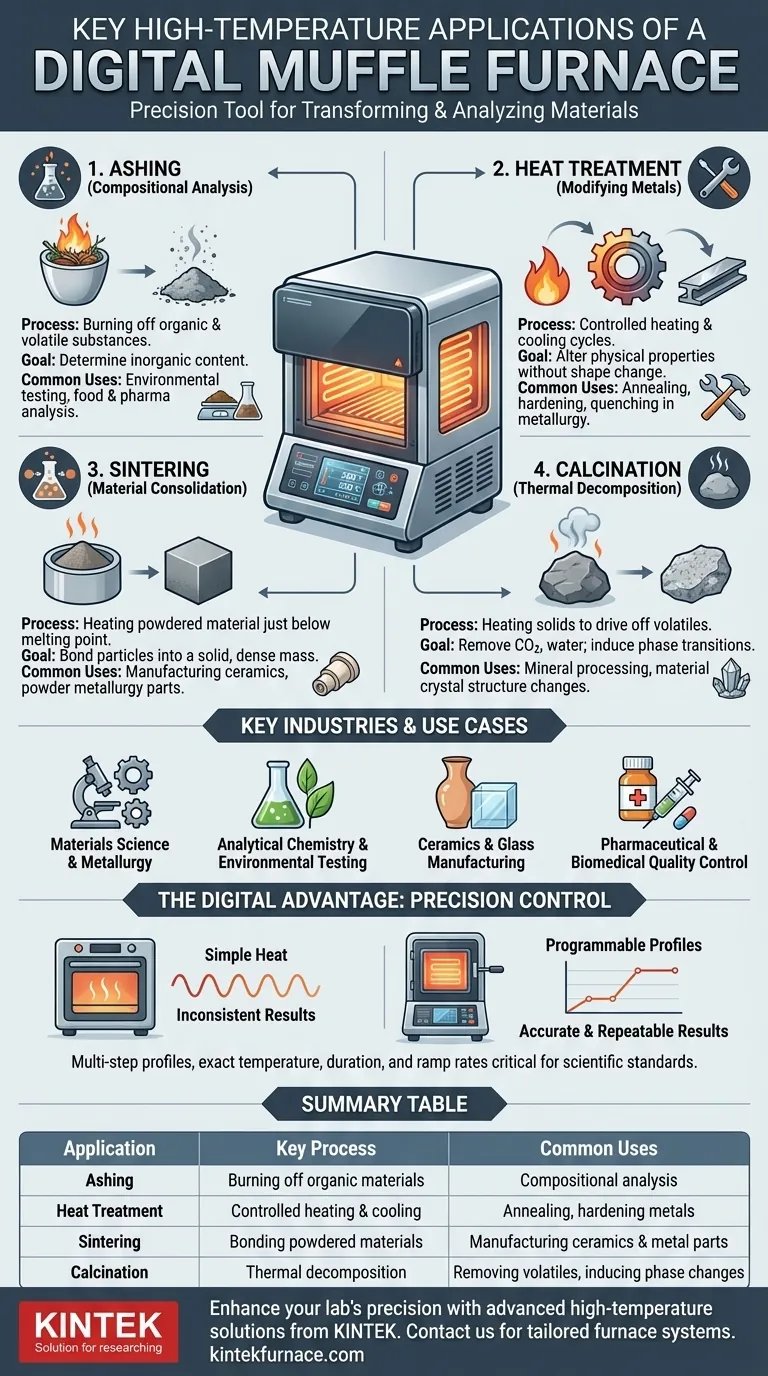
In essence, a digital muffle furnace is a high-precision oven designed for processes that require extremely high temperatures. Its key applications involve either fundamentally transforming a material's physical properties or preparing a sample for chemical analysis by burning away all combustible components. These processes include ashing, heat treatment of metals, sintering ceramics, and calcination.
A digital muffle furnace is more than just a source of heat; it is a critical tool for precisely controlling thermal processes to analyze, create, or fundamentally alter the structure and properties of materials in a laboratory or industrial setting.

Core Applications: From Analysis to Synthesis
A digital muffle furnace enables several foundational high-temperature processes. The "digital" control is what ensures the temperature accuracy and repeatability required for scientific and industrial standards.
Ashing for Compositional Analysis
Ashing is a process where a sample is heated to a high temperature in the presence of air to burn off all organic and volatile substances.
What remains is the ash, which represents the inorganic, non-combustible content of the original material. This is critical for determining the mineral or filler content in samples.
Heat Treatment for Modifying Metals
Heat treatment involves carefully controlled heating and cooling cycles to alter the physical and mechanical properties of metals without changing their shape.
Common processes include annealing (to soften metal and improve ductility), hardening (to increase strength), and quenching (rapid cooling to lock in specific properties). These are cornerstones of metallurgy.
Sintering for Material Consolidation
Sintering is the process of taking a powdered material, heating it to just below its melting point, and causing the particles to bond together into a solid, coherent mass.
This technique is fundamental to manufacturing parts from ceramics and certain metals (powder metallurgy), creating dense and durable final products from a powder base.
Calcination for Thermal Decomposition
Calcination is the heating of solids to high temperatures to drive off a volatile fraction, such as removing carbon dioxide from limestone or water from hydrated minerals.
It can also be used to induce a phase transition, changing the material's crystal structure to achieve desired properties.
Key Industries and Use Cases
The versatility of these processes makes the muffle furnace indispensable across numerous scientific and industrial fields.
Materials Science and Metallurgy
For materials scientists and metallurgists, the furnace is central to research and production. It is used for developing new alloys, testing material endurance under thermal stress, and executing the heat treatment processes that give metals their desired strength and flexibility.
Analytical Chemistry and Environmental Testing
In analytical labs, ashing is a standard sample preparation technique. It's used to measure the inorganic content in food products, analyze pollutants in soil or water samples, and prepare materials for further elemental analysis.
Ceramics and Glass Manufacturing
The furnace is the heart of ceramic production, used for firing clay and for sintering advanced ceramic components. In glassmaking, it's used for melting raw materials, annealing finished products to remove internal stresses, and creating specialty glass.
Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Quality Control
The pharmaceutical industry relies on muffle furnaces for quality control, primarily through ashing. This helps verify the composition of raw materials and final drug products, ensuring they are free of contaminants and meet strict regulatory standards.
Understanding the Key Advantage: Precision Control
The primary benefit of a digital muffle furnace over simpler high-temperature ovens is its precision. The applications described above do not just require high heat; they require the right heat, for the right duration, applied and removed at a specific rate.
Digital controllers allow users to program multi-step thermal profiles with exceptional accuracy and repeatability. This is non-negotiable for scientific research, quality control, and advanced manufacturing, where even small temperature deviations can ruin a sample or an entire batch of product. Without this control, processes like annealing or sintering would produce inconsistent and unreliable results.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To determine how a muffle furnace fits your work, consider your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is quality control or compositional analysis: Use the furnace for ashing to accurately determine the inorganic or mineral content of your samples.
- If your primary focus is materials engineering or metallurgy: Leverage heat treatment processes like annealing and hardening to modify the physical properties of metals and ceramics.
- If your primary focus is creating new materials or components: Employ sintering to consolidate powders into solid parts or use calcination to study and induce phase transitions.
Ultimately, a digital muffle furnace provides the controlled thermal environment necessary to test, transform, and create materials with precision.
Summary Table:
| Application | Key Process | Common Uses |
|---|---|---|
| Ashing | Burning off organic materials | Compositional analysis in environmental testing, food, and pharmaceuticals |
| Heat Treatment | Controlled heating and cooling | Annealing, hardening metals for improved properties |
| Sintering | Bonding powdered materials | Manufacturing ceramics and metal parts in powder metallurgy |
| Calcination | Thermal decomposition | Removing volatiles from minerals, inducing phase changes |
Ready to enhance your lab's precision with advanced high-temperature solutions?
At KINTEK, we leverage exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing to provide diverse laboratories with tailored furnace systems. Our product line—including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems—is backed by strong deep customization capabilities to precisely meet your unique experimental needs. Whether you're in materials science, metallurgy, or quality control, our digital muffle furnaces ensure accurate temperature control for reliable results.
Contact us today to discuss how we can optimize your thermal processes and drive your research forward!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- 1800℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- What is the primary use of a muffle furnace in the assembly of side-heated resistive gas sensors? Expert Annealing Guide
- How do repeat sintering processes and specialized sintering molds address the technical challenges of manufacturing oversized flywheel rotor components? Expand Scale and Integrity
- How does a stainless steel reactor function within a muffle furnace for PET to graphene? Master Carbon Synthesis
- How does a muffle furnace contribute to kaolin-modified biochar? Optimize Pyrolysis & Mineral Integration
- What role does a muffle furnace play in the conversion of S-1@TiO2? Achieve Precision Calcination of Nanospheres



















