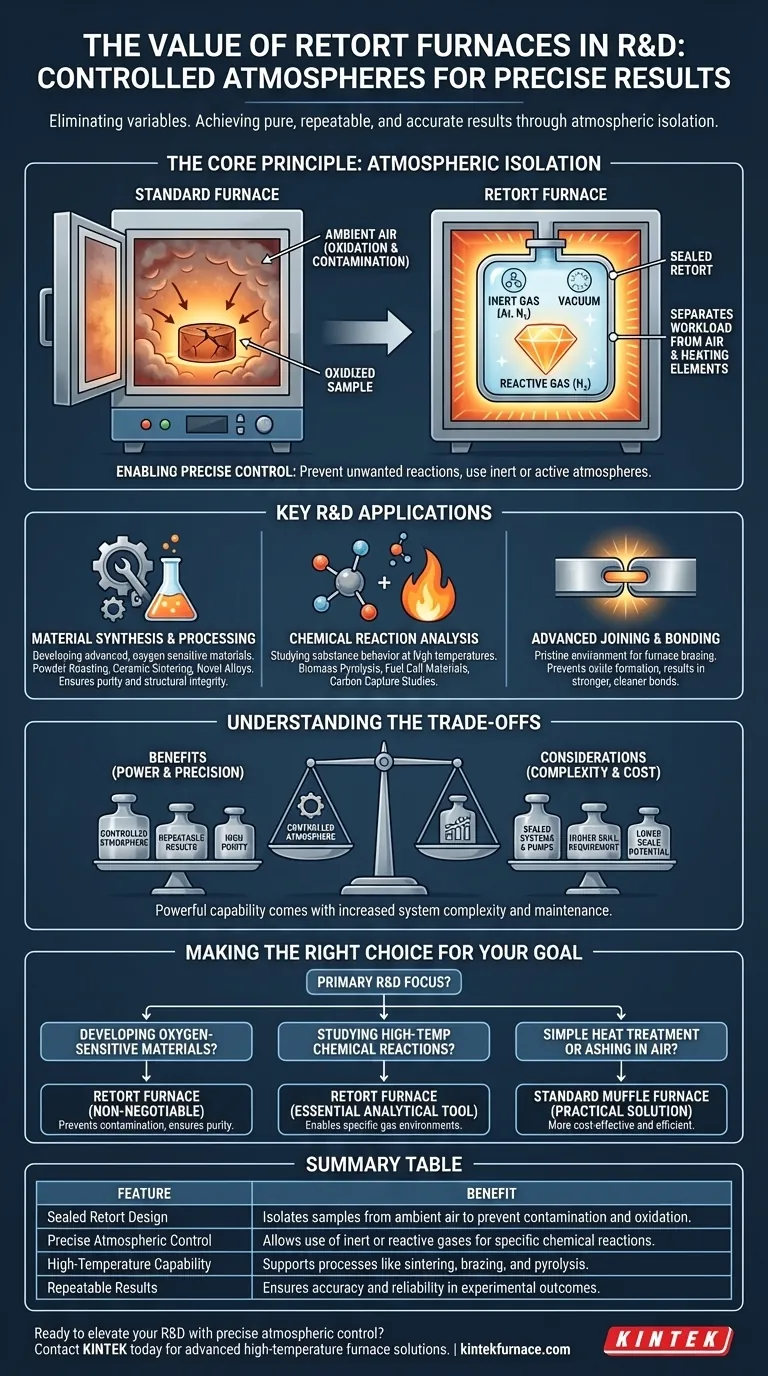
The fundamental value of a retort furnace in research and development stems from its unique ability to create a highly controlled, isolated atmosphere around a sample during high-temperature processing. Unlike standard furnaces that heat materials in ambient air, a retort furnace uses a sealed container (the "retort") to precisely manage the gaseous environment, enabling experiments that would otherwise be impossible. This atmospheric control is the key to achieving pure, repeatable, and accurate results.
At its core, successful research is about eliminating variables. A retort furnace eliminates the biggest variable in high-temperature work: the unpredictable and often contaminating effects of the surrounding atmosphere. This allows researchers to isolate and study the true impact of heat and specific gases on a material or chemical process.
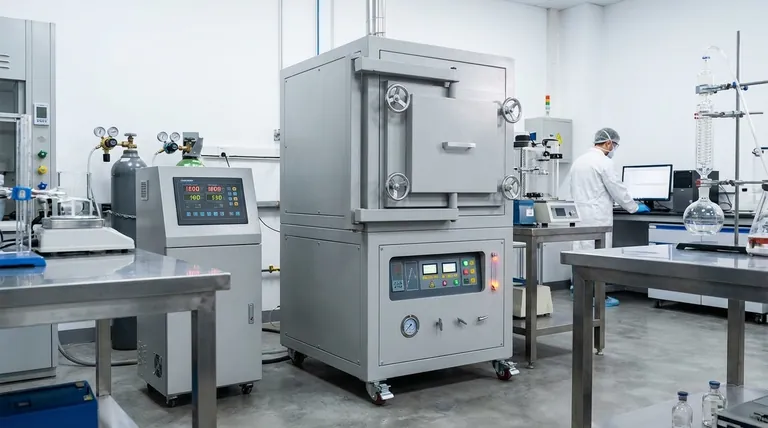

The Core Principle: Atmospheric Isolation
The defining feature of a retort furnace is its sealed inner chamber. Understanding this design is key to understanding its value in a research context.
What is a "Retort"?
A retort is a sealed, gas-tight vessel placed inside the furnace's heating chamber. The material or component being tested is placed inside this retort.
This design physically separates the workload from the furnace's heating elements and the outside air, creating a contained micro-environment.
The Power of Separation
This separation is critical because it prevents unwanted chemical reactions, most notably oxidation. In a standard furnace, heating a material in air will cause it to react with oxygen, which can fundamentally alter its properties and ruin an experiment.
By isolating the sample, a retort furnace ensures that the only factors affecting it are the ones the researcher intends to study: heat and the controlled atmosphere.
Enabling Precise Atmospheric Control
With the sample sealed, the researcher gains complete control. The retort can be purged of air and operated under a vacuum, or it can be backfilled with a specific gas.
This allows for processes to be run in inert atmospheres (using gases like argon or nitrogen) to prevent any reaction, or in active atmospheres (using gases like hydrogen or forming gas) to intentionally cause a specific chemical reaction, such as reduction.
Key Applications in Research and Development
The ability to control the atmosphere at high temperatures unlocks critical capabilities across numerous scientific and industrial R&D fields.
Material Synthesis and Processing
Retort furnaces are indispensable for developing advanced materials that are sensitive to oxygen.
Applications include powder roasting, ceramic sintering, and creating novel metal alloys. The controlled environment ensures the final material has the desired purity, density, and structural integrity.
Chemical Reaction Analysis
Chemists and material scientists use retort furnaces to study how substances behave and react at extreme temperatures under specific atmospheric conditions.
This is vital for research in biomass pyrolysis (for renewable energy), creating materials for fuel cells, and fundamental studies in carbon capture and storage technologies.
Advanced Joining and Bonding
Processes like furnace brazing rely on the pristine environment of a retort furnace. Brazing joins metal components using a filler metal in a controlled atmosphere.
This prevents the formation of oxides on the joint surfaces, resulting in a significantly stronger, cleaner, and more reliable bond than would be possible in open air.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, the specialized nature of a retort furnace comes with certain considerations.
Increased Complexity and Cost
The need for a sealed retort, vacuum pumps, gas delivery systems, and precise controls makes these furnaces more complex and expensive than standard muffle furnaces.
They also require more rigorous maintenance to ensure seals remain gas-tight and control systems are accurate.
Potential for Smaller Scale
Many R&D retort furnaces are designed for testing small samples or single components, not for mass production.
Scaling a process developed in a lab-scale retort furnace to a full-scale industrial production line can be a significant engineering challenge.
Higher Operator Skill Requirement
Operating a retort furnace, especially when working with vacuum systems or flammable reactive gases like hydrogen, demands a higher level of operator training and adherence to safety protocols compared to a simple heat-treating oven.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision to use a retort furnace must align with your specific research objectives.
- If your primary focus is developing oxygen-sensitive materials: A retort furnace is non-negotiable to prevent contamination and ensure the purity and repeatability of your process.
- If your primary focus is studying high-temperature chemical reactions: The ability to introduce specific reactive or inert gases makes the retort furnace an essential analytical tool for valid results.
- If your primary focus is simple heat treatment or ashing in air: A standard, more cost-effective muffle furnace is likely the more practical and efficient solution for your needs.
Ultimately, the retort furnace empowers researchers by providing a controlled, predictable, and clean environment, which is the absolute cornerstone of credible scientific discovery.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Sealed Retort Design | Isolates samples from ambient air to prevent contamination and oxidation |
| Precise Atmospheric Control | Allows use of inert or reactive gases for specific chemical reactions |
| High-Temperature Capability | Supports processes like sintering, brazing, and pyrolysis |
| Repeatable Results | Ensures accuracy and reliability in experimental outcomes |
Ready to elevate your R&D with precise atmospheric control? Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet unique experimental requirements. Contact us today to discuss how our retort furnaces can deliver pure, repeatable results for your material synthesis, chemical analysis, or advanced bonding projects!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Mesh Belt Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Inert Nitrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- Can box type high-temperature resistance furnaces control the atmosphere? Unlock Precision in Material Processing
- What is an atmosphere protection muffle furnace? Unlock Precise Heat Treatment in Controlled Environments
- What are the development prospects of atmosphere box furnaces in the aerospace industry? Unlock Advanced Material Processing for Aerospace Innovation
- How do argon and nitrogen protect samples in vacuum furnaces? Optimize Your Thermal Process with the Right Gas
- What are the key features of an atmosphere box furnace? Unlock Precise Heat Processing in Controlled Environments



















