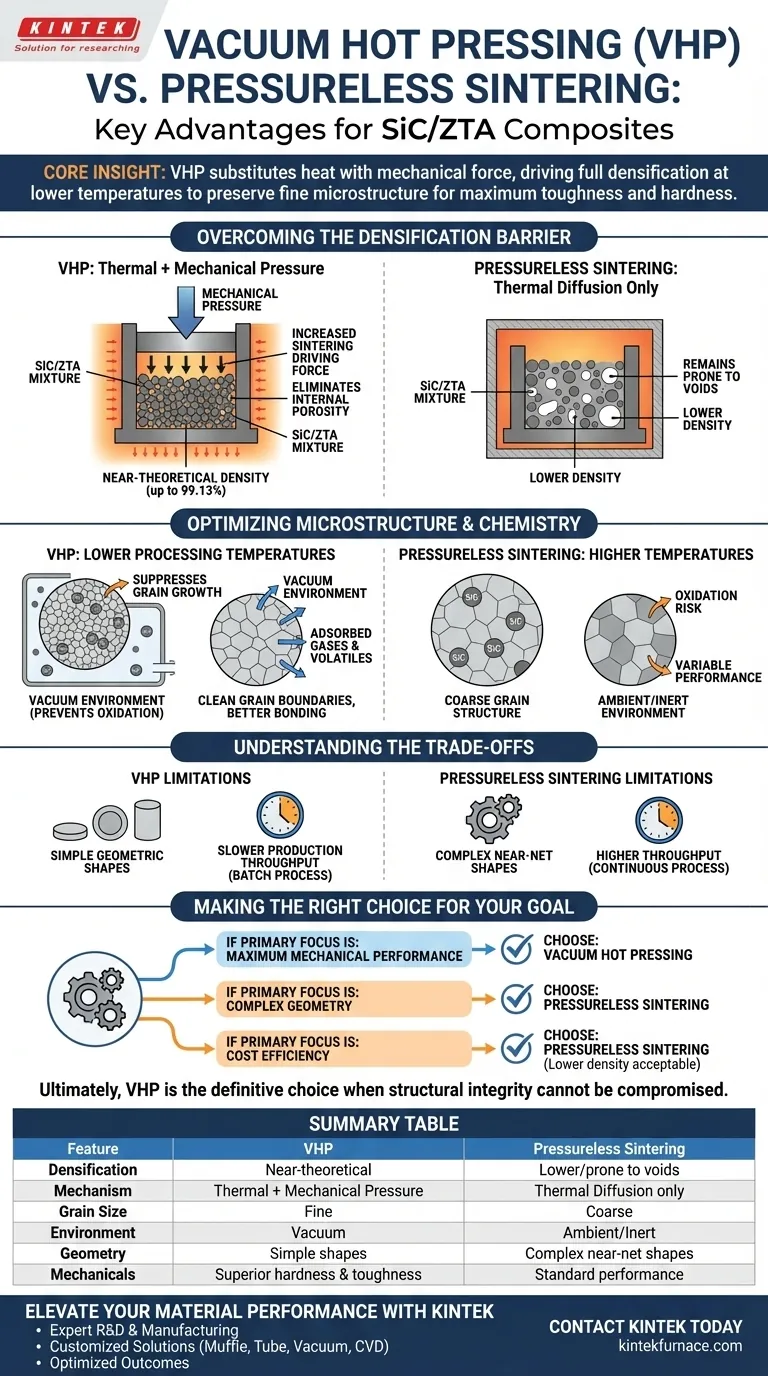
Vacuum hot pressing (VHP) represents a fundamental shift in processing strategy compared to conventional pressureless sintering, moving from a purely thermal process to a thermo-mechanical one. For SiC/ZTA (Silicon Carbide/Zirconia Toughened Alumina) composites, the key advantages are the achievement of near-theoretical density, the suppression of grain growth, and the protection of material chemistry through an oxygen-free environment.
Core Insight:
The addition of hard SiC particles into a ZTA matrix inhibits natural sintering, often leaving voids in pressureless processes. Vacuum Hot Pressing solves this by substituting heat with mechanical force, driving full densification at lower temperatures to preserve the fine microstructure required for maximum fracture toughness and hardness.

Overcoming the Densification Barrier
The Role of Mechanical Pressure
Conventional pressureless sintering relies entirely on thermal energy and diffusion to close pores. However, SiC particles are notoriously difficult to sinter and can physically block the densification of the ZTA matrix.
VHP applies external mechanical pressure (typically axial) during the heating cycle. This force physically pushes particles together, overcoming the resistance offered by the hard SiC phase.
Eliminating Internal Porosity
In pressureless sintering, trapped pores often remain because the driving force is insufficient to eliminate them.
The pressure-assisted mechanism of VHP significantly increases the sintering driving force. This effectively eliminates internal pores and overcomes the "pinning effects" of the second phase (SiC), allowing the composite to achieve relative densities as high as 99.13%.
Optimizing Microstructure and Chemistry
Suppressing Grain Growth
There is usually a trade-off in ceramics: higher temperatures maximize density but cause grains to grow large, which weakens the material.
VHP allows for sintering at significantly lower temperatures because pressure supplements the thermal energy. This lower processing temperature prevents excessive grain coarsening, resulting in a fine-grain structure that is critical for high mechanical strength.
Preventing Oxidation via Vacuum
SiC and metallic components are susceptible to oxidation at sintering temperatures, which forms brittle oxide layers that degrade performance.
The vacuum environment actively removes adsorbed gases and volatiles from the powder surfaces. This prevents the oxidation of the SiC reinforcement, ensuring "clean" grain boundaries and significantly improving the wettability and bonding between the matrix and the reinforcement phases.
Enhancing Mechanical Properties
The combination of high density, fine grain size, and strong interfacial bonding leads to superior performance.
Composites processed via VHP exhibit higher hardness and fracture toughness than those processed via conventional methods. The pressure assists in plastic deformation and particle rearrangement, creating a more robust, defect-free internal structure.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Geometry Limitations
VHP typically utilizes graphite dies to apply uniaxial pressure.
This limits the process to simple geometric shapes (discs, plates, or cylinders). Unlike pressureless sintering, which can accommodate complex near-net-shape components, VHP parts often require expensive diamond machining after sintering to achieve the final form.
Production Throughput
VHP is a batch process that is inherently slower than continuous pressureless sintering.
The cycle times are longer due to the heating and cooling rates of the heavy tooling. Consequently, VHP is generally reserved for high-performance applications where material properties justify the higher cost per unit.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To decide between VHP and pressureless sintering for your SiC/ZTA application, evaluate your specific constraints:
- If your primary focus is Maximum Mechanical Performance: Choose Vacuum Hot Pressing to ensure full density and prevent the flaws associated with porosity and oxidation.
- If your primary focus is Complex Geometry: Choose Pressureless Sintering, as VHP is restricted to simple shapes and requires costly post-process machining.
- If your primary focus is Cost Efficiency: Choose Pressureless Sintering, provided the lower density and coarser grain structure meet your minimum viable specifications.
Ultimately, VHP is the definitive choice when the material's structural integrity cannot be compromised.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Vacuum Hot Pressing (VHP) | Pressureless Sintering |
|---|---|---|
| Densification | Near-theoretical (up to 99.13%) | Lower; prone to voids |
| Mechanism | Thermal + Mechanical Pressure | Thermal Diffusion only |
| Grain Size | Fine (suppressed grain growth) | Coarse (higher heat required) |
| Environment | Vacuum (prevents oxidation) | Ambient/Inert (variable) |
| Geometry | Simple shapes (disks/plates) | Complex near-net shapes |
| Mechanicals | Superior hardness & toughness | Standard performance |
Elevate Your Material Performance with KINTEK
Don't let porosity or oxidation compromise your high-performance ceramics. At KINTEK, we specialize in advanced vacuum hot press systems designed to achieve near-theoretical density and superior grain control for SiC/ZTA composites.
Our Value to You:
- Expert R&D & Manufacturing: Access cutting-edge thermal technology for precise material development.
- Customized Solutions: From Muffle and Tube to Vacuum and CVD systems, we tailor furnaces to your specific research or production needs.
- Optimized Outcomes: Achieve maximum fracture toughness and hardness with our pressure-assisted sintering solutions.
Contact KINTEK Today to discuss your project requirements with our technical experts!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- 9MPa Air Pressure Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is it necessary to maintain a high vacuum environment during the SPS of SiC? Key to High-Density Ceramics
- Why is vacuum press technology indispensable in modern metalworking? Unlock Precision and Quality in Metal Forming
- How does vacuum hot pressing or pressureless sintering equipment facilitate GdEuZrO preparation? Achieve High Density
- What are the core functions of a vacuum hot pressing furnace in the densification of Cr2AlC ceramics?
- What is the function of a rigid mould in vacuum hot pressing? Master Structural Precision in Layered Composites
- What are the advantages of a vacuum hot pressing sintering furnace for rare earth copper composites? Density & Purity
- What role does a high-strength graphite mold play in the hot pressing and sintering of Ag-Ti2SnC? Boost Densification
- Why are graphite molds necessary during the hot pressing sintering process of Fe-Cu-Ni-Sn-VN? Essential Sintering Tools



















