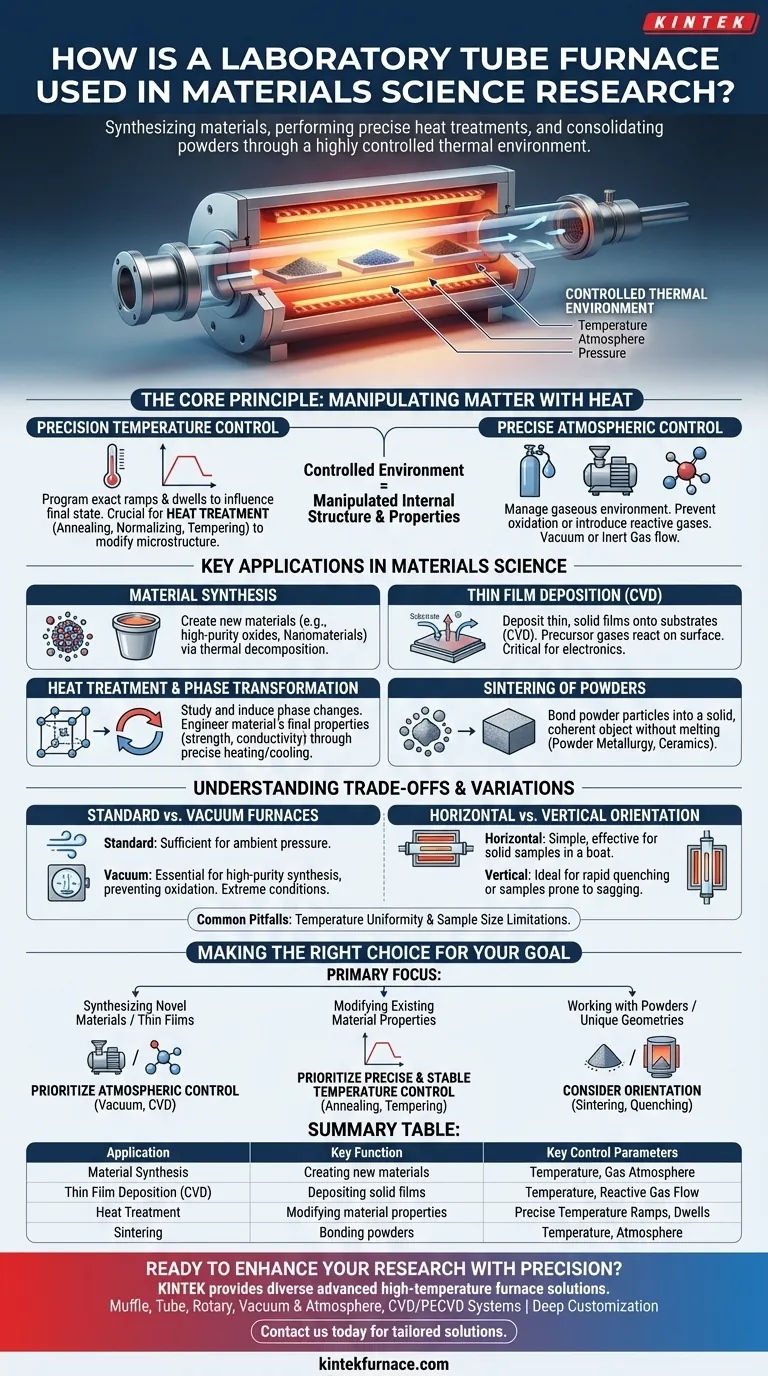
In materials science, a laboratory tube furnace is a fundamental tool used for synthesizing new materials, performing precise heat treatments, and consolidating powders into solids. Its core function is to provide a highly controlled thermal environment, enabling researchers to systematically create, test, and modify materials by manipulating temperature, atmosphere, and pressure.
A tube furnace's true value is not just its ability to generate high temperatures, but its capacity for precise environmental control. This control is the key that allows scientists to manipulate a material's internal structure and, consequently, its fundamental properties.
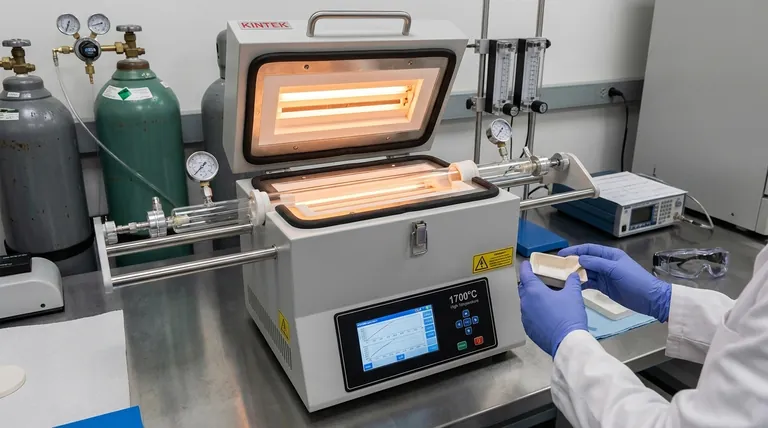

The Core Principle: Manipulating Matter with Heat
A tube furnace is more than just an oven. It is a precision instrument designed to create a specific, isolated environment where thermal energy can be applied with accuracy. This capability is built on two primary functions.
Precision Temperature Control
The ability to program and hold exact temperatures is critical for many material processes. Ramps, dwells, and controlled cooling rates are not just procedural steps; they directly influence the final state of the material.
This level of control is essential for heat treatment processes like annealing (softening), normalizing (refining grain structure), and tempering (increasing toughness). Each process requires hitting a specific temperature window to trigger desired changes in the material's crystalline structure, or microstructure.
Precise Atmospheric Control
Equally important is control over the gaseous environment surrounding the sample. Many materials will react with oxygen at high temperatures, leading to unwanted oxidation and contamination.
Tube furnaces solve this by allowing work to be done under a vacuum or a continuous flow of a specific gas. An inert gas like argon prevents reactions, while a reactive gas can be intentionally introduced as part of a chemical process.
Key Applications in Materials Science
This combination of temperature and atmospheric control makes the tube furnace indispensable for a wide range of research applications.
Material Synthesis
Tube furnaces are used to create entirely new materials. This can involve the thermal decomposition of precursor compounds to form high-purity oxides, nitrides, and carbides.
They are also foundational for synthesizing advanced materials like nanomaterials and composite materials, where the growth and formation process is highly sensitive to thermal conditions.
Thin Film Deposition (CVD)
Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) is a cornerstone technique where a tube furnace is used to deposit a thin, solid film onto a substrate.
In this process, precursor gases flow through the heated tube, react, and decompose on the sample surface, building up a high-quality film one layer at a time. This is critical in electronics and optics.
Heat Treatment and Phase Transformation
Researchers use tube furnaces to study and induce phase transformations, which are changes in a material's physical form or crystal structure.
By carefully heating and cooling samples, scientists can map out these transformations and understand how to engineer a material's final properties, such as its strength, ductility, or electrical conductivity.
Sintering of Powders
In powder metallurgy and ceramics, a tube furnace is used for sintering. This process uses heat to bond loose particles of powder together, densifying them into a solid, coherent object without melting them completely.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Variations
Not all tube furnaces are the same. The specific research goal dictates which type of furnace is appropriate, and each comes with its own set of considerations.
Standard vs. Vacuum Furnaces
A standard tube furnace is sufficient for processes that can be run in air or under a flowing gas at ambient pressure.
A vacuum tube furnace is essential when even trace amounts of atmospheric gases would compromise the experiment. This is critical for high-purity material synthesis, preventing oxidation of sensitive metals, and studying material behavior under extreme conditions.
Horizontal vs. Vertical Orientation
The vast majority of tube furnaces are horizontal. This is a simple, effective design for most applications involving solid samples placed in a boat.
Vertical furnaces are chosen for specific needs. They are ideal for processes where a sample needs to be dropped into the hot zone for rapid heating (quenching) or when dealing with samples that might sag or deform under gravity at high temperatures.
Common Pitfalls and Limitations
While powerful, these instruments have limitations. Achieving perfect temperature uniformity across the entire length of the tube can be challenging. Furthermore, the physical size of the tube inherently limits the size of the sample that can be processed.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right furnace requires a clear understanding of your experimental objective.
- If your primary focus is synthesizing novel materials or thin films: You need a furnace with excellent atmospheric control, making a system capable of vacuum or controlled gas flow (for CVD) your top priority.
- If your primary focus is modifying the properties of an existing material: Prioritize a furnace with highly programmable and stable temperature control to execute precise heat treatment schedules like annealing or tempering.
- If your primary focus is working with powders or unique sample geometries: Consider the furnace's orientation and capabilities for processes like sintering or quenching, where a vertical setup may be necessary.
Ultimately, the laboratory tube furnace is a foundational tool that empowers researchers to precisely control the conditions under which matter is transformed.
Summary Table:
| Application | Key Function | Key Control Parameters |
|---|---|---|
| Material Synthesis | Creating new materials like nanomaterials | Temperature, Gas Atmosphere |
| Thin Film Deposition (CVD) | Depositing solid films on substrates | Temperature, Reactive Gas Flow |
| Heat Treatment | Modifying material properties via annealing, tempering | Precise Temperature Ramps, Dwells |
| Sintering | Bonding powders into solids without melting | Temperature, Atmosphere |
Ready to enhance your materials science research with precision? Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet unique experimental requirements. Contact us today to discuss how our tailored solutions can optimize your material synthesis, heat treatment, and more!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
- Multi Zone Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is a tube furnace utilized for the heat treatment of S/C composite cathode materials? Optimize Battery Stability
- What recent improvements have been made to lab tube furnaces? Unlock Precision, Automation & Safety
- What are the key operational considerations when using a lab tube furnace? Master Temperature, Atmosphere & Safety
- What is an example of a material prepared using a tube furnace? Master Precise Material Synthesis
- How is a high-temperature tube furnace utilized in the synthesis of MoO2/MWCNTs nanocomposites? Precision Guide



















