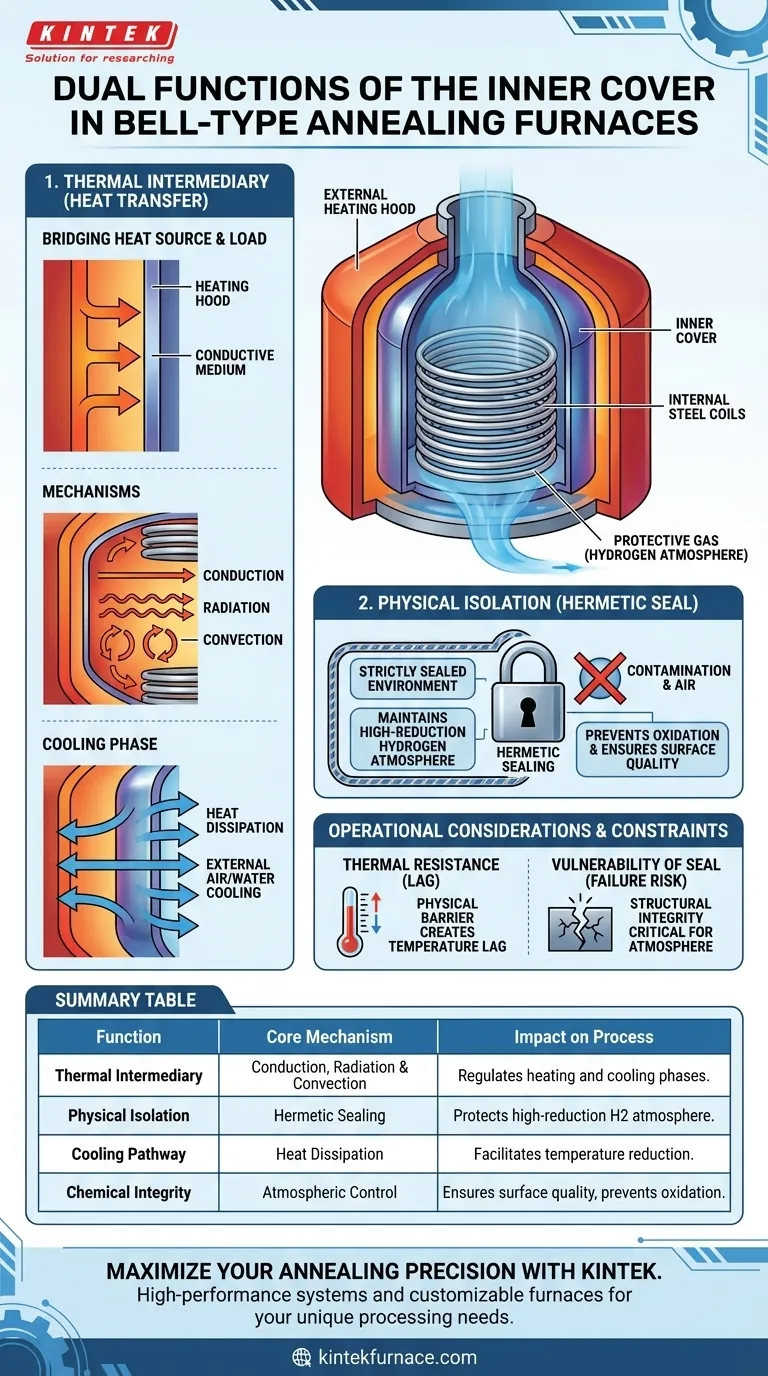
In a bell-type annealing furnace, the inner cover performs two simultaneous and critical roles: serving as a conductive medium for thermal energy and acting as a hermetic seal for the process atmosphere. It effectively bridges the gap between the external heating hood and the internal steel coils, facilitating temperature changes while isolating the load from environmental contamination.
The inner cover is the critical interface that facilitates the efficient transfer of heat into the furnace load while maintaining the pure, high-reduction hydrogen atmosphere required for effective annealing.

The Role of Heat Transfer Intermediary
The first major function of the inner cover is to act as the primary conduit for thermal energy. It does not generate heat but regulates how energy moves from the source to the product.
Bridging the Heat Source and the Load
The inner cover is positioned between the external heating hood and the internal workload. It absorbs thermal energy directly from the heating hood.
Once heated, the cover acts as a radiator and conductor. It transfers this energy inward to the protective gas and the steel coils.
Mechanisms of Transfer
The process relies on a combination of physics principles. The cover absorbs heat via conduction through its metallic structure.
It then releases this energy to the interior through radiation and convection. This ensures the heat is distributed evenly throughout the internal atmosphere and the steel coils.
Facilitating the Cooling Phase
The inner cover’s role as a thermal channel extends beyond heating. During the cooling phase, it serves as the pathway for heat dissipation.
It facilitates temperature reduction by transferring internal heat outward. This is typically accelerated using external air or water-spray cooling systems applied to the cover's surface.
The Role of Physical Isolation
The second function is equally critical: the inner cover acts as a robust physical barrier. This ensures the chemical integrity of the annealing process.
Creating a Hermetic Seal
The cover creates a strictly sealed environment around the steel coils. This isolation is mechanical and absolute, separating the internal volume from the outside world.
Without this seal, the controlled environment necessary for annealing cannot be established.
Preserving Atmosphere Integrity
The primary goal of this isolation is to maintain a high-reduction hydrogen atmosphere. The cover prevents external air from contaminating this delicate chemical balance.
By keeping the hydrogen pure, the cover ensures the steel undergoes the correct chemical reduction, preventing oxidation and ensuring surface quality.
Operational Considerations and Constraints
While the inner cover is essential, its dual nature introduces specific operational constraints. Understanding these trade-offs is vital for process control.
Thermal Resistance
Because the cover is a physical barrier, it introduces a layer of thermal resistance. It acts as an intermediary, meaning heat transfer is not instantaneous.
This physical separation creates a natural lag between the temperature of the heating hood and the temperature of the steel coils.
Vulnerability of the Seal
The requirement for a strictly sealed environment creates a single point of failure. The effectiveness of the entire process relies on the structural integrity of the cover.
Any physical damage or warping due to thermal stress compromises the high-reduction atmosphere. This leads to immediate contamination and potential degradation of the steel product.
Optimizing Furnace Operations
To maximize the efficiency of your bell-type furnace, you must treat the inner cover as both a thermal component and a pressure vessel.
- If your primary focus is Thermal Efficiency: Ensure the inner cover surfaces remain clean to maximize heat conduction and radiation during both heating and cooling cycles.
- If your primary focus is Product Quality: Prioritize the inspection of the cover's structural integrity to guarantee the high-reduction hydrogen atmosphere remains uncontaminated.
The inner cover is not merely a lid; it is the active membrane that makes the entire annealing cycle possible.
Summary Table:
| Function | Core Mechanism | Impact on Process |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Intermediary | Conduction, Radiation & Convection | Regulates heating and cooling phases by bridging the heat source and load. |
| Physical Isolation | Hermetic Sealing | Protects the high-reduction hydrogen atmosphere from oxidation and contamination. |
| Cooling Pathway | Heat Dissipation | Facilitates temperature reduction through external air or water-spray cooling. |
| Chemical Integrity | Atmospheric Control | Ensures surface quality by preventing external air ingress during reduction. |
Maximize Your Annealing Precision with KINTEK
Maintaining the perfect balance between thermal conductivity and atmospheric integrity is critical for high-performance metallurgy. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, KINTEK offers high-performance Muffle, Tube, Rotary, Vacuum, and CVD systems, alongside customizable lab high-temp furnaces designed to meet your unique processing needs.
Whether you are refining heat transfer efficiency or seeking a robust seal for high-reduction environments, our engineering team is ready to assist.
Upgrade Your Lab Efficiency — Contact Us Today
Visual Guide
References
- Yang Xiao-jing, Yu-Ren Li. Study of heat transfer model and buried thermocouple test of bell-type annealing furnace based on thermal equilibrium. DOI: 10.1038/s41598-025-97422-4
This article is also based on technical information from Kintek Furnace Knowledge Base .
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- Why are retort furnaces valuable in research and development? Unlock Precise Atmospheric Control for Your Experiments
- What industries commonly use inert atmosphere heat treating? Key Applications in Military, Automotive, and More
- What is the primary function of a controlled atmosphere device in powder metallurgy? Ensure Pure Sintering Results
- What is an atmosphere protection muffle furnace? Unlock Precise Heat Treatment in Controlled Environments
- What are the key advantages of using atmosphere furnaces? Boost Efficiency and Control in Heat Treatment
- What is the purpose of the 1000 °C pre-annealing treatment for copper foil? Optimize acm-BN Growth Success
- What are the overall environmental benefits of using an atmosphere furnace? Reduce Waste and Boost Efficiency
- What critical function does a high-temperature atmosphere sintering furnace serve? Engineer Advanced Nuclear Fuels



















