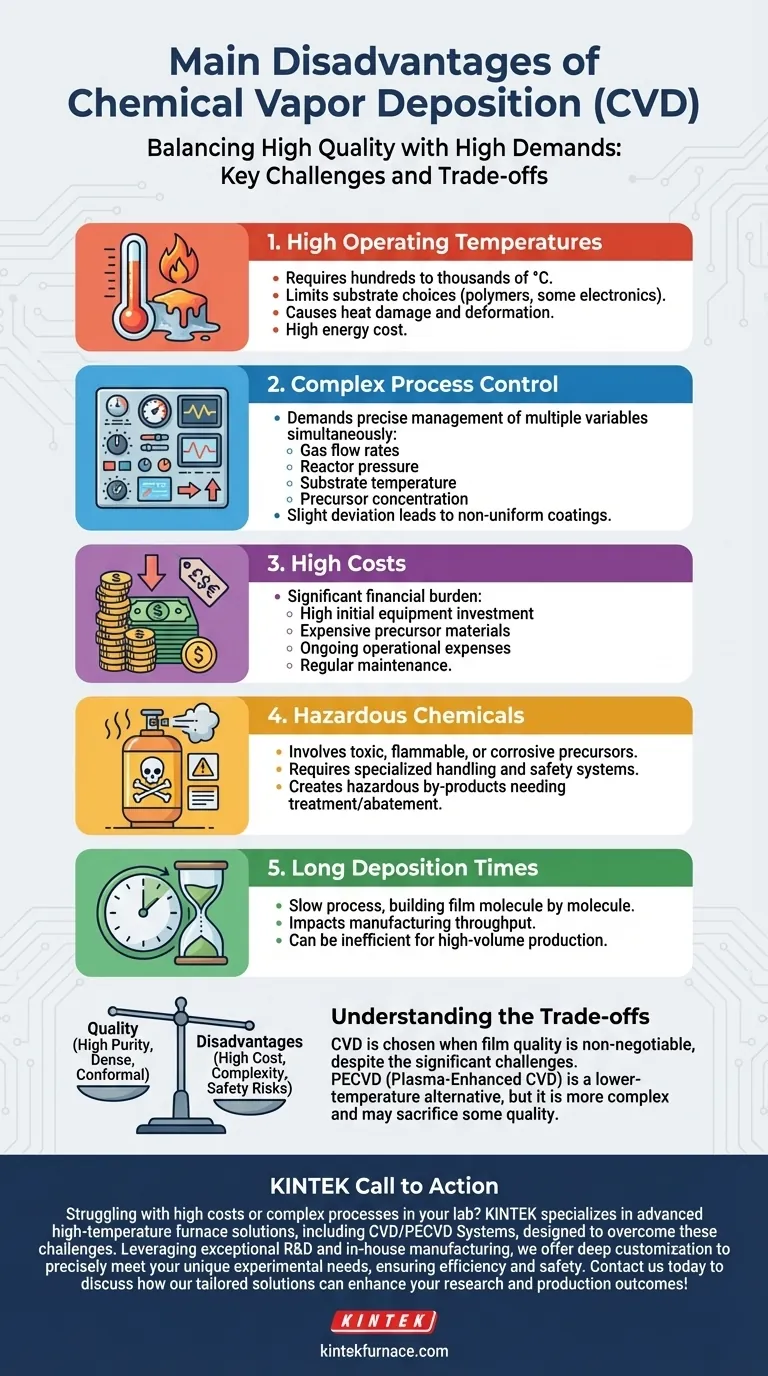
In short, the primary disadvantages of Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) are its high operational temperature, significant equipment and material costs, complex process control requirements, and the use of hazardous chemicals. These factors combine to make CVD a powerful but demanding technique that is not suitable for all applications, particularly those involving temperature-sensitive materials or limited budgets.
While Chemical Vapor Deposition is renowned for producing exceptionally high-quality, dense thin films, its fundamental reliance on high-energy chemical reactions creates significant trade-offs. The core challenge of CVD lies in managing its operational complexity, safety risks, and substantial costs, which often limit its practical application.

The Operational & Process Challenges
The theoretical elegance of CVD—transforming gas into a perfect solid layer—belies its practical complexity. Executing the process successfully requires overcoming significant operational hurdles.
High Operating Temperatures
The most frequently cited disadvantage is the high temperature required to drive the chemical reactions. Traditional thermal CVD processes often operate at several hundred or even over a thousand degrees Celsius.
This heat is not just an energy cost; it severely limits the choice of substrate materials. Many polymers, certain glasses, or pre-processed semiconductor wafers cannot withstand such temperatures without damage, deformation, or degradation.
Complex Process Control
Achieving a uniform, high-quality coating is not a simple "set it and forget it" task. It demands precise control over numerous variables simultaneously.
These include gas flow rates, reactor pressure, substrate temperature, and precursor concentration. A slight deviation in any one of these can ruin the deposition, leading to non-uniform thickness, poor adhesion, or undesirable film properties. This complexity necessitates sophisticated and expensive control systems.
Long Deposition Times
Compared to some physical deposition methods, CVD can be a relatively slow process. Building up a film of the desired thickness, molecule by molecule, can take a significant amount of time, impacting throughput in a manufacturing environment.
Material and Environmental Constraints
The "chemical" aspect of CVD introduces its own set of challenges related to the materials used and the by-products created.
Hazardous Precursors and By-products
The precursor gases used in CVD are often toxic, flammable, or corrosive. This requires specialized storage, handling, and delivery systems, adding to both the cost and the operational risk.
Furthermore, the chemical reactions are rarely 100% efficient. The exhaust stream contains unreacted precursors and toxic chemical by-products, which must be captured and treated before release. This "abatement" process adds another layer of complexity and expense.
High Cost of Precursors
The high-purity gases required for CVD can be extremely expensive. For processes involving rare or highly refined elements, the cost of the precursor materials can become a dominant factor in the total cost of the final product.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Cost vs. Quality
The decision to use CVD is a classic engineering trade-off. You must weigh its significant disadvantages against its primary, undeniable advantage: quality.
The Financial Burden
The total cost of ownership for a CVD system is high. This includes not just the high initial equipment cost for the reactor, vacuum pumps, and gas handling, but also ongoing operational expenses.
These recurring costs include expensive precursor gases, energy for heating, and regular maintenance for a complex system that operates in a harsh chemical environment. This makes CVD poorly suited for small-scale production or projects with tight budgets.
The Quality Imperative
Despite the drawbacks, CVD is often chosen when film quality is non-negotiable. It produces coatings that are highly dense, pure, and conformal, meaning they can uniformly coat even complex, three-dimensional shapes.
For demanding applications in semiconductors, aerospace, and advanced optics, the superior performance of a CVD film can justify the high cost and complexity.
Mitigating the Temperature Limitation
To address the critical issue of high temperatures, variations like Plasma-Enhanced CVD (PECVD) were developed. PECVD uses plasma to supply the energy for the reaction, allowing deposition to occur at much lower temperatures.
However, this is not a perfect solution. PECVD systems are even more complex and expensive, and the resulting film quality, while good, may not always match that of high-temperature thermal CVD.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Ultimately, the "disadvantages" of CVD are only disadvantages relative to your specific goals. You must evaluate them within the context of your project's requirements.
- If your primary focus is the absolute highest film quality, purity, and conformality: The benefits of CVD may outweigh its high costs and complexity, making it the superior choice.
- If your project involves temperature-sensitive substrates like polymers or certain electronics: You must avoid traditional thermal CVD and instead evaluate lower-temperature alternatives like PECVD or entirely different methods like sputtering.
- If your priorities are low cost, high throughput, and rapid development: The significant financial investment and process complexity of CVD likely make it an unsuitable option for your needs.
Choosing the right deposition method requires a clear understanding of what you are trying to achieve and what trade-offs you are willing to make.
Summary Table:
| Disadvantage | Key Impact |
|---|---|
| High Operating Temperatures | Limits substrate materials, risks damage to sensitive items |
| High Costs | Expensive equipment, precursors, and maintenance |
| Complex Process Control | Requires precise management of variables for quality |
| Hazardous Chemicals | Involves toxic, flammable gases needing safety measures |
| Long Deposition Times | Reduces throughput in manufacturing settings |
Struggling with high costs or complex processes in your lab? KINTEK specializes in advanced high-temperature furnace solutions, including CVD/PECVD Systems, designed to overcome these challenges. Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, we offer deep customization to precisely meet your unique experimental needs, ensuring efficiency and safety. Contact us today to discuss how our tailored solutions can enhance your research and production outcomes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition
- Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Deposition PECVD Tube Furnace Machine
- Custom Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment Machine
People Also Ask
- What gases are used in the PECVD system? Optimize Thin Film Deposition with Precise Gas Selection
- What is PECVD equipment? A Guide to Low-Temperature Thin-Film Deposition
- What is the second benefit of deposition within a discharge in PECVD? Enhance Film Quality with Ion Bombardment
- How does plasma vapor deposition work? A Low-Temperature Solution for Advanced Coatings
- What is plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition application? Enable High-Performance Thin Films at Lower Temperatures



















