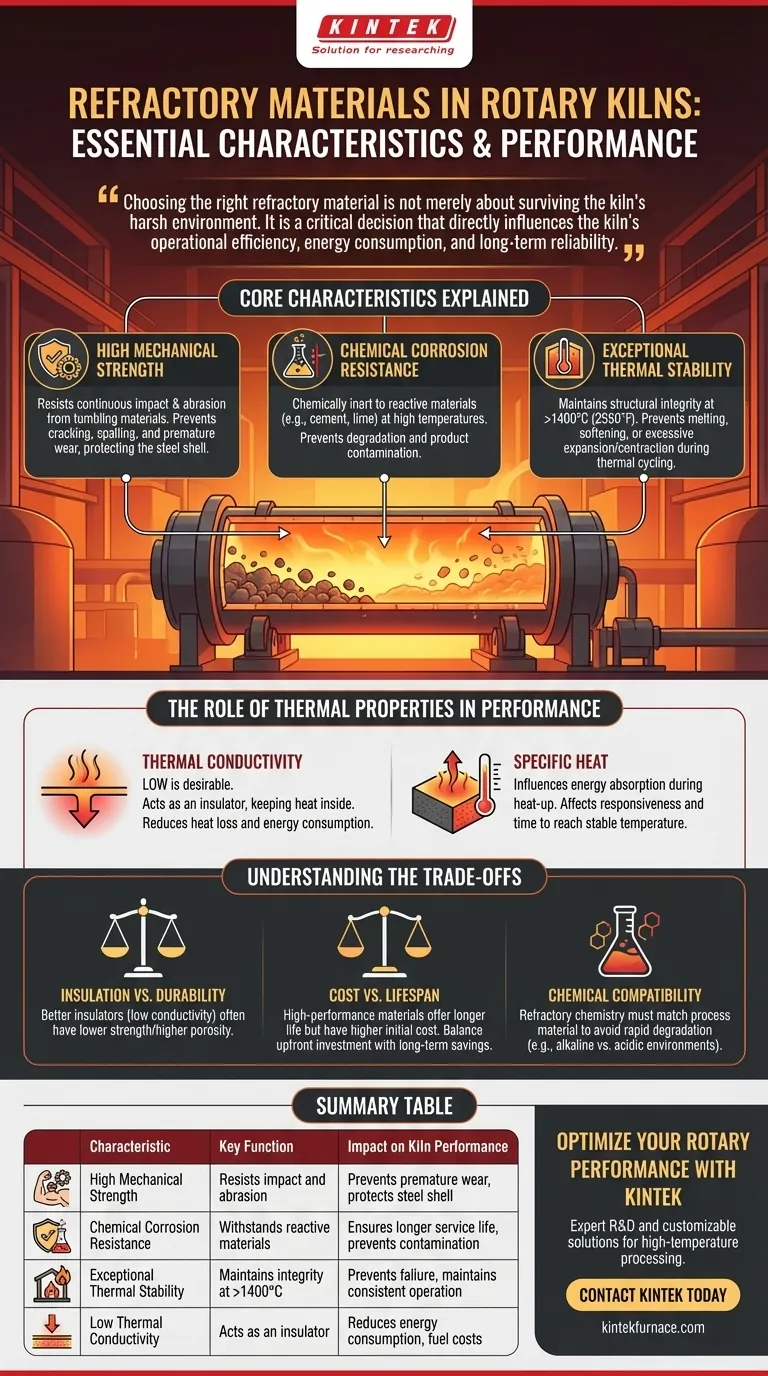
The essential characteristics of refractory materials for rotary kilns are high mechanical strength, robust resistance to chemical corrosion, and exceptional thermal stability. These properties work in concert to ensure the kiln lining can withstand the intense operational stresses of high temperatures, abrasive materials, and a chemically aggressive environment, ensuring the kiln's long-term durability and performance.
Choosing the right refractory material is not merely about surviving the kiln's harsh environment. It is a critical decision that directly influences the kiln's operational efficiency, energy consumption, and long-term reliability.
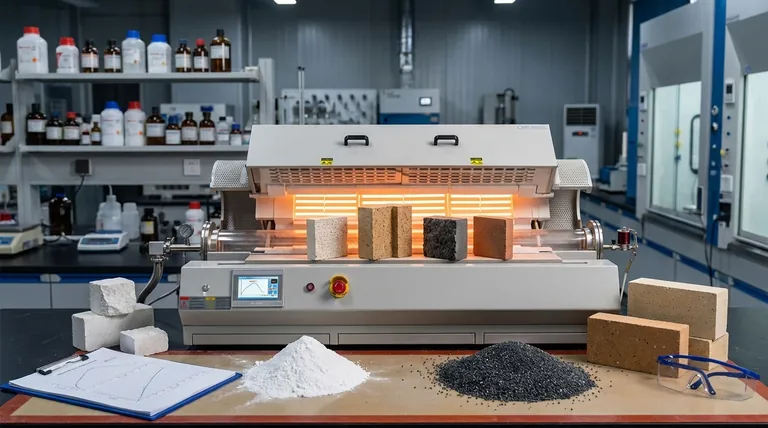

Core Characteristics Explained
The performance of a rotary kiln is fundamentally tied to the quality and suitability of its refractory lining. Each characteristic plays a specific role in protecting the steel shell and optimizing the internal process.
High Mechanical Strength
A rotary kiln is in constant motion, tumbling heavy, abrasive materials. The refractory lining must have high mechanical strength to resist the continuous impact and abrasion from this charge.
This strength prevents the lining from cracking, spalling, or wearing away prematurely, which would expose the kiln's steel shell to damaging high temperatures.
Resistance to Chemical Corrosion
The materials being processed, such as cement clinker or lime, become chemically reactive at high temperatures. The refractory must be chemically inert to this specific environment.
This resistance to corrosion prevents chemical reactions that would degrade the refractory lining, ensuring a longer service life and preventing contamination of the final product.
Exceptional Thermal Stability
Refractories must maintain their structural integrity and strength at extreme operating temperatures, often exceeding 1400°C (2550°F).
Thermal stability ensures the material does not melt, soften, or excessively expand or contract during heat-up and cool-down cycles. This property is crucial for preventing lining failure and maintaining consistent operational conditions.
The Role of Thermal Properties in Performance
Beyond simple survival, a refractory's thermal properties directly impact the kiln's efficiency. How the lining manages heat is as important as its ability to withstand it.
Thermal Conductivity
Thermal conductivity measures how well a material transfers heat. For a refractory lining, a low thermal conductivity is highly desirable.
A low-conductivity lining acts as an insulator, keeping the intense heat inside the kiln where it is needed for the process. This minimizes heat loss through the steel shell, directly reducing energy consumption and fuel costs.
Specific Heat
Specific heat refers to the amount of energy required to raise a material's temperature. The specific heat of the refractory lining influences how much energy is absorbed by the lining itself during heat-up.
While a secondary consideration to conductivity, it affects the kiln's responsiveness and the time it takes to reach stable operating temperature.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No single refractory material is perfect for every application. The selection process always involves balancing competing properties and accepting certain trade-offs.
Insulation vs. Durability
Often, materials that are excellent insulators (low thermal conductivity) are more porous and have lower mechanical strength.
Conversely, very dense, strong refractories that resist abrasion well may have higher thermal conductivity, leading to greater heat loss. The choice depends on which property is more critical for a specific zone in the kiln.
Cost vs. Lifespan
Advanced, high-performance refractory materials offer superior lifespans and efficiency but come at a significant upfront cost.
Operators must balance this initial investment against the long-term savings from reduced downtime for re-lining, lower fuel consumption, and more consistent production campaigns.
Chemical Compatibility
A refractory that is highly resistant to the alkaline environment of a cement kiln may fail quickly in the acidic environment of another industrial process.
There is no universal solution. The chemical composition of the refractory must be meticulously matched to the chemistry of the material being processed to avoid rapid degradation.
Selecting the Right Refractory for Your Goal
Your operational priorities will dictate which refractory characteristics are most important for your kiln.
- If your primary focus is maximizing energy efficiency: Prioritize refractories with the lowest possible thermal conductivity to minimize heat loss through the kiln shell.
- If your primary focus is extending campaign life: Select materials with the highest mechanical strength and proven chemical resistance to your specific process material.
- If your primary focus is process stability: Choose a refractory with excellent thermal stability to ensure consistent performance through temperature fluctuations and cycles.
Ultimately, the optimal refractory lining is a carefully balanced system tailored to the unique thermal, chemical, and mechanical demands of your specific rotary kiln process.
Summary Table:
| Characteristic | Key Function | Impact on Kiln Performance |
|---|---|---|
| High Mechanical Strength | Resists impact and abrasion from tumbling materials | Prevents premature lining wear and protects the steel shell |
| Chemical Corrosion Resistance | Withstands reactive process materials at high temperatures | Ensures longer service life and prevents product contamination |
| Exceptional Thermal Stability | Maintains integrity at extreme temperatures (>1400°C) | Prevents lining failure and maintains consistent operation |
| Low Thermal Conductivity | Acts as an insulator to retain heat inside the kiln | Reduces energy consumption and fuel costs |
Optimize Your Rotary Kiln Performance with the Right Refractory Solution
Selecting the ideal refractory lining is a critical decision that directly impacts your kiln's efficiency, energy consumption, and long-term reliability. The right choice balances mechanical strength, chemical resistance, and thermal properties to match your specific process demands.
KINTEK is your expert partner in high-temperature processing. Backed by expert R&D and manufacturing, we offer a range of advanced laboratory furnaces, including Rotary and Vacuum systems. Our solutions are customizable to meet your unique needs, ensuring you achieve superior thermal processing results.
Let our expertise guide you to a more efficient and durable operation.
Contact KINTEL today to discuss your application and discover how our tailored refractory and furnace solutions can enhance your performance and reduce operational costs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Split Multi Heating Zone Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Kiln for Pyrolysis Plant Heating
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Small Rotary Kiln Calciner
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What types of materials are suitable for processing in rotary tube furnaces? Ideal for Free-Flowing Powders and Granules
- What factors should be considered when selecting a tube for a rotary tube furnace? Ensure Optimal Performance and Longevity
- What supplementary features can enhance rotary tube furnace performance? Boost Efficiency with Precision Control
- What are the common approaches to mixing in rotary furnaces? Boost Uniformity and Efficiency in Thermal Processing
- What types of materials can be processed in a rotary tube furnace? Discover Ideal Materials for High-Temp Processing



















