In high-temperature vacuum furnace applications, graphite heating elements are the dominant choice due to their unparalleled thermal stability, mechanical strength, and design versatility. They reliably achieve temperatures that metallic elements cannot, while also offering superior resistance to the stresses of rapid heating and cooling cycles.
Graphite's value is not just its ability to reach extreme temperatures. Its true advantage lies in the combination of thermal stability, excellent machinability, and mechanical strength, which enables the design of efficient, uniform, and long-lasting heating systems for demanding vacuum processes.
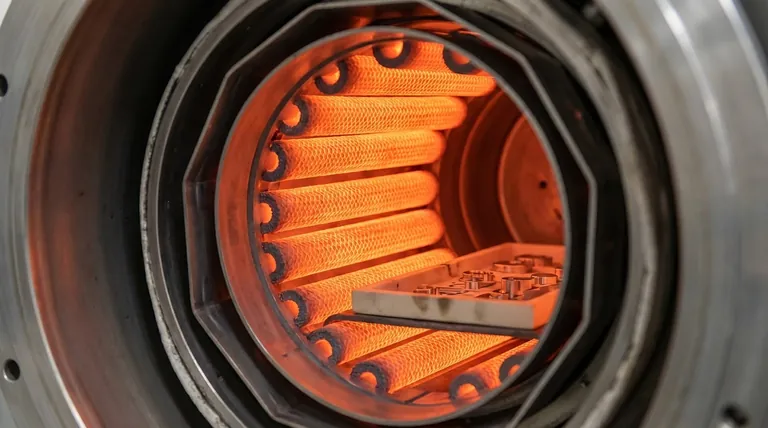
The Foundation of High-Temperature Performance
Graphite's fundamental properties make it uniquely suited for creating the extreme heat required in vacuum brazing, sintering, and heat-treating.
Extreme Temperature Stability
Graphite can operate stably at temperatures up to 3000°C (5432°F) in a vacuum or inert gas atmosphere.
Unlike metals, graphite does not melt at atmospheric pressure but sublimes at very high temperatures. It also has an extremely low vapor pressure, which is critical for maintaining a high-quality vacuum environment.
Unmatched Thermal Shock Resistance
Furnace processes often involve rapid heating and cooling. Graphite has superior resistance to thermal shock, meaning it can withstand these drastic temperature changes without cracking or failing.
This is a direct result of its high thermal conductivity and low coefficient of thermal expansion. The material dissipates stress effectively, preventing mechanical failure.
Superior Temperature Uniformity
Graphite elements can be designed with a large surface radiation area. This, combined with its high thermal conductivity, ensures excellent temperature uniformity across the furnace's hot zone.
Consistent heating is critical for achieving repeatable, high-quality results in sensitive processes like annealing or brazing complex assemblies.
Mechanical Strength and Longevity
Beyond its thermal characteristics, graphite's physical structure contributes directly to furnace reliability and a long service life.
High Strength-to-Weight Ratio
Graphite is both strong and lightweight. This makes furnace components easier and safer to handle during installation and maintenance, reducing labor costs.
The lower mass also puts less strain on the furnace's internal support structures, especially at high temperatures where most materials lose strength.
Inherent Durability
The combination of high mechanical strength, thermal shock resistance, and chemical inertness gives graphite heating elements an exceptionally long and predictable service life.
This durability reduces furnace downtime and lowers the total cost of ownership over the furnace's lifetime.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While graphite is a superior material, its effective use depends entirely on understanding its operating constraints. It is not a universal solution.
The Critical Role of the Atmosphere
Graphite's high-temperature capability is only possible in a vacuum or an inert gas atmosphere (like argon or nitrogen).
This controlled environment is essential to prevent the material from reacting with its surroundings.
The Inevitable Risk of Oxidation
If exposed to oxygen at high temperatures, graphite will rapidly oxidize, forming CO or CO2 gas. This will quickly destroy the heating element.
Even small vacuum leaks can significantly shorten the element's lifespan, making furnace integrity a top priority for any operator.
Potential for Carbon Contamination
As a carbon-based material, graphite can introduce carbon into the processing atmosphere. This can be a significant issue when heat-treating carbon-sensitive alloys.
In such cases, metallic heating elements made from molybdenum or tungsten may be a necessary alternative, despite their own limitations.
Design Flexibility and Cost-Effectiveness
Graphite's practical benefits extend to the design and economics of the entire furnace system.
Unmatched Ease of Machining
Graphite has excellent machinability. It can be easily cut, milled, or drilled into complex and precise shapes.
This allows for the creation of highly customized heating elements tailored to specific furnace geometries and process requirements, optimizing heat distribution.
Economic Advantages
The longevity and reliability of graphite elements contribute to a lower total cost of ownership. Furthermore, its lightweight nature reduces handling and installation costs.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Your specific application will determine if graphite is the optimal choice.
- If your primary focus is reaching extreme temperatures (above 2000°C) with maximum uniformity: Graphite is the industry standard due to its high sublimation point and large radiation area.
- If your primary focus is rapid thermal cycling and long-term reliability: Graphite's low thermal expansion and excellent shock resistance minimize maintenance and replacement costs.
- If your primary focus is process purity for carbon-sensitive materials: You must carefully evaluate potential carbon transfer or consider alternative refractory metal elements like molybdenum or tungsten.
Ultimately, selecting graphite is a strategic choice for achieving consistent, high-performance results in demanding vacuum furnace environments.
Summary Table:
| Key Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Extreme Temperature Stability | Operates up to 3000°C in vacuum/inert atmospheres with low vapor pressure. |
| Thermal Shock Resistance | Withstands rapid heating/cooling due to high thermal conductivity and low expansion. |
| Temperature Uniformity | Ensures even heating across the furnace for consistent results. |
| Mechanical Strength & Longevity | High strength-to-weight ratio and durability reduce maintenance costs. |
| Design Flexibility | Easy to machine for custom shapes, optimizing heat distribution. |
| Cost-Effectiveness | Long service life and lower handling costs improve total ownership value. |
Unlock Peak Performance in Your High-Temperature Processes with KINTEK
Leveraging exceptional R&D and in-house manufacturing, KINTEK provides diverse laboratories with advanced high-temperature furnace solutions. Our product line, including Muffle, Tube, Rotary Furnaces, Vacuum & Atmosphere Furnaces, and CVD/PECVD Systems, is complemented by our strong deep customization capability to precisely meet unique experimental requirements. Whether you need extreme temperature stability, uniform heating, or durable components for demanding applications, we deliver reliable, cost-effective solutions that enhance efficiency and results.
Contact us today to discuss how our graphite heating elements and custom furnace designs can elevate your lab's capabilities!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 2200 ℃ Graphite Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace with Bottom Lifting
- Silicon Carbide SiC Thermal Heating Elements for Electric Furnace
- High Pressure Laboratory Vacuum Tube Furnace Quartz Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the mechanism and effect of post-annealing NiTi thin films in a vacuum furnace? Unlock Superelasticity
- Why are vacuum furnaces used for the re-quenching of samples after a boriding treatment? Master Core Toughness
- What is the primary function of a vacuum graphite furnace? Achieve Extreme-Temperature Material Purity
- How does graphite contribute to energy efficiency in vacuum furnaces? Achieve Faster, More Uniform Heating
- How does vacuum heat treatment reduce workpiece deformation? Achieve Superior Dimensional Stability



















