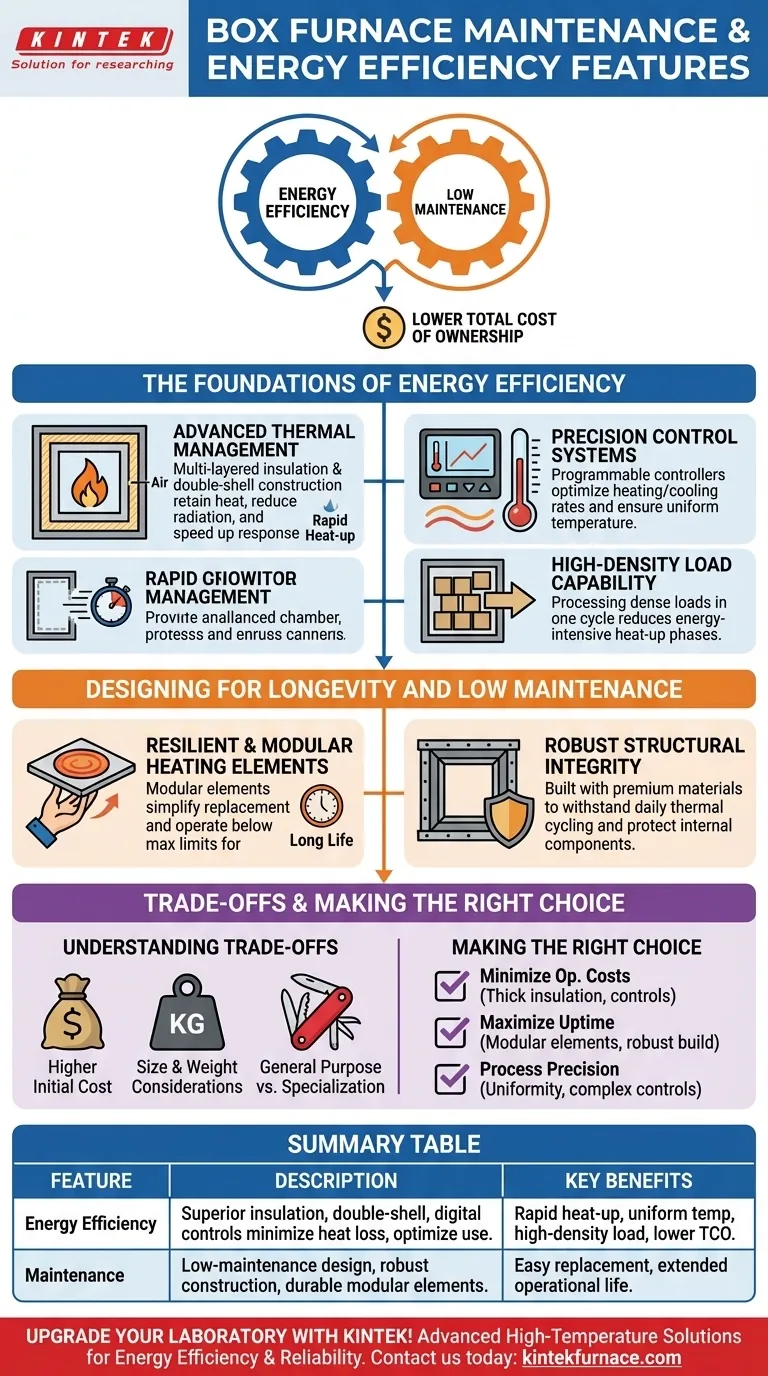
At their core, box furnaces achieve high energy efficiency through a combination of superior insulation, double-shell construction, and precise digital controls that minimize heat loss and optimize energy use. Their low-maintenance profile is a direct result of robust construction and the use of durable, modular heating elements designed for extended operational life.
The key takeaway is that the efficiency and maintenance features of a box furnace are not isolated add-ons. They are integrated design principles that work together to lower the total cost of ownership by maximizing thermal performance while ensuring long-term reliability.

The Foundations of Energy Efficiency
The primary goal of any furnace is to get hot and stay hot with minimal energy waste. Box furnaces accomplish this through several key design features that collectively manage thermal energy.
Advanced Thermal Management
A box furnace’s most significant efficiency feature is its ability to retain heat. This is achieved through a multi-layered insulation package designed for maximum performance.
This is coupled with a double-shell construction. An air gap between the inner and outer furnace walls drastically reduces the amount of heat that radiates to the external surface, keeping the energy focused on the workload and making the unit safer to operate.
The result of this superior thermal containment is a rapid heat-up time and quick system response, minimizing the energy wasted while waiting for the furnace to reach its target temperature.
Precision Control Systems
Modern box furnaces utilize fully programmable temperature controllers. This allows you to precisely define the heating rates, soak times, and cooling rates for a specific process.
By tailoring the energy input exactly to the needs of the load, you eliminate the significant waste associated with overshooting the target temperature or holding it for longer than necessary.
This level of control also ensures highly uniform temperature throughout the chamber, which leads to process repeatability and prevents energy waste from uneven heating.
High-Density Load Capability
An often-overlooked aspect of efficiency is throughput. The robust design of a box furnace allows it to handle dense loads of material.
Processing more material in a single cycle is inherently more energy-efficient than running multiple, smaller cycles, as it reduces the total number of energy-intensive heat-up and cool-down phases.
Designing for Longevity and Low Maintenance
A furnace that is frequently down for repairs is neither efficient nor cost-effective. Box furnaces are engineered with reliability and ease of service as primary considerations.
Resilient and Modular Heating Elements
Many box furnaces feature modular plate heating elements. The modular design simplifies maintenance, as a single failed element can be replaced without disturbing the entire heating system.
These elements are also known for their longevity. They are designed to operate well below their maximum watt-loading limits, which significantly reduces stress and drastically lowers the risk of premature failure.
Robust Structural Integrity
The phrase "extra sturdy construction" points to a core design philosophy. Box furnaces are built with premium components and heavy-gauge materials to withstand the intense thermal cycling of daily operation.
This robust build quality ensures a long service life, minimizes downtime, and protects the internal components, such as insulation and wiring, from mechanical stress and environmental factors.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No design is without its compromises. Understanding them is critical for making an informed decision.
Higher Initial Cost
The use of premium components, advanced insulation, and heavy-duty construction means that a high-quality box furnace often carries a higher upfront purchase price than lighter-duty alternatives. This investment is justified by a lower total cost of ownership through energy savings and reduced maintenance.
Size and Weight Considerations
The same robust construction and thick insulation that make a box furnace efficient and durable also make it larger and heavier. This can be a factor in facilities with limited floor space or load-bearing capacity.
General Purpose vs. Specialization
A box furnace is an excellent general-purpose tool for a wide range of heat-treating and laboratory applications, such as the pyrolysis of waste materials. However, for highly specialized processes like vacuum brazing or processing in a controlled inert atmosphere, a dedicated specialty furnace may be more efficient.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the right furnace depends on balancing your operational priorities with your budget.
- If your primary focus is minimizing operational costs: Look for models with the thickest insulation packages and the most sophisticated programmable controls to maximize long-term energy savings.
- If your primary focus is maximizing uptime and reliability: Prioritize furnaces that explicitly feature modular heating elements and have a documented history of robust, heavy-duty construction.
- If your primary focus is process precision: Ensure the furnace specifications guarantee high temperature uniformity (+/- °C) and the programmable controls meet the complexity of your process cycles.
Ultimately, understanding these core design principles empowers you to select a box furnace that serves not just as a tool, but as a reliable and cost-effective long-term asset.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Energy Efficiency | Achieved through superior insulation, double-shell construction, and precise digital controls to minimize heat loss and optimize energy use. |
| Maintenance | Low-maintenance design with robust construction, durable modular heating elements for easy replacement and extended operational life. |
| Key Benefits | Rapid heat-up, uniform temperature, high-density load capability, and reduced total cost of ownership. |
Upgrade your laboratory with KINTEK's advanced high-temperature furnace solutions! Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we provide diverse laboratories with reliable box furnaces, Muffle Furnaces, Tube Furnaces, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems. Our strong deep customization capability ensures we precisely meet your unique experimental needs, delivering energy efficiency, low maintenance, and long-term cost savings. Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can enhance your operations and reduce your total cost of ownership!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Quartz Tube Furnace RTP Heating Tubular Furnace
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What role does a high-temperature box resistance furnace play in sintering? Mastering Electrolyte Tube Densification
- Why is calcination essential for NaFePO4 phase formation? Engineering High-Performance Sodium Iron Phosphate
- Why is immediate water-quenching required after thermal simulation? Preserve (CoCrNi)94Al3Ti3 Alloy Microstructure
- What is the significance of the thermal environment in calcination? Achieve Pure Ceramic Phases with KINTEK
- How is a laboratory muffle furnace utilized during the debinding stage of HAp green bodies? Precision Thermal Control



















