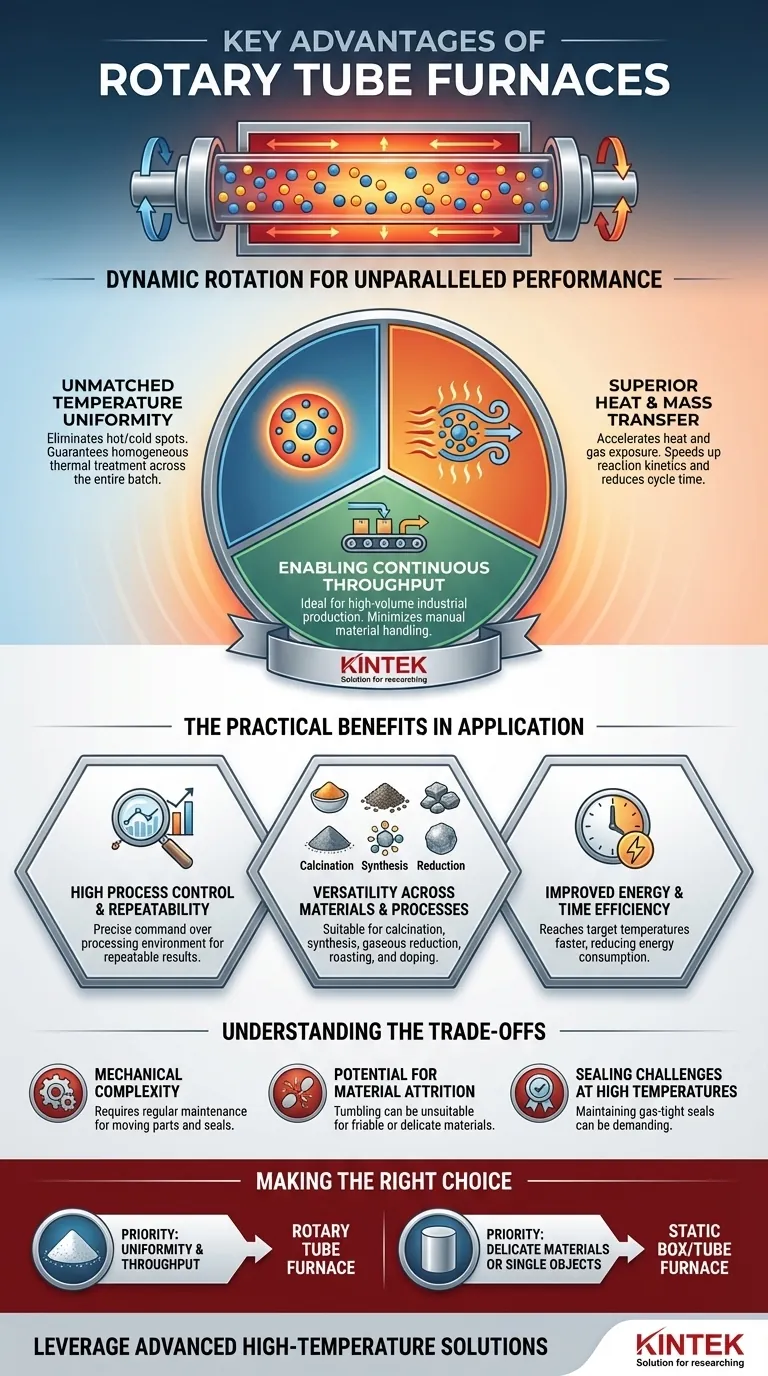
At their core, the key advantages of a rotary tube furnace stem from one defining feature: the dynamic rotation of the processing tube. This movement ensures unparalleled material uniformity, highly efficient heat transfer, and precise process control, making it superior to static furnaces for treating powders, granules, and other loose materials.
A rotary tube furnace solves the fundamental problem of non-uniformity in static thermal processing. By continuously tumbling the material, it guarantees every particle is exposed to the same temperature and atmospheric conditions, resulting in a more consistent and higher-quality end product.

Why Rotation Fundamentally Changes Material Processing
The simple act of rotating the furnace tube introduces benefits that are impossible to achieve in a stationary system. This dynamic environment is the source of its primary advantages.
Unmatched Temperature Uniformity
In a static furnace, material at the edges of a container heats faster than material in the center, creating significant temperature gradients. A rotary furnace eliminates this by constantly mixing the batch.
This tumbling action ensures that every particle is continuously moved, preventing hot spots and cold spots. The result is a homogenous thermal treatment across the entire volume of material.
Superior Heat and Mass Transfer
The continuous agitation dramatically accelerates the rate of heat transfer into the material. As particles tumble, their entire surface area is exposed to the heat source, reducing the overall time required to reach the target temperature.
This same principle enhances mass transfer. For processes involving reactive gases (like reduction or oxidation), rotation ensures that fresh gas can consistently reach the surface of each particle, speeding up reaction kinetics and improving efficiency.
Enabling Continuous Throughput
While static furnaces are limited to one-off batch processing, rotary furnaces are perfectly suited for continuous or semi-continuous operation.
Materials can be fed into one end of the tilted tube and slowly travel to the discharge end as it rotates. This design is ideal for industrial-scale production where high throughput is essential, minimizing manual material handling.
The Practical Benefits in Application
These fundamental principles translate into tangible advantages for a wide range of scientific and industrial processes.
High Process Control and Repeatability
The combination of uniform heating and a controlled atmosphere gives operators precise command over the processing environment. This leads to highly repeatable results, a critical factor in both R&D and quality-controlled production.
Versatility Across Materials and Processes
Rotary tube furnaces are not limited to a single function. Their unique capabilities make them the tool of choice for a diverse set of applications, including:
- Calcination of materials like oil shale or pigments
- Synthesis of catalysts and advanced ceramics
- Gaseous reduction of metallic ores
- Roasting and oxidation processes
- Doping of materials with trace elements
Improved Energy and Time Efficiency
Because heat is transferred into the material so effectively, target temperatures are reached more quickly, shortening process cycle times. Modern designs also incorporate high-quality insulation and efficient heating elements, which reduces overall energy consumption compared to less efficient methods.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No technology is perfect for every scenario. The advantages of a rotary furnace come with specific considerations.
Mechanical Complexity
The rotation mechanism, including the drive motor and gas-tight seals, adds mechanical complexity not found in static furnaces. These components require regular maintenance and can be potential points of failure.
Potential for Material Attrition
The tumbling action that provides such excellent mixing can be a disadvantage for friable or delicate materials. The mechanical stress can cause particles to break down, which may be undesirable for certain applications.
Sealing Challenges at High Temperatures
Maintaining a perfectly controlled atmosphere requires effective seals at both ends of the rotating tube. Achieving a durable, gas-tight seal on a moving component, especially at very high temperatures, can be more challenging than on a static system.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Selecting the correct furnace depends entirely on the nature of your material and your processing goals.
- If your primary focus is maximum product homogeneity: A rotary tube furnace is the definitive choice for processing powders, granules, or any loose material where uniformity is critical.
- If your primary focus is high-throughput, continuous production: The flow-through design of a rotary furnace offers a clear advantage over batch-based static systems.
- If your primary focus is processing large, single objects or delicate materials: A static box furnace or a stationary tube furnace will provide a gentler, more suitable processing environment.
Ultimately, choosing a rotary tube furnace is a decision to prioritize uniformity and efficiency for dynamic materials.
Summary Table:
| Key Advantage | Description |
|---|---|
| Unmatched Temperature Uniformity | Continuous rotation eliminates hot/cold spots for consistent heating. |
| Superior Heat and Mass Transfer | Tumbling action accelerates heat and gas exposure, boosting efficiency. |
| Continuous Throughput | Ideal for high-volume production with minimal manual handling. |
| High Process Control | Ensures repeatable results in R&D and industrial applications. |
| Versatility | Suitable for calcination, synthesis, reduction, and more. |
| Energy and Time Efficiency | Reduces cycle times and energy consumption compared to static systems. |
Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet unique experimental requirements. If you're processing powders, granules, or need continuous throughput for applications like calcination or synthesis, our rotary tube furnaces can deliver superior uniformity and efficiency. Contact us today to discuss how we can optimize your thermal processing!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz or Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ High Temperature Laboratory Tube Furnace with Quartz and Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- How is the structure of a rotary tube furnace characterized? Discover Its Key Components and Benefits
- Why is efficient heat transfer important in rotary tube furnaces? Boost Uniformity and Throughput
- What other fields utilize rotary tube furnaces? Discover Versatile Heating Solutions for Multiple Industries
- What are the benefits of continuous sample movement in rotary tube furnaces? Boost Uniformity and Efficiency
- What are some applications of rotary tube furnaces? Ideal for Continuous High-Temperature Material Processing



















